CTS1131_Mod3_System Components
advertisement
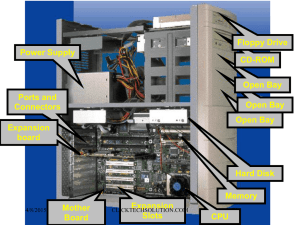
Module 3 System Components Case Form Factors Form Factor ATX Characteristics The most common form factor for full-sized computers. ATX boards measure 12" x 9.6“ and the CPU sits at the back top below the power supply. The power supply can use a soft switch or soft power (the operating system can turn the computer off). Mini-ATX Slightly smaller variation of the full ATX (11.2” x 8.2”) Micro-ATX Smaller variation of the full ATX (9.6" x 9.6“) Mini-ITX Smallest variation of the ATX standard (6.7" x 6.7“) NLX NLX is an older form factor used for slimline desktop-style computers BTX The BTX form factor was designed to give developers better options for managing system performance and balancing thermal management. Mounting holes for both are located in the same place, making them interchangeable in most cases. Mounting holes for both are located in the same place, making them interchangeable in most cases. The mini-ATX standard also includes standards for a power supply that provides less than 100 Watts. Uses a riser card for expansion slots in the middle of the system board. Supports AGP video cards. The processor is at the front and turned on an angle to increase air flow across the processor. Power Supply Facts • Power supplies must be matched to the motherboard and case form factor. ATX motherboard, purchase an ATX power supply. • The power supply converts AC current to DC current and supplies provide + 3.3 volts, +/- 5 volts, and +/- 12 volts (DC power). • Power supplies are rated in watts. The more devices you have in your computer, the more wattage you will require. Calculate the system's wattage requirements with the following method: – Find the wattage requirements of each individual circuit by multiplying volts by amps (W = V x A). – Add the circuit wattage requirements together to find the total system wattage requirement. Power Supply Facts • An ATX power supply provides soft power. This is a condition where the motherboard always has power, even when the computer is turned off. This feature enables the operating system to power off the system and enables other features such as power on for network or other events. • The power supply includes connectors for powering various computer components. When choosing a power supply make sure it includes the necessary connectors for your motherboard. Specifically, some motherboards and processors require an extra 4-pin and/or 8-pin connector in addition to the main 20- or 24-pin power connector. • Power supply connectors are standardized following the ATX specifications. However, some computer manufacturers, such as Dell, produced power supplies with proprietary connectors. Motherboard Component Function / Characteristics Processor interface The motherboard socket must match the socket type and design used by the processor. Some motherboards support multiple processors and will have a socket for each processor. Memory modules Memory modules must be compatible with the type supported by the motherboard, total memory capacity, and the processor and chipset support. Expansion slots Expansion slots allow you to add features to your computer by inserting expansion cards into the available slots Onboard components Many motherboards include onboard devices (such as network cards, audio cards, video cards, or USB and Firewire connections). Faceplate connectors A faceplate fits over the motherboard's ports to secure them and protect the motherboard from dust and debris. Motherboard Component Features BIOS chip The BIOS chip is firmware (hardware hard-coded with software) attached to the motherboard and is essential in booting the computer. The CMOS battery supplies power to the CMOS to retain system settings used CMOS battery by the BIOS during system boot. Chipset The chipset is a group of chips that facilitate communication between the processor, memory components, and peripheral devices. The chipset controls the bus speed and also power management features Jumpers Jumpers are electrical connection points that can be set to control devices and functions attached to the motherboard. Many functions previously performed by jumpers can now be configured in the CMOS or are configured automatically. Expansion Buses Slot Characteristics PCI Peripheral Component Interconnect supports a 32- or 64-bit I/O bus providing compatibility with both 486 and Pentium. PCI slots are typically white. PCIe Peripheral Component Interconnect Express PCI Express (PCIe) is a next generation I/O bus architecture. Rather than a shared bus, each PCIe slot links to a switch which prioritizes and routes data through a point-to-point dedicated connection and provides a serial full-duplex method of transmission. PCIe slots are typically white. AGP Accelerated Graphics Port AGP is similar to PCI, but designed specifically for graphics support. Motherboards that provide AGP support have a single AGP slot. AGP is commonly used for video cards in modern computer systems, but is being replaced by PCIe. AGP slots are typically brown. Processors • • • • • • • • Both Intel and AMD processors work in PC systems and support Windows software. A 32-bit processor can process 32-bits of information at a time; a 64-bit processor can process 64-bits of information. The biggest advantage of 64-bit processors over 32-bit processors is in the amount of memory they can use. 32-bit processors have a limit of 4GB. Processors operate using an internal clock that is the same as, or is a multiple of, the motherboard bus speed. The speed is represented in MHz and is also referred to as the frequency. A multiple core processor has multiple processors within a single processor package. Cache is memory that the processor can access directly without using the system RAM. There are three types of processor cache: L1, L2 and L3. Hyper-threading is a feature of some Intel processors that allows a single processor to run threads in parallel, Hyper-threading enables a processor to execute two threads at the same time. Throttling is the process of modifying the operating characteristics of a processor based on current conditions. Virtualization allows a single physical machine (known as the host operating system) to run multiple virtual machines (known as the guestoperating systems) RAM • • • • • • • Random Access Memory (RAM) can be classified as one of two types: Dynamic or Static SDRAM is synchronized with the system bus clock, allowing it to receive instructions in a continuous flow. DDR accepts a single command and two consecutive data sets per bus clock cycle. DDR2 doubles the data transfer rate of DDR, for four times the bandwidth of SDRAM. DDR3 doubles the data transfer rate of DDR2, for eight times the bandwidth of SDRAM (twice that of DDR2). Dual-channel systems use two memory controllers, while triple channel systems use three memory controllers. Each memory controller can communicate with one or more memory modules at the same time. DDR3 can all work in dual-channel systems (depending on the memory supported by the motherboard); a triple channel system can only use DDR3 BIOS and CMOS Component Basic Input Output System (BIOS) Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) Description The BIOS is a program stored in a read-only memory (ROM) chip that the CPU automatically loads and executes when it receives power. • The BIOS program controls the startup process and loads the operating system into memory. CMOS memory is a special RAM chip powered and maintained by a small battery that holds basic configuration data your computer needs in order to start. • The CMOS battery can be a low-voltage dry cell, lithium mounted on the motherboard. • The electric current is about 1 millionth of an amp and can provide effective power for years. • If the voltage of the battery drops significantly, you may lose your CMOS settings every time you power-off or power-on your computer. If a CMOS battery fails, replace it and afterwards reenter the CMOS information. CMOS Common reasons for editing the CMOS settings are: • To change the boot device order. • To enable or disable motherboard devices. • To add a password to the setup program to prevent unauthorized access. Note: If you set a BIOS password and then forget it, you will be unable to edit CMOS settings. To remove the password for most motherboards, move or remove a jumper, then replace it after a specific period of time. Removing the battery also works, but will remove all CMOS data, not just the BIOS password. • To configure processor or memory settings (such as when you need to set operating speeds or when you want to overclock hardware settings). • (In rare cases) To manually configure device properties for legacy devices. Video • • • • • • • • • Video cards must be compatible with the buses or slots on the motherboard. Common slot types used by video cards are typically AGP and PCI express. Video cards include a processor (called a graphics processing unit or GPU) that takes over video rendering from the CPU, thereby increasing video performance. Video cards have built-in memory. The amount of memory on the card effects performance as well as other characteristics of the display. The quality of images and animations are determined by the following characteristics of display. The capability of your display depends on both the video card and the monitor support. Many videos cards include an HDMI connector for connecting to an HD TV or monitor with an HDMI port. By purchasing a video card with dual heads (two output connectors capable of displaying video simultaneously), you can use dual monitors (as long as the operating system supports dual monitors). Some video cards include features that allow them to receive video signals and output them to a TV source. – Analog: S-video, Digital: HDMI, or DVI A VGA (analog) monitor connects using a DB-15 connector. A LCD (digital) Monitor usually connects to an DVI connector.