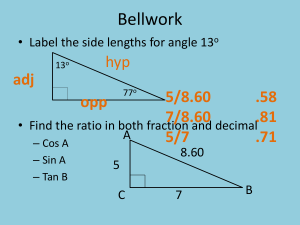
The theodolite and angles

Z
L
R
Types of angles
A
MLN – Horizontal angle
ALM – Vertical angle
NLB – Vertical angle
ZLA – Zenith angle
ZLB – Zenith angle
M
N
B
The theodolite
Measure: vertical and horizontal angles
• Main components - sighting telescope, horizontal and vertical circles and leveling system.
Horizontal (Trunian) axis
Line of sight
Vertical axis
Axis of plate level
In a well condition theodolite
• 1- Line of sight axis + H-H axis
• 2-H-H axis + V-V axis
• 3- V-V axis + L-L axis
•
If these axis are not perfectly perpendicular
, errors in angles will occur
•
To reduce these errors the mean of the face left and face right reading is taken
Types of theodolite
• 1- Optical reading theodolite
• 2- Digital reading theodolite
•
The total station : Digital reading theodolite
• +EDM( electronic distance measurement device )
• + processor and memory
Major Components of a theodolite
• Telescope
• Vertical circle+ horizontal circle
• Horizontal/vertical clamp
• Horizontal/vertical slow motion screws
• Plate bubble (Level tube)
Optical reading theodolite
Setting up a theodolite
• Centering
• Levelling
• Elimination of parallax
• Sighting the target
• Reading the angle
Measuring horizontal angles
• Sight point A on face left
• Set reading on horizontal circle ( e.g.
00
00´ 00
˝
)
• Direct the telescope to point B and record ‘ face left
’ directions (e.g. 35
26´ 20
˝
)
• Reverse the telescope to ‘ face right
’ and read direction to point B ( 215
26 40˝
)
• Back to point A on face right and record the reading ( 180 00 20 )
In the figure, the horizontal angle was measured at B to C and A.
Compute the angle CBA.
Station at Station observed Face left
B C
A deg min sec
00 03 20
83 50 10 deg
180
263
Face Right min sec
03
50
50
40
A
B
C
Errors in Angle Measurement
• Mistakes –pointing, setting up over the wrong point, booking, reading
• Random – settling of tripod, wind, temperature, refraction
• Systematic/instrumental
– Horizontal axis not perpendicular to the vertical axis
– Axis of sight not perpendicular to the horizontal axis
– Axis of the plate bubble not perpendicular to the vertical axis.
Total station
ZA (Line of Sight / Collimation
Axis)
SA (vertical axis :Standing Axis)
KA (Trunian Axis)
V (Zenith Angle)
VK (Vertical Circle)
Hz (Horizontal Angle)
HK (Horizontal Circle )
HEIGHT OF REMOTE POINT
SD (Slope Distance)
HD (Horizontal Distance) dH (Difference of Height) hr (Height of Reflector) hi (Height of Instrument)
E0 (Easting of Station)
N0 (Northing of Station)
H0 (Height of Station)
E (Easting of Target Point)
N (Northing of Target Point)
H (Height of Target Point)
Vertical angles
( zenith angle ) .
V% .
The vertical angle
• Is the angle above or below a horizontal plane through the point of observation
• The angle above the horizontal plane is +ve vertical angle (angle of elevation)
• The angle below the plane is –ve angle
(angle of depression)
Measuring vertical angles
Theodolite is set over point P the following vertical angles circle readings were recorded on targets at points A and B.
Calculate the vertical angles to points A and B
Point observed
F.L
F.R
Reduced
F.L
Reduced
F.R
Mean vertical angle
A
B
85
36´ 274
28´ 4
24´ 4
28´ 4
26´
98º 48´
261
08´ -8
48´ -8
52´ -8
50´