IntroNeuroimaging_280314
advertisement

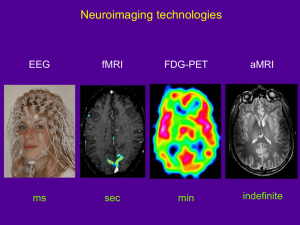
Neuroimaging Processing : Overview, Limitations, pitfalls, etc. etc. Neuroimaging Neuroimaging includes the use of various techniques to either directly or indirectly image the structure or function of the brain. Structural neuroimaging deals with the structure of the brain (e.g. shows contrast between different tissues: cerebrospinal fluid, grey matter, white matter). Functional neuroimaging is used to indirectly measure brain function (e.g. neural activity) Molecular neuroimaging measures biological processes in the brain at the molecular and cellular level. Malhi et al. 2007 MRI acquisition MRI Basics Water = H2O Each Hydrogen = one proton Protons Spin Generates detectable signal in externally applied magnetic field: that is, it causes protons to precess at a frequency proportional to the strength of the magnetic field – the ‘resonant’ frequency Water Content of GM 70% WM 85% Blood 93% Hydrogen Atom PROTON Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Excitation Radio frequency (RF) pulse is applied at the precession frequency (Lamour Frequency) Sending an RF pulse at Lamour freq, particular amplitude and length of time – possible to flip the net magnetism 90° - perpendicular to Magnetic Field (B0) Relaxation T1-weighted is the time it takes for the protons to relax to B0 Not all protons bound by their molecules in same way, dependant on tissue type Preprocessing: Structural MRI Volume/Thickness/Surface Area/Curvature …. Structural MRI Region of Interest (ROI) Voxel based morphometry (SPM/FSL) Surface based morphometry (FreeSurfer) Structural MRI Region of Interest (ROI) Voxel based morphometry (SPM/FSL) Surface based morphometry (FreeSurfer) Volume Structural MRI Region of Interest (ROI) Voxel based morphometry (SPM/FSL) Surface based morphometry (FreeSurfer) Thickness Left Surface Area Curvature Gyrification Right Region of Interest What can we measure in a Region of Interest (ROI)? Total volume Shape Average diffusion Average blood flow Average level of Glutamate Average Dopamine levels Region of Interest Manual v Automated Caudate Manual v FS ICC 0.95 Hippocampus Manual v FS ICC 0.79 52% Volume Difference What’s the problem with ROI? FreeSurfer Manual Region of Interest Volume Temporal lobe epilepsy patients (TLE) v Healthy controls (HC) HC TLE Manual HC TLE FreeSurfer Voxel-based Mophometry Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) FMRIB Software Library (FSL) No a priori hypothesis Volume Change Chronic Schizophrenia patients after Clozapine treatment for 6 months < Healthy Controls (FDR correction p<0.05) Voxel-based Mophometry Original MNI Brain Segmentation Normalisation Modulation Smoothing VBM - Limitations Accuracy of the spatial normalisation Regular SPM uses 1000 parameters – just fits overall shape of the brain - mis-registrations Deformation-based morphometry (e.g. DARTEL) – deformation field is analysed Grey matter matched with grey matter – doesn't’t indicate whether sulci/gyri are aligned FreeSurfer The cortex Volume, thickness or surface area? Volume = surface area * thickness Volume, thickness & surface area Related but don’t necessarily track each other .... Morphometry Differences between Young, Elderly and Mild Alzheimer’s in entorhinal cortex. *p<0.05 Dickerson et al.2007 Cortical Curvature Temporal Lobe Epilepsy (MR-negative) Cortical curvature abnormality in the ipsilateral temporal lobe - Not explained by volume or thickness Possible surrogate marker for malformations of cortical development Ronan et al. 2011 FreeSurfer Cortical Reconstruction Cortical Analysis - cortical thickness, surface are, volume, cortical folding and curvature Cortical and sub-cortical segmentation Surfaces: White and Pial Surface Model • • • • Mesh (“Finite Element”) Vertex = point of 6 triangles XYZ at each vertex Triangles/Surface Element ~ 150,000 • Area, Curvature, Thickness, Volume at each vertex Cortical Thickness • Distance between white and pial surfaces • One value per vertex mm white/gray surface pial surface Curvature (Radial) • Circle tangent to surface at each vertex • Curvature measure is 1/radius of circle • One value per vertex • Signed (sulcus/gyrus) Inter-subject registration subject 1 subject 2 subject 3 subject 4 • Gyrus-to-Gyrus and Sulcus-to-Sulcus • Some minor folding patterns won’t line up Template • Atlas registration is probabilistic, most variable regions get less weight. • Done automatically in recon-all Query Design Estimate Contrast - QDEC Average brain Advantages of FreeSurfer Analysis of separate components of volume – thickness and surface area Geometry is used for inter-subject registration (major sulcal and gyral patterns) 2-D surface smoothing versus 3-D volume smoothing – more biologically meaningful Temporal Lobe Epilepsy (MTS) Regular VBM - Volume DBM - Volume/Shape FreeSurfer - Cortical Thinning Temporal Lobe Epilepsy (MR-negative) Volume Deformation/ Shape Cortical Thinning Use FreeSurfer Be Happy Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) Diffusion MRI White Matter Organisation Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) λ1 λ3 λ2 Eigenvectors: the 3 directions Eigenvalues: the rate of diffusion, λ1, λ2 and λ3 Apparent diffusion Coefficient (Mean diffusivity) = average of λ1, λ2 and λ3 Direction of least resistance to water diffusion, λ1 Tractography Tractography Tractography Cortical Spinal Tract Voxel-based Morphometry for dMRI Issues with regular VBM analysis Not-perfect alignment Smoothing - arbitrary Tract-based Spatial Statistics Smith et al. 2006 – FMRIB Fractional Anisotropy (FA) map DTI-TK with TBSS High level warping using all the tensor information for better alignment DTI and Schizophrenia Widespread FA reduction in Schizophrenia versus controls DeCC neuroimaging MDD = 153 HC = 153 Matched age and gender Gaussian Process Classifier LOOCV Accuracy = 59%