Probability-1
advertisement
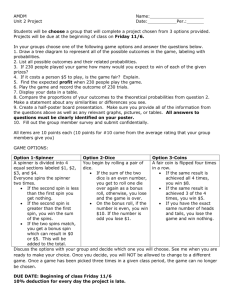
Probability OCR Stage 6 1 Probability • In an experiment, things that can happen are called possible outcomes • Each of these has a possibility 2 Probability of an event happening • Probability = Required Outcome Total Possible Outcomes • i.e. The number of required outcomes divided by the total number of possible outcomes 3 Getting a 4 on a single dice • There is 1 required outcome – a four • There are 6 possible outcomes • P(4) = 1 6 The P says, “The probability of” The answer may be written as a fraction, decimal or percentage NEVER as “one out of six” 4 The probability of not getting a 4? • There are five numbers on the single dice that are not a 4 • There are six possible outcomes • So, P(Not getting a 4) = 5 6 P 4 5 It is important that you notice that the two probabilities add together to give 1 • The total probabilities of any event have a total of 1 • 1/6 + 5/6 = 1 Probability of getting a 4 on a single dice Probability of not getting a 4 on a single dice 6 Sum of all probabilities equal 1. Example The probability of a football team’s results in the next match are: • P(Win) = 0.3 • P(Lose) = 0.5 • What is the probability of a draw? 7 Remember the total of all the probabilities is 1 The team must win, lose or draw. • P(Win) + P(Lose) + P(Draw) = 1 This is 0.3 This is 0.5 • 0.3 + 0.5 + P(Draw) = 1 • 0.8 + P(Draw) = 1 • P(Draw) = 0.2 8 Mutually Exclusive events • Can NOT happen at the same time • Examples – A HEAD and a TAIL when coin is spun – A 6 and an odd number when die rolled – A level 5 and a level 6 on a SAT paper 9 Example • • • • • • • Sam and Pete play chess P(Sam wins) = 0.4 P(Pete wins) = 0.3 What is P(Draw) ? 0.4 + 0.3 + P(Draw) = 1 0.7 + P(Draw) = 1 P(Draw) = 0.3 10 Exercises – to be completed next lesson • • • • • • OCR Stage 5/6 Text, Stage 6, Chapter 4, Page 182 Ex 4.1A Ex 4.1B Ex 4.2A Ex 4.2B 11