DFS_6_Stack
advertisement
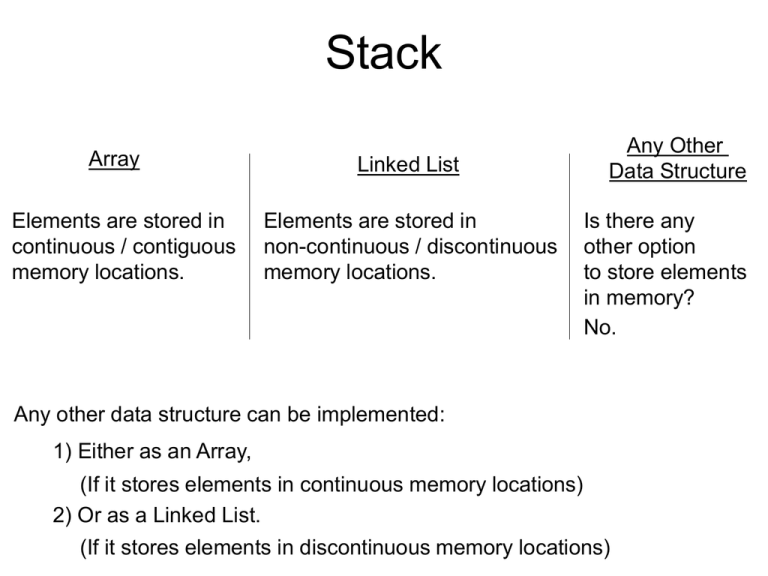
Stack Array Elements are stored in continuous / contiguous memory locations. Linked List Elements are stored in non-continuous / discontinuous memory locations. Any Other Data Structure Is there any other option to store elements in memory? No. Any other data structure can be implemented: 1) Either as an Array, (If it stores elements in continuous memory locations) 2) Or as a Linked List. (If it stores elements in discontinuous memory locations) Stack Examples Stack of Books Box of Tennis Balls (Closed at 1 end) Stack of Plates Stack of Clothes. Trains in a railway yard. Goods in a cargo. Type: Stack of Rings / Discs LIFO / FILO Stack of Chairs Stack •Stack: –Collection of, •Homogeneous data elements where, •Insertion and deletion take place, –At one end only. –Also called, •LIFO structure. –Last In First Out. •FILO structure. –First In Last Out. –Stack can be implemented, •Either as an Array, –Stores the elements in continuous memory locations and, –Has all advantages/disadvantages of array. •Or as a Linked List. –Stores the elements in discontinuous memory locations and, –Has all advantages/disadvantages of linked list. Stack Implemented using an Array PUSH operation (Stack Overflow) Insert an Element 35 15 25 5 45 Delete an Element 45 4 55 Delete an Element 55 3 25 Delete an Element 25 2 15 Delete an Element 15 1 35 75 Delete an Element 35 Delete an Element NULL Array A 55 45 75 POP operation (Stack Underflow) Stack Implemented using a Linked List PUSH Stack_Head NULL 35 45 25 25 35 NULL 1st solution PUSH: InsertFront POP: DeleteFront 45 NULL 2nd solution POP 45 POP 25 POP 35 POP NULL PUSH: InsertEnd POP: DeleteEnd (Stack Underflow) Stack •Stack: –Insertion operation in a Stack is called: •PUSH –When PUSH is not possible, situation is called: »Stack Overflow –Deletion operation in a Stack is called: •POP –When POP is not possible, situation is called: »Stack Underflow Stack using Array PUSH an element 25 15 35 65 55 Array A 5 55 4 65 3 35 2 15 1 25 POP POP POP POP 55 65 35 15 Is this logic efficient? No Inefficient for a bigger array. Stack using Array PUSH an element Item 25 15 35 65 55 75 Array A Steps: Top 5 55 Top 4 65 Top 3 35 Top 2 15 Top 1 25 U If(Top >= 5) print “Stack overflow.” Else Top = 0 Top = Top + 1 Item A[Top] = 25 EndIf Stack using Array POP POP POP POP POP POP 55 Array A 65 35 15 25 NULL Steps: Item = Null L If(Top < 1) Top 5 55 Top 4 65 Top 3 35 Top 2 15 Item = A[Top] // 5565 31 5525 A[Top] = Null Top 1 25 Top = Top - 1 print “Stack underflow.” Else Top = 0 EndIf Return(Item) Stack using Array PUSH an element POP an element Steps: Steps: Item = Null If(Top >= U) If(Top < L) print “Stack underflow.” print “Stack overflow.” Else Else Item = A[Top] EndIf Top = Top + 1 A[Top] = Null A[Top] = Item Top = Top - 1 EndIf Return(Item) Tracing of PUSH and POP on Stack using Array. PUSH If(Top >= U) 1) POP() print “Stack overflow.” Else Top = Top + 1 3 If(Top < L) 3 print “Stack underflow.” Else 2 Top = Top - 1 EndIf Return(Item) 1 Array A POP Item = Null A[Top] = Null 2 0 Top = -1 Stack underflow. Item = NULL A[Top] = Item EndIf Item = A[Top] 3 2) PUSH(20) 1 Top 0 20 1 Top 0 Top = -1 L = 0, U = 3 2 20 3) PUSH(10) 4) PUSH(50) 5) PUSH(70) 6) PUSH(80) 7) POP() Stack using Array •Algorithm: –Push_Array •Input: –Top: Pointer to the Top of Stack. –Item: Data to be pushed onto the Stack. •Output: –Stack with newly pushed item at Top if successful, message otherwise. •Data Structure: –Stack implemented using Array A[L...U] with TOP as the pointer. Algorithm: Push_Array Steps: If(Top >= U) print “Stack overflow.” Else Top = Top + 1 A[Top] = Item EndIf Stop Stack using Array •Algorithm: –Pop_Array •Input: –Top: Pointer to the Top of Stack. •Output: –Item: Data removed (popped) from Top of Stack if successful, NULL and message otherwise. •Data Structure: –Stack implemented using Array A[L...U] with Top as the pointer. Steps: Algorithm: Pop_Array Item = Null If(Top < L) print “Stack underflow.” Else Item = A[Top] A[Top] = Null Top = Top - 1 EndIf Return(Item) Stop Stack using Array Just look and tell the value of element on Top of Stack. Do not POP the element. PEEP 65 Array A PEEP 65 POP 65 PEEP 35 Steps: Item = Null If(Top < L) 5 print “Stack underflow.” Top 4 65 Top 3 35 2 15 A[Top] = Null 1 25 Top = Top - 1 Else Item = A[Top] // 65 35 EndIf Return(Item) Stack using Array •Algorithm: –Peep_Array •Input: –Top: Pointer to the Top of Stack. •Output: –Item: Data returned (not deleted) from Top of Stack if successful, message otherwise. •Data Structure: –Stack implemented using Array A[L...U] with Top as the pointer. Steps: Algorithm: Peep_Array Item = Null If(Top < L) print “Stack underflow.” Else Item = A[Top] EndIf Return(Item) Stop Stack using Linked List Top new 35 PUSH an element 55 65 35 3000 4000 Stack_Head NULL Top 65 NULL 3000 4000 1000 Top NULL new = GetNode(NODE) If(new == NULL) print “Memory Insufficient. PUSH not possible.” Top 2000 3000 Steps: Else Item 55 NULL 2000 Steps: (cntd) new->Data = 35 new->Link = Top Stack_Head->Link = new Top = new EndIf Stop Stack using Linked List POP an element 35 Stack_Head NULL 3000 4000 1000 Top ptr Top 35 3000 65 4000 2000 3000 Steps: Item = Top->Data ptr = Top->Link Stack_Head->Link = ptr ReturnNode(Top) Top = ptr Return(Item) Stop 55 NULL 2000 Stack using Linked List Steps: POP 55 POP NULL Item = NULL If(Top == NULL) print “Stack Underflow.” Else Item = Top->Data ptr = Top->Link Stack_Head->Link = ptr ReturnNode(Top) Top = ptr EndIf Return(Item) Stop Top Stack_Head NULL 55 NULL 2000 1000 Top NULL NULL 2000 ptr NULL Stack using Linked List PUSH an element Steps: new = GetNode(NODE) If(new == NULL) print “Memory Insufficient. PUSH not possible.” Else new->Data = Item new->Link = Top Stack_Head->Link = new Top = new EndIf Stop POP an element Steps: Trace the following steps on an Item = NULL empty Stack If(Top == NULL) implemented print “Stack Underflow.” using a Linked List: Else 1) PUSH(20) Item = Top->Data 2) POP() ptr = Top->Link 3) PUSH(10) Stack_Head->Link = ptr 4) PUSH(30) 5) POP() ReturnNode(Top) 6) POP() Top = ptr 7) POP() EndIf Convert into Return(Item) a program. Stop Stack using Linked List •Algorithm: –Push_LL •Input: –Stack_Head: Pointer to the starting of linked list. –Top: Pointer to the Top of Stack. –Item: Data to be pushed onto the Stack. •Output: –Stack with newly pushed item at Top if successful, message otherwise. •Data Structure: –Stack implemented using Single Linked List with, •Stack_Head as pointer to the starting of linked list and, •Top as the pointer to the Top of Stack. Algorithm: Push_LL Steps: new = GetNode(NODE) If(new == NULL) print “Memory Insufficient. Push not possible.” Else new->Data = Item new->Link = Top Stack_Head->Link = new Top = new EndIf Stop Stack using Linked List •Algorithm: –Pop_LL •Input: –Stack_Head: Pointer to the starting of linked list. –Top: Pointer to the Top of Stack. •Output: –Item: Element removed (popped) from the Top of Stack if successful, message otherwise. •Data Structure: –Stack implemented using Single Linked List with, •Stack_Head as pointer to the starting of linked list and, •Top as the pointer to the Top of Stack. Algorithm: Pop_LL Steps: Item = NULL If(Top == NULL) print “Stack Underflow.” Else Item = Top->Data ptr = Top->Link Stack_Head->Link = ptr ReturnNode(Top) Top = ptr EndIf Return(Item) Stop Applications of Stack •Uses of Stack: –Main uses of Stack are: •Evaluation of Arithmetic Expression –Example: »( A + B ) * C or ( 1 + 2 ) * 3 •Execute recursive function calls / Recursion. Applications of Stack Evaluation of Arithmetic Expression using a Stack How can it be solved by a computer? E= A+B 2+3 [A = 2, B = 3] Scanning the input once from Left to Right and doing appropriate processing. E= A+B-C 1+2-3 [A = 1, B = 2, C = 3] Scanning the input once from Left to Right and doing appropriate processing. E= A+B*C 1+2*3 [A = 1, B = 2, C = 3] Requires scanning of the input multiple times from Left to Right. E= A–((B+C)*D) 1–((2+3)*4) [A = 1, B = 2, C = 3, D = 4] Requires scanning of the input several times from Left to Right. Applications of Stack Evaluation of Arithmetic Expression using a Stack Symbols Right Parenthesis / Bracket Operators E =A – ( ( B + C ) * D ) Left Parenthesis / Bracket Evaluation depends on, Precedence / Priority: Operands 1) Operators in Brackets () 2) ^ (Power / Exponentiation) 3) *, / 4) +, - Applications of Stack •Evaluation of Arithmetic Expression using a Stack: –Process consist of 2 steps: •1) Convert the given arithmetic expression into a special notation/representation using a Stack. –Algorithm would be required for this step. •2) Evaluate (Find the value of) that special notation (obtained from step-1) again using a Stack. –Algorithm would be required for this step. Evaluation of Arithmetic Expression using a Stack Step-1: Convert expression into special notation using a Stack. Input Expression: A + B Enclose / Put the input in Parentheses (if not already enclosed) So input Expression becomes: Infix Expression ( A + B ) Step Symbol Stack T Output Expression T 1 ( ( 2 A T 3 + A ( T ( + T 4 B ( + 5 ) - A AB AB+ Postfix Expression Stack should be empty at the end of the conversion. Infix to Postfix Postfix expression never contains parentheses. Infix Expression: A * B + C Infix Expression enclosed in parentheses: ( A * B + C ) Step Symbol Stack 1 2 A T * ( * 4 B 5 + 6 C 7 ) Output Expression T ( 3 T ( A ( T T ( * T ( + T ( + A AB AB* AB *C AB *C + Infix to Postfix Step Symbol Stack Output Expression Infix Expression 1 ( ( ((A + B) * (C – D)) 2 ( (( Already enclosed in parentheses. 3 A (( A 4 + ((+ A 5 B ((+ AB 6 ) ( AB+ 7 * (* AB+ 8 ( (*( AB+ 9 C (*( AB+C 10 - (*(- AB+C 11 D (*(- AB+CD 12 ) (* AB+CD- 13 ) AB+CD-* Infix to Postfix Infix Expression A+B*C^D Infix Expression enclosed in parentheses (A + B * C ^ D) Step Symbol Stack Output Expression 1 ( ( 2 A ( A 3 + (+ A 4 B (+ AB 5 * (+* AB 6 C (+* ABC 7 ^ (+*^ ABC 8 D (+*^ ABCD 9 ) ABCD^*+ Infix to Postfix Infix Expression A+B/C-D Infix Expression enclosed in parentheses (A + B / C - D) Step Symbol Stack Output Expression 1 ( ( 2 A ( A 3 + (+ A 4 B (+ AB 5 / (+/ AB 6 C (+/ ABC 7 - (- ABC/+ 8 D (- ABC/+D 9 ) ABC/+D- Infix to Postfix Convert the following arithmetic expressions from Infix to Postfix. (A+B)^C–(D*E)/F (A+((B^C)–D))*(E–(A/C)) A+(B*C)/D (A+B)*C A*B^C+D Evaluation of Arithmetic Expression using a Stack Step-2: Evaluate (Find the value of) special notation (Postfix) using Stack. Step-1 Infix Expression: A + B Postfix Expression: A B + Values: A = 3, B = 5 Postfix Expression: A B + 3 5+ 3 Push(3) 1) 5 Push(5) 2) 3) 3 Operands Operator + 5 3 35+ 8 y = Pop() // y = 5 x = Pop() // x = 3 result = x operator y // result = 3 + 5 = 8 Push(result) Evaluation of Arithmetic Expression using a Stack Step-2: Evaluate (Find the value of) special notation (Postfix) using Stack. 3 5+ 3 5 + Push(3) Push(5) 1) 2) 3) 5 3 3 8 y = Pop() // y = 5 x = Pop() // x = 3 result = x operator y // result = 3 + 5 = 8 Push(result) Step Symbol Stack Operation 1 3 3 Push(3) 2 5 3, 5 Push(5) 3 + 8 y = Pop() // 5, x = Pop() // 3, result = x operator y // 3+5, Push(result) Evaluate Postfix Infix Expression: A * B + C Step-1 Postfix Expression: A B * C + Values: A=3, B=5, C=5 Postfix Expression: A B * C + 35*5+ 3 5*5+ Step Symbol Stack Operation 1 3 3 Push(3) 2 5 3, 5 Push(5) 3 * 15 y = Pop() // 5, x = Pop() // 3, result = x operator y // 3*5, Push(result) 4 5 15, 5 5 + 20 Push(5) y = Pop() // 5, x = Pop() // 15, result = x operator y // 15+5, Push(result) Evaluate Postfix Infix: ( (A+B) * (C-D) ) Step-1 Postfix: A B + C D -* [A=1, B=2, C=5, D=3] 12+53-* Step Symbol Stack Operation 1 1 1 Push(1) 2 2 1, 2 Push(2) 3 + 3 4 5 3, 5 Push(5) 5 3 3, 5, 3 Push(3) 6 - 3, 2 y = Pop() // 3, x = Pop() // 5, result = x operator y // 5-3, Push(result) 7 * 6 y = Pop() // 2, x = Pop() // 3, result = x operator y // 3*2, Push(result) y = Pop() // 2, x = Pop() // 1, result = x operator y // 1+2, Push(result) Evaluation of Arithmetic Expression using a Stack Exercise: Evaluate the following Arithmetic Expression using a Stack: (A*B)-(C/D) [ A = 1, B = 3, C = 8, D = 2 ] Steps: 1) Infix to Postfix AB*CD/- 2) Evaluate Postfix -1 Algorithm: InfixToPostfix •Algorithm-InfixToPostfix: –Enclose the entire expression in parentheses (brackets) if not already enclosed. •Add ‘(‘ at the beginning and ‘)’ at the end of the expression. –Scan 1 symbol at a time from left to right and do the following things depending on the type of symbol scanned: •If symbol is ‘(‘: –Push it onto the stack. •If symbol is ‘Operand’: –Add/Append it to the Output Expression/Output String/Postfix Expression. •If symbol is ‘Operator’: –Pop all the operators one by one from TOP of stack which have, »The same or higher precedence than the symbol and go on, »Adding them to the Output String. –Then push the incoming operator onto the stack. •If symbol is ‘)’: –Pop all the operators one by one from TOP of stack and go on adding them to the Output String until, »‘(‘ is encountered / obtained. –Remove that ‘(‘ from the Stack and do not do anything with ‘)’. Algorithm: InfixToPostfix Steps: Push(symbol) symbol = E.ReadSymbol() While(symbol != NULL) case: symbol = ‘(‘ case: symbol = operand case: symbol = operator case: symbol = ‘)’ Output(symbol) item = Pop() While( item is operator ) AND (PREC(item) >= PREC(symbol)) Output(item) item = Pop() EndWhile Push(item) Push(symbol) item = Pop() While( item != ‘(’ ) case: otherwise print “Invalid input.” symbol = E.ReadSymbol() EndWhile Output(item) item = Pop() EndWhile Steps: Algorithm: EvaluatePostfix symbol = E.ReadSymbol() While(symbol != NULL) case: symbol = operand Push(symbol) case: symbol = operator y = Pop() x = Pop() result = x symbol y Push(result) case: otherwise print “Invalid input.” symbol = E.ReadSymbol() EndWhile value = Pop() Return(value) Stop