Modeling Computers and Error Analysis
advertisement

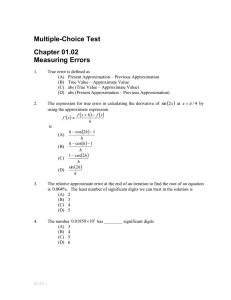
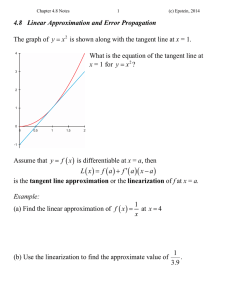
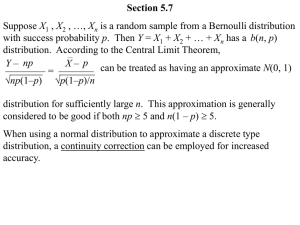
Round off and Truncation Errors CS 431 : Numerical Analysis I Chapter 4 • Errors are mainly associated with calculations and measurements • Accuracy: How closely a computed value or measured value agrees with true value • Precision: How individual computed values or measured values agree with one another. • Inaccuracy is also called bias • Imprecision is also called uncertainty Figure 4.1 Chapter 4 • Absolute or True Error: Et = true value – approximation • True Fractional Relative Error: Єt = true value – approximate value true value • True Percent Relative Error: Єt = true value – approximate value * 100% true value Chapter 4 • When true value is not known • Approximate relative error: Єa= approximate error * 100% approximation • Numerical methods using iteration Єa= (present approximate – previous approximate )* 100% present approximation • Stopping criterion: Relative error is less than some tolerance value Chapter 4 • Accuracy of result up to n significant digits Єs= (0.5 X 10 2 - n) % • When |Єa| < Єs then the result is correct up to n significant digits ROUND OFF ERRORS • Size and Precision limitations – Integer representation – Floating point representation – Machine epsilon (machine precision) • Numerical manipulations are sensitive to round off errors – Subtractive cancellation – Large computations TRUNCTION ERRORS • Result of using a approximation instead of exact mathematical procedure – Using Taylor series to approximate a polynomial function TOTAL NUMERICAL ERROR • Summation of truncation and roundoff errors