File
advertisement

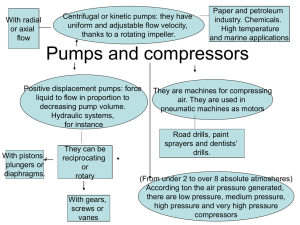
Pumps • Machine that provides energy to a fluid in a fluid system. • Converts the mechanical energy supplied to it externally to hydraulic energy and transfers it to the liquid flowing through a pipe • Flow is normally from high pressure to low pressure Pumps • On the basis of mode of action of conversion of mechanical energy to hydraulic energy, pumps are classified as – Rotodynamic pumps – Positive displacement pumps • In rotodynamic pumps, increase in energy level is due to combination of centrifugal energy, pressure energy and kinetic energy • In displacement pumps, liquid is sucked and then displaced due to the thrust exerted on it by a moving member that results in the lifting of liquid to a desired height. Centrifugal Pumps • Introduction: Centrifugal pumps are the rotodynamic machines that convert mechanical energy of shaft into kinetic and pressure energy of water which may be used to raise the level of water. The wheel in which this conversion is to realized is known as a impeller. A centrifugal pump is named so, because the energy added by the impeller to the fluid is largely due to centrifugal effects. Classification of Centrifugal Pumps Centrifugal pumps may be classified according to, 1. Working head 2. Specific speed 3. Type of casing 4. Direction of flow of water 5. Number of entrances to the impeller 6. Disposition of shaft 7. Number of stage Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 1. Working Head Centrifugal pumps may be classified in to low, medium and high-head pumps. • Low-Head Centrifugal Pumps These are usually single-stage-centrifugal pumps and work below 15m head. • Medium-Head Centrifugal Pumps When the head lies between 15 and 45 m, the pumps are called medium-head-centrifugal pumps. Classification of Centrifugal Pumps • High-Head Centrifugal Pumps When the head exceeds 45m, the pumps are known as high-head-centrifugal pumps. Usually these are multistage pumps, and are provided with guide vanes. These pumps may have horizontal or vertical shafts. Vertical shafts are useful in deep wells. Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 2. Specified Speed Specific speed of a pump is defined as the speed of a geometrically similar pump which delivers unit discharge under unit head. Ns = N√ Q / H3/4 --------------------------(10.4) Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 2. Specified Speed Following table gives the values of specific speed of different types of pumps: Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 3. Types of Casing Pumps can be divided into following type according to their casing: a) Volute-Chamber Pump b) Vortex-chamber Pump c) Diffuser Pump Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 3. Types of Casing a) Volute-Chamber Pump Such type of casing is of spiral form, and has a sectional area, which increase uniform ally from the tongue to the delivery pipe as shown in fig.10.1 more area is provided to accommodate increased quantity of water as the water moves towards the delivery pipe. Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 3. Types of Casing a) Volute-Chamber Pump Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 3. Types of Casing b) Vortex-chamber Pump In a vortex chamber, a uniformly increasing area is provided between the impeller outer periphery and the volute casing as shown in fig. 10.2 water, on leaving the impeller becomes free to adopt its path. Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 3. Types of Casing b) Vortex-chamber Pump Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 3. Types of Casing c) Diffuser Pump In a diffuser Pump, the guide vanes are arranged at the outlet of the impeller vanes. Water enters the guide without shock. As the guide vanes are of enlarging cros-sectional area, the velocity of water decreased and pressure increases Since the vanes provide better guidance to flow, eddy losses are reduced which increases the efficiency. Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 3. Types of Casing c) Diffuser Pump Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 4. Direction of Flow of Water Pumps can also have flow as under: a) Radial Flow b) Mixed Flow c) Axial Flow Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 4. Direction of Flow of Water a) Radial Flow Radial flow is one in which the flow in the impeller is completely in a radial direction. This is used when the requirements are high and low discharge. Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 4. Direction of Flow of Water b) Mixed Flow In a mixed-flow, by changing the direction of flow from pure radial to a combination of a radial and axial, area of flow is increased. Thus mixed-flow pumps are used where medium discharge is needed to raise the water to medium heads. These are mostly used for irrigation purposes. Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 4. Direction of Flow of Water c) Axial Flow These pumps find their use where high discharge at low heads is required, as in irrigation. Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 4. Direction of Flow of Water Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 5. Number of Entrances to the Impeller Pumps can have either single or double entrance according to the discharge needed: a) Single – Suction Pump b) Double – Suction Pump Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 5. Number of Entrances to the Impeller a) Single – Suction Pump Pumps which have suction pipe only on one side of the impeller are called single-suction pumps Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 5. Number of Entrances to the Impeller b) Double – Suction Pump In double suction pumps, the suction is made from both sides of the impeller (Fig. 10.5b). This increases the discharge considerably. Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 5. Number of Entrances to the Impeller Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 6. Disposition of Shaft Usually, the centrifugal pumps are used with horizontal shafts. Vertical shafts are used where there is space limitation i.e. in deep wells, mines etc. Classification of Centrifugal Pumps 7. Number of Stages A centrifugal pump can have a single stage with one impeller keyed to the shaft or it can be a multi-stage pumps. A multistage pump has a number of impellers mounted on the same shaft and enclosed in the same casing. Example No.1 A double-suction centrifugal pump delivers 2000 litres of water per second against a head of 25 m while running at 725 rmp. What type of impeller should be used for this pump? Sol. Considering only one half of the impeller, H= 25 m Q = 2000/2=1000 lit/s = 1 m3/s N= 725rmp Ns = N√ Q / H3/4 = 725√1/ (25)3/4 = 64.8 Thus a high-speed radial impeller should be used. Example No.2 A six-stage centrifugal pumps delivers 0.1 m3/s against a total head of 480 m. What is its specific speed if it routes at 1450 rpm ? What type of impeller would you recommended for the pump? Sol. Q = 0.1 m3/s N= 1450 rmp Head developed per impeller, H = 480/6 = 80 m Ns = N√ Q / H3/4 = 1450√0.1/ (80)3/4 = 17.14 For this specific speed, low-speed-radial impeller is suitable.