The Copernican Revolution
advertisement

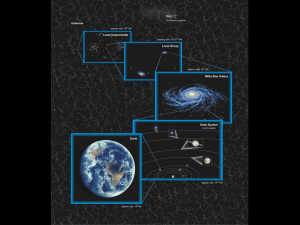
The Copernican Revolution The Birth of Modern Science Ancient Astronomers • • Found several large, important structures in the ancient world that appear astronomically aligned Used for rituals, timekeeping, agrarian cycles E pluribus unum • Western astronomy was influenced by: • Antediluvian Civilizations • • Ancient Greece • • Time divisions, ratios, zodiacal relations Muslim Caliphates • • Agrarian Timekeeping Too much to list here Adapted into the Scientific Revolution • Revolution against what? Which of these is believed to be an ancient observatory? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Stonehenge El Caracol The Quabba All of these 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 What is one practical reason for studying the skies? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. 0% 5. Zodiacal influence Fortune-telling Agriculture Myths Religion 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 What label is given to the most ancient civilizations? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. 0% 5. Ancient Old Older Antediluvian Postdiluvian 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 For what were structures like this believed to be used? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Astronomical reasons Religious reasons Cultural reasons All of the above 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Identify this structure 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Stonehenge El Caracol The Sun Dagger Newgrange 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Identify this structure 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Stonehenge El Caracol The Sun Dagger Newgrange 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Identify this structure 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Stonehenge El Caracol The Sun Dagger Newgrange 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Geocentrism • • Belief that the Earth is the center of the Universe Easy to prove the bodies rotate around Earth, just look up • • Early models just matryoshka-style nesting spheres Opposite to Heliocentrism, that the Sun is the center of the Solar System G E O C E N T R I C H E L I O C E N T R I C Unheard Cries • • • • Many Classical Astronomers believed in, and had proof of, a heliocentric universe They did not get public acceptance, as Aristotle was held in high regard by many kings, publican members, etc. Aristarchus, Eratosthenes, Nasir al-Din alTusi There were a few problems with the “perfect spheres” Retrograde • • • Inner planets dive back towards the Sun Outer planets make small loops in the sky every so often… Could this mean the Heavens weren’t perfect? • Of course, not! All it takes is a little creative imagining… Mars 1997 The Aristotelian Cycles • • • Aristotle thought maybe each planet on its sphere moved in a small circle centered on the larger sphere Epicycle – the smaller circle Deferens – the larger circle (orbit) • • epi- surface cycle- circle Ptolemaic System • • • • Ptolemy was a Greek scholar living in Egypt Refined Aristotle’s epicycle theories Ptolemy’s epicyclebased system required no less than some 80 different cycles Imagine a clock with many gears Close-minded? • • • The Ptolemaic Model was popular for some 1300 years Many religions consider us, and the Earth, special and specially located A heliocentric model made them feel less significant The Earth is at the center of a 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Geocentric model Heliocentric model Gaiacentric model Galactican model 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 The primary refusal to keep the Earth at the center of the universe was 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Religion Open-mindedness Laziness “mental inertia” 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 The Sun is at the center of a 0% Geocentric model Heliocentric model Juliacentric model Galactican model 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Circles on spheres that allow for retrograde motion were called 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Cycles Minicycles Dermicycles Epicycles 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 One Greek scientist who is credited with “codifying” planetary motion is 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. 0% 5. 0% 6. Copernicus Galileo Epicurius Aristotle Newton Ptolemy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Identify this view of the universe 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Heliocentric Egocentric Geocentric Gynocentric 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Identify this view of the universe 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Heliocentric Egocentric Geocentric Gynocentric 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 What is a small circle centered on a planets’ nested sphere? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Epidermals Epiladis Epicycles Epidurals 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Epicycles were devised to explain which motion of a planet in the sky? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Prograde Retrograde Downgrade Upgrade 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 The “Scientific Revolution” was a rebellion against what? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Ignorance Close-mindedness Superstitions All of the above 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Nicholas Copernicus • • • Rediscovered Aristarchus’s heliocentric model Used it to show harmony and simplicity Explained retrograde motion and brightness changes Huh? • • • • • Still stuck to epicycles Believed in his theory rather than proved it Unimpressed public Some 70 years (two ancient generations) passed until his work was proven/improved upon Still declared a heretic The Downfall of the Epicycle • • • Occam’s Razor Increasing accuracy of observations Longevity of observations Tycho Brahe • • • True “Renaissance Man” Built Uraniborg, an observatory in Denmark Kept some of the most accurate naked-eye observations for almost 50 years • Brahe’s naked-eye observations were extremely accurate due to the overly-large instruments he built Johannes Kepler • • • • Met up with Tycho in Prague in 1600 When Tycho died, Kepler inherited his copious tables of data Was more controlled scientifically than his peers Used math to promote several principles But, then again… • Kepler was wrong about a great many things… • • He believed in a perfect geometry of the Universe as evidence of God This caused him to reject the correct answer that orbits weren’t circular more than once What was the flaw in the Copernican view of the solar system? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Kept the Earth at the center Had the Moon in orbit around the Sun Still used epicycles He couldn’t read ancient Greek 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Which astronomer kept some of the best naked-eye observations? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Aristarchus Tycho Brahe Johannes Kepler Nicolas Copernicus 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Beside their outstanding accuracy, what was special about Brahe’s observations? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. He used a telescope Their unparalled accuracy He wrote backwards and upside down He kept these logs for many years 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Johannes Kepler rejected many sound scientific arguments while pursuing… 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. An online degree Geometric perfection Mrs. Johannes Kepler The Unification Theory 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Brahe’s accuracy in his observations was due to the 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Longevity of his observations Sizes of his astronomical tools Excellent assistants he hired Copious quantities he quaffed 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Participant Scores 500 500 Thomas Armstrong Darryl Blye 500 500 Steven Pecko Adam Ruth 500 500 500 Carlos Bogantes Sid Cooper Michael Holliday 500 500 500 Ryan Seymour Cavender Sutton Jamie Thrift 500 500 500 500 Melissa James Tamar Kiernan Jeremy King Kenneth Lewis 500 Brittany Madero Kepler’s First Law • The orbital paths of the planets are elliptical with the Sun at one focus Semi-Major Axis FOCI Eccentricity How “not circular” an orbit is The Sun is at one focus CIRCULAR ORBIT e=0 Small planets around single stars Single stars around galaxies NEAR-CIRCULAR ORBIT 0.005 e 0.250 Most single planets around single stars Asteroids, “dwarf” planets around single stars Single stars around galaxies HIGHLY ELLIPTICAL ORBIT 0.250 e Certain “dwarf” planets around single stars Comets “Perturbed” items Jupiter “perturbing” a comet Aphelion and Perihelion • • • • Perihelion Point of an orbit closest to the Sun • = a (1 – e) Aphelion Point of an orbit farthest from the Sun • = a (1 + e) Kepler’s Second Law • An imaginary line connecting the Sun to a planet sweeps equal areas of the ellipse in equal intervals of time Kepler’s Third Law • • • The square of the planet’s orbital period is proportional to the cube of its semi-major axis p2 = a3 Obeyed by all planets, not just the six Kepler knew about For the planets Ceres For the Galilean satellites Kepler’s star • • Seen in 1604 The HST snapped this picture a few years ago, showing the expanding gas cloud Galileo Gallilei • Used a telescope • • • • • • • Mountains on the Moon Sunspots Jovian Moons Phases of Venus Rings of Saturn Found many “imperfections” Wasn’t trying to anger the Church Sidereus Nuncius • • • Published in 1610 In 1616 his works were declared heresy Published a second treatise, Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems, in 1632 • • • Published in Italian rather than Latin Placed under house arrest until he died “Forgiven” in 1992 Latter-Day Proofs • • Aberration of starlight, c. 1720 Apparent shift of a star due to the revolution and rotation of the Earth Latter-Day Proofs • Parallax • • If the Earth was the center, there wouldn’t be parallax from June to January Multiple launched vehicles that follow predicted paths Who first used a telescope to observe and quantify the heavens? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Ptolemy Copernicus Galileo Brahe 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Who made multiple-year, high quality observations with large instruments in order to quantify the heavens? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Ptolemy Copernicus Galileo Brahe 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Many of Galileo’s observations challenged the Church views because 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. They were mathematical They were unorganized They showed “imperfections” They were a challenge to modesty 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Which type of orbit would you expect Ceres or Vesta to exhibit? 0% A B C 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. A B C 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Who used mathematics to provide explanations for astronomical movements? 0% Kepler Copernicus Galileo Brahe 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Which of these are not one of Galileo’s controversial observations? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Mountains on the Moon Saturn’s Rings The Andromeda Galaxy Venus’s phases 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 What would Eris’s period be in years if she lies some 67.7 AU from the Sun? 0% 4583 yrs 557 yrs 16.7 yrs 310288 yrs 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Which type of orbit would you expect Halley’s comet to exhibit? 0% A B C 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. A B C 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 For his work, Copernicus and Galileo were both 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Celebrated in their time Considered heretics Mostly ignored by others Honored as living heroes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 What is Ceres’s semimajor axis if she takes 4.6 yrs to orbit the Sun? 0% 2.8 AU 9.9 AU 21.1 AU 97 AU 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Participant Scores 900 900 Julia Burke Elisa Cooper 800 800 Sam Campbell Brandon Cole 900 900 900 Josh Cote Natalie Danna Briana O'Bryant 800 800 800 Ivy Lopez Ashden Norton Melvin Pearson 900 900 900 900 Brittany Simmons Tony Torres Justin Valerio Enrique Elias 800 Tony Blatz