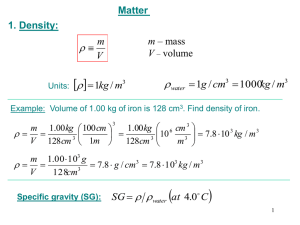
Lecture 28.BuoyancyA..
advertisement

Buoyancy and Archimedes Principle Lecturer: Professor Stephen T. Thornton Reading Quiz B) stop altogether C) go out in a straight line D) curve upwards Coca-Cola When a hole is made in the side of a Coke can holding water, water flows out and follows a parabolic trajectory. If the container is dropped in free fall, the water flow will: A) diminish Reading Quiz When a hole is made in the side of a Coke can holding water, water flows out and follows a parabolic trajectory. If the container is dropped in free fall, the water flow will: A) diminish B) stop altogether C) go out in a straight line D) curve upwards Water flows out of the hole because the pressure outside. The water pressure is due to the weight of the water. When the can is in free fall, the water is weightless, so the water pressure is zero, and hence no water is pushed out of the hole! Coca-Cola water pressure inside is larger than the air Last Time Density, fluids Pressure Pressure gauges and barometers Today More on pressure Pascal’s Principle Buoyancy Archimedes Principle Mass flow – equation of continuity Today we are studying fluid dynamics after Archimedes Principle. Measurement of Pressure; Gauges and the Barometer There are a number of different types of pressure gauges. This one is an open-tube manometer. The pressure in the open end is atmospheric pressure; the pressure being measured will cause the fluid to rise until the pressures on both sides at the same height are equal. Tire pressure gauge. Pascal’s Principle: An external pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted unchanged to every point within the fluid. Do Pascal’s vases demo Do Cartesian diver demo A Hydraulic Lift F1 F2 P A1 A2 In the hydraulic lift (show demo at end), the liquid is enclosed, and the pressure is the same throughout. F1 F2 P A1 A2 A2 F2 F1 large increase in force A1 But volumes are equal, V A1d1 A2 d 2 A1 d 2 d1 so d 2 d1 A2 Pascal’s Principle Conceptual Quiz Three open containers are filled with water to the A) container 1 same height and have the same surface area at the base, but the total weight of water is different for each. Which container has the greatest total force acting on its base? B) container 2 C) container 3 D) all three are equal Conceptual Quiz Three open containers are filled with water to the A) container 1 same height and have the same surface area at B) container 2 the base, but the total weight of water is different for each. Which container has the greatest total force acting on its base? The pressure at the bottom of each container depends only on the height of water above it! This is the same for all the containers. The total force is the product of the pressure times the area of the base, but since the base is also the same for all containers, the total force is the same. C) container 3 D) all three are equal Conceptual Quiz A) water pressure When you drink liquid through a straw, which of the items listed is primarily responsible for this to function? B) gravity C) inertia D) atmospheric pressure E) mass Conceptual Quiz A) water pressure When you drink liquid through a straw, which of the items listed below is primarily responsible for this to function? B) gravity C) inertia D) atmospheric pressure E) mass When you suck on a straw, you expand your lungs, which reduces the air pressure inside your mouth to less than atmospheric pressure. Then the atmospheric pressure pushing on the liquid in the glass provides a net upward force on the liquid in the straw sufficient to push the liquid up the straw. Follow-up: Is it possible to sip liquid through a straw on the Moon? Conceptual Quiz You put a straw into a glass of water, place your finger over the top so no air can get in or out, and then lift the straw from the liquid. You find that the straw retains some liquid. How does the air pressure P in the upper part compare to atmospheric pressure PA? A) greater than PA B) equal to PA C) less than PA Conceptual Quiz You put a straw into a glass of water, place your finger over the top so no air can get in or out, and then lift the straw from the liquid. You find that the straw retains some liquid. How does the air pressure P in the upper part compare to atmospheric pressure PA? A) greater than PA B) equal to PA C) less than PA Consider the forces acting at the bottom of the straw: PA – P – r g H = 0 This point is in equilibrium, so net force is zero. Thus, P = PA – r g H and so we see that the pressure P inside the straw must be less than the outside pressure PA. H Buoyant Force Due to a Fluid P2 P1 r gL Pressure is higher below The buoyant force is due to the difference in force at the bottom and the top of the cube of sides L. Fb F2 F1 P2 P1 L r gL L r gL 2 2 3 Fb r gV mg General result Archimedes’ principle: An object completely immersed in a fluid experiences an upward buoyant force equal in magnitude to the weight of fluid displaced by the object. Buoyant force equals the weight of the displaced liquid, not the weight of the object! Buoyancy and Archimedes’ Principle Archimedes’ principle: The buoyant force on an immersed object equals the weight of displaced fluid. The picture below shows an object in the air, partially submerged, and completely submerged. Do Archimedes’ Principle I demo. Start Archimedes’ Principle II demo. Flotation An object floats when it displaces an amount of fluid equal to its weight. The total weight of the block equals the weight of the fluid displaced. Floating an Object That Is More Dense than Water The wood and water in (a) have the same weight, and the metal block and water in (b) have the same weight. Note in (c) that bowl made of the metal floats, because the bowl is hollow. Volume of submerged block = Vsub FB mg rfVsub g rsVs g Vsub rs Vs rf weight of displaced water = weight of block Vs volume of solid is water density Remember icebergs! Conceptual Quiz: What happens to the water level when the ice melts? A) Water overflows. B) Water level decreases. C) Water level stays the same. Answer: C Water level stays the same. Because the ice cube is floating, it displaces a volume of water equal to its weight. When it melts it becomes water and displaces the same volume of water it displaced. Remember the density of ice is less than that of water. Conceptual Quiz: Two identical glasses are filled to the same level with water. One of the two glasses has ice cubes floating in it. Which weighs more? A) The glass without ice cubes. B) The glass with ice cubes. C) The two weigh the same. Answer: C The ice cubes displace exactly their own weight in water, so the two glasses weigh the same amount. It is essential that the ice sticks out above the level of the water. Conceptual Quiz: Now a pebble sits on top of the ice, and the water is filled to the brim of the glass. What happens when the ice melts? A) B) C) D) The water overflows. The water level decreases. The water level stays the same. The pebble explodes. Answer: B The ice makes no difference, but now the pebble also displaces an amount of water equal to the pebble’s weight. When the ice melts, the pebble drops to the bottom and displaces a volume of water equal to its own volume. Because the volume of the pebble is less than the volume of the water it displaced originally, there is less water displaced afterwards. The water level drops. Turbulent flow Laminar flow, also known as streamline flow. Consider a mass m passing through a particular point in time t. The ratio m/ t must be constant at every point or mass will build up. m r Av makes sense, because Av is t volume/time. If mass flow is constant, then r1 A1v1 r2 A2v2 called "equation of continuity" Gases are compressible, but liquids are not. For liquid flow, the density r is constant. Then A1v1 = A2 v2 for liquids. Useful equation for many applications: for example, water hoses. When using a water hose, we put our thumb over end to increase water speed. Hose nozzle does the same thing. Decrease area, increase speed. Water nozzle A1v1 = A2v2 small A, large v Conceptual Quiz Imagine holding two identical bricks in place underwater. Brick 1 is just beneath the surface of the water, and brick 2 is held about 2 feet down. The force needed to hold brick 2 in place is: A) greater B) the same C) smaller 1 2 Conceptual Quiz Imagine holding two identical bricks in place underwater. Brick 1 is just beneath the surface of the water, and brick 2 is held about 2 feet down. The force needed to hold brick 2 in place is: A) greater B) the same C) smaller The force needed to hold the brick in place underwater is W – FB. According to Archimedes’ Principle, FB is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced. Because each brick displaces the same amount of fluid, then FB is the same in both cases. 1 2