Thermodynamics I
advertisement

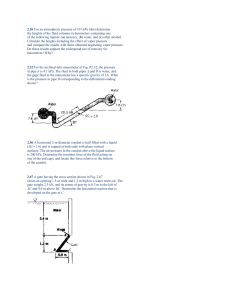
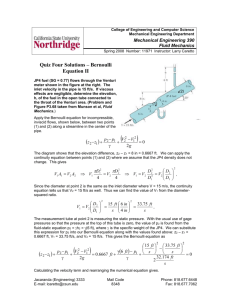
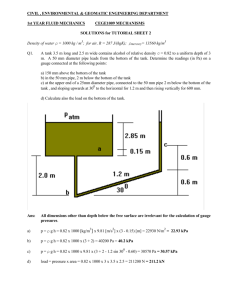
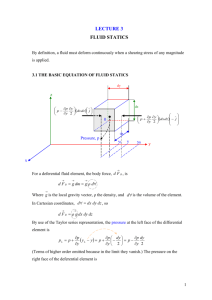
QUESTIONS Homework Jack load 12.2kN Gage pressure: 27.7kPa SG = 0.8 Examples Mercury manometer is connected to an air duct to measure its insice pressure. The manometer deflection is 15mm. Atmospheric pressure is 100kPa. Find the duct’s absolute pressure. Hg = 13,600kg/m3. Manometer Liquid flow deflection large; manometer fluid can be Hg, SG = 13.6 Gas flow deflection small; manometer fluid SG <~ 0.9. Use inclined manometer Example Mott 3.71 Figure 3.36 Gage fluid has a SG = 0.87 and L = 115mm. = 15o. Find PA. Fluid statics • Liquid at rest: F = 0 Horizontal: equal in all directions Horizontal: dependent on depth Vertical: pressure prism P = h Hydrostatic forces • • • Pressure prism Distributed forces Force → vector Direction Magnitude Line of action: center of pressure Fluid statics F = hcA magnitude hcp = hc + (I/ hcA) center of pressure Submerged surface location Top edge at liquid surface Top edge submerged Pressurized surface –equivalent depth of fluid Inclined surface Curved surface Example A heavy car veers off the road into a lake. It settles upright on the bottom. The front car door is 1.2m high and 1m wide. The top of the door is 8m below the lake surface. What is the force holding the door closed? Can the driver open the door? What can he do to survive? Example A rectangular gate is installed in a vertical wall of a reservoir. Find the magnitude of the resultant force and the center of pressure. What is the force of each latch? Example The square gate is eccentrically pivoted so that it automatically opens at a certain value of h. What is that value in terms of l ? Homework A gate for the spillway holds water at a normal high level mark. The spillway crest elevation is 2090.0 ft. The gate span is 30 ft. What is the force on the two pins holding the gate in place? Homework The air above the liquid is at 40psig. The SG of the liquid is 0.8. The rectangular gate is 1.0m wide; y1 = 1.0m; and y2 = 3m. What force P is needed to hold gate in place? Homework The inclined wall is 4m wide. Find the magnitude of the resultant force and the center of pressure. Centroid of compound area Moment of compound area about any axis is equal to sum of the moments of its parts around the same axis = (A1 x1 + A2 x2)/ AT Assignment Mott Chapters 3 & 4 References Images & examples • • • Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals & Applications, 6th Edition, Cengel & Cimbala, McGraw Hill Applied Fluid Mechanics, 6th Edition, Mott, Prentice Hall Engineering Fluid Mechanics, 5th Edition Crowe, & Roberson, Wiley Which of the examples were helpful? Why?