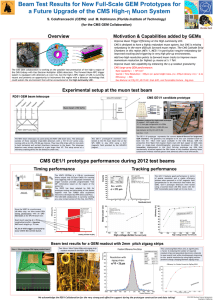
PPT - Florida Institute of Technology

Beam Test Results for a Large-area GEM Detector
Read Out with Radial Zigzag Strips
Aiwu Zhang,
V. Bhopatkar, M. Hohlmann, M. Phipps, J. Twigger
Dept. of Physics and Space Sciences,
Florida Institute of Technology
APS April meeting, Savannah, Georgia
08/04/2014
Outline
Motivation for the beam test
Large-area GEM detector & zigzag readout
Beam test setup at Fermilab
Basic characteristics of the GEM detector
Tracking & Resolution results
Summary
4/8/2014 Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 2
Motivation
• The next QCD frontier can be explored at a new Electron-Ion Collider (EIC).
The proposed EIC candidates are eRHIC at BNL and MEIC at J-Lab.
• The FLYSUB consortium is performing R&D on tracking and particle ID with
GEM detectors at a future EIC detector.
• FLYSUB: FL orida Tech (FIT), Y ale U., S tony Brook U., U . of Virginia and
B rookhaven National Lab. New members are joining into this consortium.
• The consortium conducted a joint beam test at Fermilab in October 2013.
• A 1-m long trapezoidal GEM detector with zigzag readout strips designed by FIT was studied as an option for EIC forward tracking during this beam test.
Conceptual design of
EIC detector eRHIC
Forward/backward
GEM trackers
EIC at Brookhaven National Lab.
4/8/2014
EIC at Jefferson Lab. (MEIC/ELIC)
Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 3
Large GEM detector with zigzag readout
• CMS GE1/1-III GEM foils with trapezoidal shape (1m long, 22-45cm wide) are used
• Readout boards
Left: Zigzag strips designed by FIT
Right: Straight strips (for CMS upgrade).
8 7 6
5 4
-sectors
3 2 1
Zigzag strips (1.37mrad pitch)
Zigzag strips
Straight strips
4/8/2014
1.37 mrad
• Both zigzag and straight strips are radial: strips develop in a fan-shape, full opening angle for zigzag strips is 10° .
• Eight sectors with 8 APVs (128 channels each) fully read out; need only 1/3 electronic channels of std. CMS GE1/1-III
0.1mm
GEM detector (see Vallary Bhopatkar’s talk at beginning of this session).
Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 4
Beam test setup at Fermilab
• 4 reference GEM detectors (trackers)
• Gas: Ar/CO
2
(70:30)
• Beam: 25GeV, 32GeV mixed hadrons
(π, K etc.) and 120GeV protons
• Zigzag 3-GEM det. gaps: 3/1/2/1mm
Trackers
Trackers
4/8/2014
1-m GEM w/ zigzag readout
Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 5
Basic performances of the zigzag GEM
Mean cluster size vs. HV on sector 5
(number of hits in a cluster)
Stat. errors smaller than marker size
• Cluster size: number of strips in a cluster. Mean cluster size value increases exponentially with HV
(approximately).
• Cluster charge distribution fits well to a Landau function.
• We find the typical increase of
“gain” with HV for the middlesector 5.
Total cluster charge distribution
MPV value of charge distribution vs. HV peak pos.
4/8/2014 in sector 5 at 3200V
Stat. errors smaller than marker size
Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 6
Basic performances (cont.)
Charge in different sectors (uniformity) Detection efficiency
• We scanned two positions on each sector from sector 1 to 7. From sector to sector the response varies by 20%, which is probably caused by uneven foil gaps.
• Detector efficiency on sector 5 vs. HV can be fitted with a Sigmoid function.
• Different thresholds were compared: N sigma, N=3,4,5,6, where sigma is width of pedestal distribution.
• Plateau efficiency with 5 sigma cut is (98.4 ± 0.2)%
4/8/2014 Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 7
Tracking method for the zigzag GEM
Inclusive residual for 1 st tracker Resolution in ϕ for trackers Aligning trackers to zigzag GEM det.
σ=21μrad vertex
10° Eta
5
REF
Det.
X
X offset
Errors smaller than marker size
• After aligning the trackers to each other with shifts and rotations, they are giving resolutions of 70μm or better (≈ typical spatial resolution for std. GEM detectors) in both X and Y.
• The radial zigzag strips measure the azimuthal coordinate ϕ and have a pitch of
1.37mrad, so we study the resolution in natural polar coordinates (r, ϕ) .
• Tracking in polar system was demonstrated to be working as well as in the Cartesian system. The trackers have azimuthal resolutions around 30μrad.
• The ϕ resolution of the zigzag GEM detector can be studied if its vertex is taken as the origin of the tracking system. (X,Y) offsets need to be found to align the tracker origin to the vertex of the zigzag GEM detector .
4/8/2014 Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 8
Three alignment checks for (X,Y) offsets
Track χ 2 in ϕ vs. tracker X offset for Y = -36.5mm
Minimal point gives
X = -1866.4mm
Residual mean should be centered at 0
Inclusive residual width
4/8/2014 Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 9
Residuals after the alignment
Inclusive residual
(zigzag GEM is
included in track fit)
σ = 215μrad
Exclusive residual
(zigzag GEM is
excluded from track fit)
σ = 270μrad
• After (X,Y) offsets are optimized, both inclusive and exclusive residuals are calculated for the zigzag GEM detector.
• The residuals shown above are for sector 5 @3300V.
4/8/2014 Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 10
Spatial resolution for the zigzag GEM
Resolution vs. HV in middle-sector 5 Resolution as a function of
-sectors
• Left: Higher voltage, i.e. higher gas gain, gives better resolution as expected.
• Right: Resolutions in different sectors at 3200V. We observe similar azimuthal
resolutions (variation about 10%) in the first six sectors. Resolution in sector 7 is a little worse; the reason is likely to be lower gas gain in that sector.
4/8/2014 Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 11
Summary and Conclusion
• The zigzag strip readout method reduces the number of strips and readout channels by a factor of 3 which reduces system cost.
• The FNAL beam test was successful. We operated 10 GEM detectors including a large trapezoidal Triple-GEM with zigzag readout strips.
• The large-area zigzag GEM detector was working quite well. It had high and stable gain, plateau detection efficiency of 98% and spatial resolution of 241μrad (449μm) at 3300V.
• The resolution is expected to be improved further by also correcting for the non-linearity of charge sharing between strips (response fct.)
• The structure of zigzag strips can be optimized to get even better resolution. For example, the interleaving between zigs and zags can be improved by industrial PCB factories to yield better charge sharing.
• We conclude that a zigzag GEM detector can be an option for the cost-conscious construction of a forward tracker in an EIC detector.
4/8/2014 Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 12
The FLYSUB consortium
We would like to acknowledge BNL for the support of this work through the EIC RD-6 collaboration and the staff of the FNAL test beam facility for all their help.
4/8/2014 Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 13
Backup - EIC physics
• (inclusive or semi-inclusive) DIS is a powerful way to probe the internal structure of nucleons
• Transverse Momentum Dependent parton distributions (TMDs) open a new window to understand some of the most fundamental aspects of QCD
• Address the spin problem of the nucleon; illuminate the role played by angular momentum of partons
• Two golden measurements on an EIC:
3-d imaging of gluons and quarks, and their spins
Di-jet measurements
4/8/2014 Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 14
Backup- how to transfer resolution from μrad to μm
<r>[μm] σ r
[μm] <ϕ>[μrad] σ ϕ
[μrad] <x>[μm] σ x
[μm] <y>[μm] σ y
[μm] σ y
[μm]
REF2 3.6
46 4.2
21 3.7
46 9 45 45
REF3 -3.6
69
UVA3 -11.6
55
-5.7
-3.6
31
23
-3.6
-11.6
69
55
-12
-8
69
50
66
49
REF1 10 59 5 25 10 59 10 55 53
• Resolutions in (x,y) are also calculated at this origin.
• Resolutions in r are almost the same as resolutions in X.
• The last column shows the calculated resolutions in y from resolutions in ϕ, they match with the measured resolutions in y .
• Also, <x>≈<r> and <y>≈<ϕ>*L
• Tracking in polar coordinates works well and gives high resolutions.
σ ϕ
L
σ y
4/8/2014 Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 15
Backup – electronics, SRU
• The test beam took data for 60 APVs (128ch/ea.) simultaneously through the Scalable Readout Unit (SRU).
• Data were taken with DATE and amoreSRS under Linux system.
4/8/2014 Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag Readout / Aiwu Zhang 16
4/8/2014
Backup -- Rotation
• The detector might be rotated a small angle relative to the first tracker. The angle should be close to 0 if alignment is correct.
Rotation of the Zigzag detector should be minimal at 0 if the alignment is correct rotation
Beam Test of a GEM Detector with Zigzag
Readout / Aiwu Zhang
17