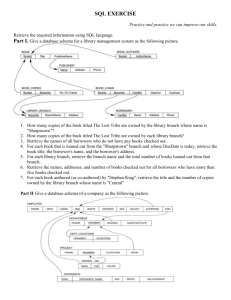
Lecture 1
Relational Algebra and Relational Calculus
Unary Relational Operations
► SELECT
Operation
To select the EMPLOYEE tuples whose department number is four
DNO = 4 (EMPLOYEE)
To select the EMPLOYEE tuples whose salary is greater than $30,000
SALARY > 30,000 (EMPLOYEE)
Unary Relational Operations
► PROJECT
Operation
To list each employee’s first and last name and
salary, the following is used
LNAME, FNAME,SALARY(EMPLOYEE)
Show the full name and salary of every
employee.
Show the gender and salary of every
employee.
Select the gender and salary of all
Select employees in dep. 4 with salaries
employees in dep. 4 with salaries
exceeding 25000 or in dep. 5 with
exceeding 25000 or in dep. 5 with
salaries exceeding 30000
salaries exceeding 30000
Unary Relational Operations
►
To retrieve the first name, last name, and salary of all employees
who work in department 5, we must apply select and project
operations.
We can write a single relational algebra expression as follows:
► FNAME, LNAME, SALARY(
DNO=5
(EMPLOYEE))
OR We can explicitly show the sequence of operations, giving a name to
each intermediate relation:
► TEMP DNO=5(EMPLOYEE)
► R FNAME, LNAME, SALARY (TEMP)
Slide 6- 9
Operations From Set Theorys
► CARTESIAN
(or cross product) Operation
Find the cross product between female employees
(Fname, LName and SSN) and dependents
SEX=’F’(EMPLOYEE)
►EMPNAMES FNAME, LNAME,SSN (FEMALE_EMPS)
►EMP_DEPENDENTS EMPNAMES x DEPENDENT
►FEMALE_EMPS
The rest are
spurious
To get
employees’
dependant
s, SSNs
must
match
Binary Relational Operations
►
Retrieve the manager of each department
we need to combine each DEPARTMENT tuple with the EMPLOYEE tuple
whose SSN value matches the MGRSSN value in the department tuple
We do this by using the join
operation
►
DEPT_MGR DEPARTMENT
MGRSSN=SSN
EMPLOYEE
Binary Relational Operations
► Get
the locations of every department
DEPT_LOCS DEPARTMENT
DEPT_LOCATIONS
DNUMBER=DNUMBER
Examples of Relational Algebra Queries
Q1: Retrieve the names and addresses of all employees
who work for the ‘Research’ department
RESEARCH_DEPT DNAME=‘Research’ (DEPARTMENT)
RESEARCH_EMPS (RESEARCH_DEPT
RESULT FNAME, LNAME, ADDRESS (RESEARCH_EMPS)
DNUMBER= DNOEMPLOYEE
EMPLOYEE)
Q2: For every project located in ‘Stafford’, list the project number
and the controlling department name
STAFFORD_PROJS PLOCATION=‘STAFFORD’ (PROJECT)
CONTR_DEPT (STAFFORD_PROJS
RESULT PNUMBER, DNAME (RESEARCH_EMPS)
DNUM=DNUMBER
DEPARTMENT)
Examples of Relational Algebra Queries
Q3: For every project located in ‘Stafford’, list the project number,
the controlling department name and the department manager’s
last name, address and birth date
STAFFORD_PROJS PLOCATION=‘STAFFORD’ (PROJECT)
CONTR_DEPT (STAFFORD_PROJS
PROJ_DEPT_MGR (CONTR_DEPT
RESULT PNUMBER, DNAME,LNAME, ADDRESS, BDATE (RESEARCH_EMPS)
DEPARTMENT)
EMPLOYEE)
DNUM=DNUMBER
MGRSSN=SSN
Examples of Relational Algebra
Queries
Q4: Find the names of employees who work on ALL projects controlled by
department number 5
DEPT5_PROJS(PNO) PNUMBER( DNUM=5 (PROJECT))
EMP_PROJ(SSN, PNO) ESSN, PNO(WORKS_ON)
RESULT_EMP_SSNS EMP_PROJ ÷ DEPT5_PROJS
RESULT FNAME, LNAME (RESULT_EMP_SSNS
ESSN = SSN EMPLOYEE)
Q5:Make a list of project numbers for projects that involve an employee
whose last name is ‘Smith’ either as a worker or as a manager of the
department that controls the project
SMITHS SSN( LNAME=‘Smith’(EMPLOYEE))
SMITH_WORKER_PROJ PNO(WORKS_ON
ESSN = SSN SMITHS)
MGRS LNAME, DNUMBER(EMPLOYEE
SSN=MGRSSN DEPARTMENT)
SMITH_MANAGED_DEPTS (DNUM) DNUMBER( LNAME=‘Smith’(MGRS))
SMITH_MANAGED_PROJS (PNO) PNUMBER(SMITH_MANAGED_DEPTS
RESULT (SMITH_WORKER_PROJS
SMITH_MGR_PROJS)
DNUMBER =DNUM
PROJECT)
Additional Relational Operations
►
Use of the Functional operator ℱ (script f)
ℱFUNCTION ATTRIBUTE (R)
► ℱMAX Salary
► ℱMIN Salary
(Employee) retrieves the maximum salary value from Employee
(Employee) retrieves the minimum Salary value from Employee
► ℱSUM Salary
(Employee) retrieves the sum of the Salary from Employee
Sometimes we want to get aggregate functions over groups of tuples
(e.g. for all employees in every department separately)
► GROUPING_ATTRIBUTES
ℱFUNCTION ATTRIBUTE (R)
ℱCOUNT SSN, AVERAGE Salary (Employee) groups employees by DNO (department
number) and computes the count of employees and average salary per
department
DNO
R(DNO, NO_OF_EMPLOYEES, AVERAGE_SAL )
(DNO ℱCOUNT SSN, AVERAGE Salary
(Employee))
Get the number of employees and the
average salary in each department
DNO
ℱCOUNT SSN, AVERAGE Salary (Employee)
If no names are specified for aggregates:
FUNCTION_ATTRIBUTE
Get the number of employees in the company
and the average salary of an employee
ℱCOUNT SSN, AVERAGE Salary (Employee)
Default Names
Examples of Relational Algebra Queries
►
Q6: List the names of all employees with two or more
dependents
T1(SSN, NO_OF_DEPTS)
ESSN
ℱ Count DEPENDENT_NAME (DEPENDENT)
T2 NO_OF_DEPS >=2 (T1)
RESULT
►
LNAME, FNAME (T2
SSN=SSN
EMPLOYEE)
Q7: Retrieve the names of employees who have no
dependents
ALL_EMPS SSN(EMPLOYEE)
EMPS_WITH_DEPS(SSN) ESSN(DEPENDENT)
EMPS_WITHOUT_DEPS (ALL_EMPS - EMPS_WITH_DEPS)
RESULT
LNAME, FNAME (EMPS_WITHOUT_DEPS
SSN=SSN
EMPLOYEE)
EMPLOYEE
SSN = MGRSNN
DEPARTMENT
SSN
SUPERSSN