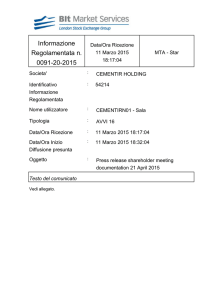
Permeability Determination
advertisement

Platzhalter Titelbild Superabsorbent Polymers (SAP) as Water-Blocking Components in Cables Martin Tennie (martin.tennie@evonik.com) ICC Meeting November 2012 St.Petersburg, Florida, USA Modern Superabsorbents Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 2 Modern Superabsorbents SAP is a crosslinked and partely neutralized (mostely with Sodium) poly-Acrylic-Acid forming a 3-dimensional network Na OOC HOOC COO Na Na OOC Na OOC COO Na COO Na COO Na COOH COOH COOH COO Na COO Na HOOC COO Na COO Na COOH COO Na COO Na Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 3 Polymerisation Radical Chain Polymerisation I + CH2=CH-COOH I-CH2-CH-COOH + CH2=CH-COOH I-CH2-CH-COOH I-CH2-CH-CH2-CH-COOH COOH I-CH2-CH-CH2-CH-COOH + CH2=CH-COOH COOH I-CH2-CH-CH2-CH-CH2-CH COOH COOH COOH I : Radicalic Starter Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 4 Crosslinking Temp. Time Temp. Time Temp. Time COOH COOH I I I-CH2-CH-CH2-CH-CH2-CH- I I COOH Short chains „Extractables“ Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 5 Polymerdesign and Properties Absorption/Retention: Funktion of cross-linking High retention capacity Retention / Absorption Degree of crosslinking (crosslinker/ monomer ratio) Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 6 Polymerdesign and Properties Elasic Modulus: Funktion of cross-linking Gel Strength / Absorption under load Soft swollen gel Easily deformed Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida High gel strength SAP Not easily deformed Degree of crosslinking Seite | 7 Polymerdesign and Properties Absorption speed: Function of elasticity (cross-linking) and particle size Small particle large outer surface Large particle small surface area Swelling Force Relaxing force vs swelling force Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Relaxing Force Seite | 8 Hydrolysis Stability Turning from a particle of hydrogel into a viscous liquid Energy/Water Breaking the x-linking Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Energy/Water Breaking the chains Seite | 9 Product Properties Absorption Speed Hydrolysis Stability Water Conductivity “Permeability” Absorption/Retention “Gelstrength” Elastic Modulus Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 10 Core Property - Permeability Permeability means water transport through a mass of swollen SAP High permeability Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Low Permeability Seite | 11 Influencing the Permeability Particle shape Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 12 Influencing the Permeability Extractables: Short to mid chain length and not incorporated to the network and water soluble. Acting as thickener and increase the viscosity of water. dv D AP L dt Darcy´s Law: = Specific permeability of sample A = Cross-sectional area of sample P = Pressure difference driving the permeation L = Length of sample = Viscosity of fluid D Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 13 Tested SAP Materials Sample Code Morphology Absorption in DI Water [g/g] Absorption Speed [mm after 1 min.] 1 2 3 4 5 6 Bead Bead Bead Crystal Crystal Crystal 460 440 380 260 200 210 > 16 > 16 16 12 3 7 Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 14 Gel Degradation at 80 °C Degradation of hydrogel made with DI-water (x-axis not linear) Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 15 Gel Degradation at 80 °C Degradation of hydrogel made with Synthetic Sea Water (DIN 50900) (x-axis not linear) Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 16 Gel Degradation at 80 °C Degradation of hydrogel made with hard tap-water (Grade4) (x-axis not linear) Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 17 Gel Degradation What the numbers mean in reality – A non stable product Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 18 Gel Degradation What the numbers mean in reality – A non stable product 3 weeks later Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 19 Gel Degradation What the numbers mean in reality– A non stable product Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 20 Gel Degradation What the numbers mean in reality – A stable product Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 21 Gel Degradation What the numbers mean in reality – A stable product 3 weeks later Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 22 Gel Degradation What the numbers mean in reality– A stable product Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 23 Rheological Properties Correlation E-modulus and degree of saturation (DI-water) 12 Viscosity/Gelstrength [[logPa] 10 8 Quarter Saturated 6 Half Saturated Full Saturated 4 2 0 #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 Sample Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 24 Rheological Properties Gelstrength of 100% saturated (DI-water) SAP 7 6 Gelstrength [Pa] 5 4 3 2 1 0 #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 Sample Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 25 Permeability Determination Shematic and real set-up of test equipment Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 26 Permeability Determination Picture of a treated capillary. The red lines indicates the measured penetration distance. Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 27 Permeability Determination DI Water at 20 °C Time Minutes 5 10 20 60 120 480 Days 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Density [g/g] Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3 Sample 4 Sample 5 Sample 6 1 2 2 2 2 3 1 2 2 2 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 1 1 1 2 2 3 1 1 1 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 6 8 10 12 15 18 30 365 9 14 18 20 23 24 36 375 6 8 11 12 13 14 16 385 4 6 8 9 10 12 13 380 5 8 10 11 12 14 15 360 5 7 8 8 10 11 11 385 Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 28 Permeability Determination DI-Water at 60 °C Time Minutes 5 10 20 60 120 480 Days 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Density [g/g] Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3 Sample 4 Sample 5 Sample 6 0 0 0 1 1 2 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 2 2 4 6 0 1 1 1 2 3 1 1 2 2 2 4 1 2 2 2 3 3 4 18 20 28 34 45 55 375 3 20 26 33 48 54 60 385 8 14 18 21 23 25 26 380 7 9 12 15 17 19 20 390 7 9 12 14 16 18 20 380 5 8 10 12 14 15 15 375 Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 29 Permeability Determination Tap Water (Hardness 4) at 20 °C Time Minutes 5 10 20 60 120 480 Days 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Density [g/g] Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3 Sample 4 Sample 5 Sample 6 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 3 2 3 4 4 5 5 2 2 3 3 3 5 0 1 1 2 2 4 3 4 4 4 4 4 5 12 15 20 22 24 28 365 7 13 16 23 25 28 31 370 9 10 12 13 15 18 20 385 10 12 15 18 20 22 24 390 8 12 15 17 20 22 24 385 6 7 8 10 13 14 14 375 Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 30 Permeability Determination Tap Water (Hardness 4) at 60 °C Time Minutes 5 10 20 60 120 480 Days 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Density [g/g] Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3 Sample 4 Sample 5 Sample 6 0 1 1 1 2 2 0 1 1 1 2 3 1 2 2 3 4 4 1 1 2 2 3 3 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 4 5 7 15 18 25 30 35 40 380 10 18 24 30 37 45 50 395 10 14 16 18 22 27 30 375 12 14 17 21 24 29 32 380 10 13 17 21 23 25 27 390 9 11 13 15 16 17 17 370 Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 31 Permeability Determination Synthetic Seawater (DIN 50900) at 20 °C Time Minutes 5 10 20 60 120 480 Days 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Density [g/g] Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3 Sample 4 Sample 5 Sample 6 2 3 3 3 3 3 2 5 5 5 7 7 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 1 2 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 3 3 5 14 16 20 22 24 26 365 10 26 29 34 38 40 44 370 8 12 14 16 17 19 20 395 10 14 16 17 18 18 24 385 5 8 10 12 14 16 18 370 7 9 10 12 14 15 15 375 Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 32 Permeability Determination Synthetic Seawater (DIN 50900) at 60 °C Time Minutes 5 10 20 60 120 480 Days 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Density [g/g] Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3 Sample 4 Sample 5 Sample 6 0 1 1 2 2 3 1 1 1 2 2 3 0 0 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 3 1 1 1 2 3 4 2 2 2 3 3 3 7 16 20 25 27 30 32 395 9 18 25 31 36 42 48 390 6 15 19 22 25 27 29 370 10 16 18 20 23 25 30 375 6 10 12 15 18 19 21 365 8 11 13 14 17 18 18 380 Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 33 Discussion and Conclusion Correlation E-Modulus and Penetrationlength (DI-Water at 20 °C] Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 34 Discussion and Conclusion Not the initial swell speed and high absorption capacity guaranted long term sealing. Important is rheological structure and hydrolysis stability of swollen SAP is key factor. Testing the parameters hydrolysis-stability and permeability of swollen SAP at higher temperatures show performance differences in short time. Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 35 Expression of Thanks Mr. Alton Deaton Dr. Jochen Houben Mr. Bobby Mitra Dr. Scott Smith and all of you for your interest. Martin Tennie ICC Meeting Nov.2012, St. Petersburg, Florida Seite | 36