surroundsense
advertisement

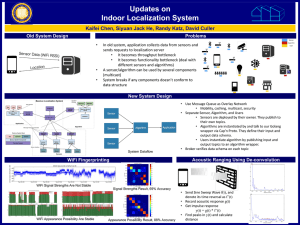
SurroundSense: Mobile Phone Localization via Ambience Fingerprinting 1 Context Pervasive wireless connectivity + Localization technology = Location-based applications 2 Location-Based Applications (LBAs) For Example: GeoLife shows grocery list when near Walmart MicroBlog queries users at a museum Location-based ad: Phone gets coupon at Starbucks iPhone AppStore: 3000 LBAs, Android: 500 LBAs 3 Most emerging location based apps do not care about the physical location GPS: Latitude, Longitude 4 Most emerging location based apps do not care about the physical location GPS: Latitude, Longitude Instead, they need the user’s logical location Starbucks, RadioShack, Museum, Library 5 Physical Vs Logical Unfortunately, most existing solutions are physical GPS GSM based SkyHook Google Latitude RADAR Cricket … 6 Given this rich literature, Why not convert from Physical to Logical Locations? 7 Physical Location Error 8 Starbucks Pizza Hut Physical Location Error 9 Starbucks Pizza Hut Physical Location Error The dividing-wall problem 10 SurroundSense: A Logical Localization Solution 11 Hypothesis It is possible to localize phones by sensing the ambience such as sound, light, color, movement, WiFi … 12 Hypothesis It is possible to localize phones by sensing the ambience such as sound, light, color, movement, WiFi … 13 Multi-dimensional sensing extracts more ambient information Any one dimension may not be unique, but put together, they may provide a unique fingerprint 14 SurroundSense Multi-dimensional fingerprint Based on ambient sound/light/color/movement/WiFi Starbucks QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Pizza Hut Wall 15 Should Ambiences be Unique Worldwide? H J P I A K CB D E Q R O F Q L N M G 16 GSM Ambiences provides macro location (strip mall) Should be Unique Worldwide? SurroundSense refines to Starbucks H J P I A K CB D E Q R O F Q L N M G 17 Why does it work? The Intuition: Economics forces nearby businesses to be diverse Not profitable to have 3 adjascent coffee shops with same lighting, music, color, layout, etc. SurroundSense exploits this ambience diversity 18 SurroundSense Architecture Ambience Fingerprinting Matching Sound Color/Light + Test Fingerprint Acc. = WiFi GSM Macro Location Logical Location Fingerprint Database Candidate Fingerprints 19 Acoustic fingerprint (amplitude distribution) Fingerprints 0.14 Sound: (via phone microphone) Normalized Count 0.12 0.1 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 0 -1 -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 Amplitude Values 1 Lightnes s Color: (via phone camera) Color and light fingerprints on HSL space 0.5 0 0 0.5 Hue 1 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 Saturation 20 Fingerprints Movement: (via phone accelerometer) Cafeteria Clothes Store Grocery Store Moving Static 21 Fingerprints Movement: (via phone accelerometer) Cafeteria Clothes Store Grocery Store Moving Static Queuing Seated 22 Fingerprints Movement: (via phone accelerometer) Cafeteria Clothes Store Grocery Store Moving Static Pause for product browsing Short walks between product browsing 23 Fingerprints Movement: (via phone accelerometer) Cafeteria Clothes Store Grocery Store Moving Static Walk more Quicker stops 24 Fingerprints Movement: (via phone accelerometer) Cafeteria Clothes Store Grocery Store Moving Static WiFi: (via phone wireless card) ƒ(overheard WiFi APs) 25 Discussion Time varying ambience Collect ambience fingerprints over different time windows What if phones are in pockets? Use sound/WiFi/movement Opportunistically take pictures Fingerprint Database War-sensing 26 Evaluation Methodology 51 business locations 46 in Durham, NC 5 in India Data collected by 4 people 12 tests per location Mimicked customer behavior 27 Evaluation: Per-Cluster Accuracy Cluster 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 No. of Shops 4 7 3 7 4 5 5 6 5 5 Accuracy (%) Localization accuracy per cluster Cluster 28 Evaluation: Per-Cluster Accuracy Cluster 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 No. of Shops 4 7 3 7 4 5 5 6 5 5 Localization accuracy per cluster Accuracy (%) Fault tolerance Cluster 29 Evaluation: Per-Cluster Accuracy Cluster 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 No. of Shops 4 7 3 7 4 5 5 6 5 5 Accuracy (%) Sparse WiFi Localization accuracy perAPs cluster Cluster 30 Evaluation: Per-Cluster Accuracy Cluster 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 No. of Shops 4 7 3 7 4 5 5 6 5 5 Accuracy (%) Localization accuracy per cluster No WiFi APs Cluster 31 Evaluation: Per-Scheme Accuracy Mode WiFi Snd-Acc-WiFi Snd-Acc-Lt-Clr SS Accuracy 70% 74% 76% 87% 32 Evaluation: User Experience Random Person Accuracy 1 WiFI Snd-Acc-WiFi Snd-Acc-Clr-Lt SurroundSense 0.9 0.8 0.7 CDF 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Average Accuracy (%) 80 90 100 33 Limitations and Future Work Energy-Efficiency Continuous sensing likely to have a large energy draw 34 Limitations and Future Work Energy-Efficiency Continuous sensing likely to have a large energy draw Localization in Real Time User’s movement requires time to converge 35 Limitations and Future Work Energy-Efficiency Continuous sensing likely to have a large energy draw Localization in Real Time User’s movement requires time to converge Non-business locations Ambiences may be less diverse 36 Limitations and Future Work Electroic compasses can fingerprint layout Tables and shelves laid out in different orientations Users forced to orient in those ways Quick Time™ and a TIFF ( Uncompr ess ed) decompr ess or ar e needed to s ee this pic ture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. a d na ™emi Tkci uQ ro sser pmo ced ) des serp mocn U( F FIT .erut cip s iht e es ot ded een era QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. 37 Conclusion Ambience can be a great clue about location Ambient Sound, light, color, movement … None of the individual sensors good enough Combined they may be unique Uniqueness facilitated by economic incentive Businesses benefit if they are mutually diverse in ambience Ambience diversity helps SurroundSense Current accuracy of 89% 38 Questions? 39 Summary SurroundSense evaluated in 51 business locations Achieved 89% accuracy But perhaps more importantly, SurroundSense scales to any part of the world 40 SurroundSense Today’s technologies cannot provide logical localization Ambience contains information for logical localization Mobile Phones can harness the ambience via sensors More sensors, beter reliability Evaluation results: 51 business locations, 87% accuracy SurroundSense can scale to any part of the world 41 42 Evaluation: Per-Shop Accuracy Localization Accuracy per Shop 1 WiFi Snd-Acc-WiFi Snd-Acc-Clr-Lt SurroundSense 0.9 0.8 0.7 CDF 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Average Accuracy (%) 80 90 100 43 Architecture: Filtering & Matching Candidate Fingerprints 44 Fingerprinting Sound Fingerprint generation : Signal amplitude Amplitude values divided in 100 equal intervals Sound Fingerprint = 100 normalized values • valueX = # of samples in interval x / total # of samples Filter Metric: Euclidean distance Discard candidate fingerprint if metric > threshold г Threshold г Multiple 1 minute recordings at the same location di = max dist ( any two recordings ) г = max ( di of candidate locations ) 45 Fingerprinting Motion Fingerprint generation: stationary/moving periods Sitting (restaurants, cafes, haircutters ) Slow Browsing (bookstores, music stores, clothing) Speed-Walking (groceries) Filter Metric: R tmoving t static 0.0 ≤ R ≤ 0.2 0.2 ≤ R ≤ 2.0 2.0 ≤ R ≤ ∞ sitting slow browsing speed-walking Discard candidate fingerprints with different classification 46 Fingerprinting WiFi Fingerprint generation: fraction of time each unique address was overheard Filter/Ranking Metric Discard candidate fingerprints which do not have similar MAC frequencies 47 Fingerprinting Color Floor Pictures Rich diversity across different locations Uniformity at the same location Fingerprint generation: pictures in HSL space K-means clustering algorithm Cluster’s centers + sizes Ranking metric 48 Thinking about Localization from an application perspective… 49 Emerging location based apps need place of user, not physical location Starbucks, RadioShack, Museum, Library Latitude, Longitude 50 Emerging location based apps need place of user, not physical location Starbucks, RadioShack, Museum, Library Latitude, Longitude We call this Logical Localization … 51 Can we convert from Physical to Logical Localization? 52 Can we convert from Physical to Logical Localization? State of the Art in Physical Localization: 1. GPS Accuracy: 10m 2. GSM Accuracy: 100m 3. Skyhook (WiFi+GPS+GSM) Accuracy: 10m-100m 53 Can we convert from Physical to Logical Localization? State of the Art in Physical Localization: 1. GPS Accuracy: 10m 2. GSM Accuracy: 100m 3. Skyhook (WiFi+GPS+GSM) Accuracy: 10m-100m Widely-deployable localization technologies have errors in the range of several meters 54 Physical Vs Logical Lot of work in physical localization GPS (5m accuracy, outdoor only) GSM based (high coverage, 200m accuracy) SkyHook (40m accuracy, need war-driving) Google Latitude (similar) RADAR (5m accuracy, need indoor mapping) Cricket (install per-room devices) … Each of them has distinct problems … 55 Physical Vs Logical Lot of work in physical localization GPS (5m accuracy, outdoor only) GSM based (high coverage, 200m accuracy) SkyHook (40m accuracy, need war-driving) Google Latitude (similar) RADAR (5m accuracy, need indoor mapping) Cricket (install per-room devices) … Each of them has distinct problems … 56 Even if we assume the best of all solutions (5m accuracy indoors) logical localization still remains a challenge. 57 Contents SurroundSense Evaluation Limitations and Future Work Conclusion 58 Contents SurroundSense Evaluation Limitations and Future Work Conclusion 59 Contents SurroundSense Evaluation Limitations and Future Work Conclusion 60 Contents SurroundSense Evaluation Limitations and Future Work Conclusion 61 Contents SurroundSense Evaluation Limitations and Future Work Conclusion 62 Evaluation: Per-Cluster Accuracy Cluster 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 No. of Shops 4 7 3 7 4 5 5 6 5 5 Accuracy (%) Localization accuracy per cluster Multidimensional sensing Cluster 63 Limitations and Future Work Energy-Efficiency Localization in Real Time Non-business locations 64 Limitations and Future Work Energy-Efficiency Continuous sensing likely to have a large energy draw Localization in Real Time Non-business locations 65 Limitations and Future Work Energy-Efficiency Continuous sensing likely to have a large energy draw Localization in Real Time User’s movement requires time to converge Non-business locations 66 Limitations and Future Work Camera inside pockets Detect phone when out of pocket Takes pictures when camera pointing downward 67