Adding and Subtracting Polynomials
advertisement

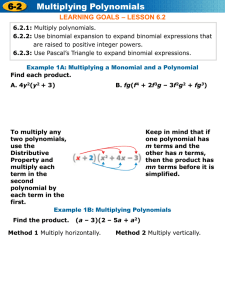
Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Section 0.3 Polynomial A polynomial in x is an algebraic expression of the form: an x n an1x n1 an2 x n2 ...a2 x 2 a1x a0 The degree of the polynomial is n (largest exponent) The leading coefficient is an ( the coefficient on term with highest exponent) The constant term is a0 (the term without a variable) The polynomial should be written in standard form. (Decreasing order according to exponents) Polynomials 3x 4 2 x 3 15x 9 Degree: 4 Leading Coefficient: Constant: -9 3 Polynomials Naming a polynomial: 1 term - monomial 2 terms - binomial 3 terms - trinomial 4 or more - terms polynomial Example 2x + 7 has 2 terms so it is called a binomial Classifying Polynomials (a) 2 t 4 + 7 Two terms. (b) 3 e 2 + 5 e 2 – 9 e 2 = –e2 One term. The polynomial cannot be simplified. The degree is 4. The polynomial is a binomial. The polynomial can be simplified. The degree is 2. The simplified polynomial is a monomial. Combine like terms and put the polynomial in standard form. What degree is the polynomial? Name the polynomial by the number of terms. 5x x 3 x 7 x 4 8x x 7 x 4 7 x5 8x 4 x Degree is 5 Trinomial 4 5 5 Adding Polynomials Adding Polynomials Horizontally Add 2n 4 – 7n 3 – 4 and – 5n 4 – 8n 3 + 10. ( 2n 4 – 7n 3 – 4 ) + ( – 5n 4 – 8n 3 + 10 ) = – 3n4 – 15n 3 + 6 Adding Polynomials 3 2 3 2 Find the sum (8y – 7y – y + 3) + (6y + 2y – 4y + 1). 14y 3 – 5y 2 – 5y + 4 Subtracting Polynomials Subtracting Polynomials To subtract two polynomials, change all the signs of the second polynomial and add the result to the first polynomial. (Distribute the negative) Subtracting Polynomials Perform the subtraction ( 3x – 5 ) – ( 6x – 4 ). ( 3x – 5 ) – ( 6x – 4 ) = 3x – 5 – 6x + 4 = – 3x – 1 Change the signs in the second polynomial. Subtracting Multivariable Polynomials Add or subtract as indicated. ( 2a2 b – 4ab + b 2 ) – ( 5a 2 b – 3ab + 7b 2 ) = 2a 2b – 4ab + b 2 – 5a 2 b + 3ab – 7b 2 = – 3a 2 b – ab – 6b2 Multiplying Polynomials Use the distributive property to find each product. (a) 5x2 ( 6x 4 + 7 ) = 5x 2 ( 6x 4) + = 30x6 + 5x 2 ( 7 ) 35x2 Distributive property Multiply monomials. Multiplying Polynomials Use the distributive property to find each product. (b) – 2h4 ( – 3h9 + 8h 2 – 1 ) 6h13 16h 6 2h 4 Multiplying Binomial times Binomial F ( 3g + 2 ) ( 9g – 4 ) O I L = 27g 2 – 12g + 18g – 8 = 27g 2 + 6g – 8 Multiply the First terms: 3g ( 9g ) F Multiply the Outer terms: 3g ( – 4 ) O Multiply the Inner terms: 2 ( 9g ) I Multiply the Last terms: 2(–4) L Multiplying Polynomials ( 6a + 3b ) ( 4a – 2b ) 24a 12 ab 12 ab 6b 2 = 24a2 – 6b2 2 Multiplying Binomial times Trinomial (Megafoil) Multiply ( 2y 2 – 5 )( 2y 3 – 7y + 4 ). ( 2y 2 – 5 )( 2y 3 – 7y + 4 ) Distributive property = (2y 2)(2y3 ) + (2y2 ) (–7y) + (2y 2)(4) + (–5)(2y3 ) + (–5)(–7y) + (–5)(4) = 4y 5 – 14y 3 + 8y2 – 10y 3 + 35y – 20 = 4y 5 – 24y 3 + 8y2 + 35y – 20 Combine like terms. Square a binomial (x+4)² (x+4)(x+4) x² + 4x + 4x + 16 x² + 8x + 16 (x-7)² (x-7)(x-7) x² - 7x - 7x + 49 x² - 14x + 49 Square the binomial (2a-3b)² (2a-3b)(2a-3b) 4a² - 6ab - 6ab + 9b² 4a² - 12ab + 9b² Find the product (x+7)(x-7) x² - 7x + 7x – 49 x² - 49 (2x - ½)(2x + ½) 4x² + x – x - ¼ 4x² - ¼ Simplify as much as possible -(2x – 6)² -(2x – 6) (2x – 6) -(4x² - 12x – 12x + 36) -(4x² - 24x + 36) -4x² + 24x – 36 3(2x – 4y)² 3(2x – 4y) (2x – 4y) 3(4x² - 8xy – 8xy + 16y²) 3(4x² - 16xy + 16y²) 12x² - 48xy + 48y² Cubing a Binomial (x + 4)³ = (x + 4) (x + 4) (x + 4) = (x + 4)(x² + 8x + 16) = x(x²) + x(8x) + x(16) + 4(x²) + 4(8x) + 4(16) = x³ + 8x² + 16x + 4x² + 32x + 64 = x³ + 12x² + 48x + 64 Cubing a Binomial (2x – 3)³ (2x – 3)(2x – 3)(2x – 3) (2x – 3)(4x² - 12x + 9) 2x(4x²) + 2x(-12x) + 2x(9) – 3(4x²) – 3(-12x) – 3(9) 8x³ - 24x² + 18x – 12x² + 36x – 27 8x³ - 36x² + 54x – 27