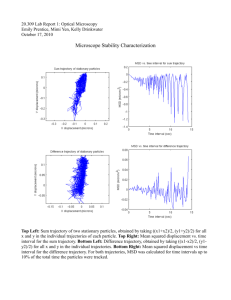
advanced_stata_overview for 081412
advertisement

Using Stata a Plug-in to Estimate Group-Based Trajectory Models Daniel S. Nagin Carnegie Mellon University Installing the Plug-in Traj can be installed by issuing the following commands within Stata. An additional command, trajplot, supports plotting the results. . net from http://www.andrew.cmu.edu/user/bjone s/traj . net install traj, replace Physical Aggression Trajectories of Physical Aggression (Child Development, 1999) 4.5 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 4% 28% 52% 16% 6 Low-actual Low-pred. 10 11 12 13 14 Mod. desister-actual Age High desister-actual Mod. desister-pred. High desister-pred. 15 Chronic-actual Chronic-pred Calculation & Use of Posterior Probabilities of Group Membership pˆ ( group j | datai ) pˆ (datai | group j )ˆ j pˆ (data | group j)ˆ i j Maximum Probability Group Assignment Rule j Group Profiles Variable Group Never Low Desister High Desister Years of School - Mother 11.1 10.8 9.8 8.4 Years of School - Father 11.5 10.7 9.8 9.1 Low IQ (%) 21.6 26.8 44.5 46.4 Completed 8th Grade on Time (%) 80.3 64.6 31.8 6.5 Juvenile Record (%) 0.0 2.0 6.0 13.3 # of Sexual Partners at Age 17 (Past Year) 1.2 1.7 2.2 3.5 Chronic Trajectories of Convictions 0 1 2 3 Cambridge Study of Delinquent Development 1 1.5 1 4 69.5% 5.9% 2 scaled age 2 12.4% 2.5 3 3 12.2% Logit Model for Binary Data p( y 1) e 0 1age 2 age 2 3age 3 1 e 0 1age 2 age 2 3age 3 where y=1 if yes & y=0 if no 0 .2 .4 .6 .8 Trajectories of Delinquent Group Membership (Development & Psychopathology, 2003) 1 1.2 1 74.3% 1.4 scaled age 2 13.1% 1.6 1.8 3 12.6% Statistically Linking Group Membership to Individual Characteristics (Chapter 6) Use of Multinomial Logit Model to Create a Multivariate Probabilistic Linkage e j ( xi ) x i j e x i j Risk Factors for Physical Aggression Trajectory Group Membership Broken Home at Age 5 Low IQ Low Maternal Education Mother Began Childbearing as a Teenager 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 Low Moderate Declining High Declining Ho me Lo w Ed M om Te en M om Al lR is k s IQ Br ok en Lo w sk Chronic Ri No probability Impact of Risk Factors on Group Membership Probabilities Does School Grade Retention and Family Break-up Alter Trajectories of Violent Delinquency Themselves? (Nagin, 2005; Development and Psychopathology 2003) Trajectories of Violent Delinquency 10 9 8 7 Rate 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 11 12 Low 1 (34.8$) Declining (16.7%) 13 14 Age Low 2(30.6%) Chronic (4.5%) 15 16 Rising (13.4%) 17 The Overall Model Z1 Z2 Z3 Z4 Z5 ………. …. Zm Probability of Trajectory Group Membership Trajectory 1 Trajectory 2 X1t X2t Trajectory 3 Trajectory 4 X3t……………Xlt Model of Impact of Grade Retention and Parental Separation on Trajectory Group j Model without retention or separation impact: ln(tj ) 0j 1j Aget 2j Aget2 Trajectory with retention and separation impacts: ~j ~j ~j ln( ) 0 1 Aget 2 Aget2 1j Failt 2j Separationt j t Dual Trajectory Analysis: Trajectory of Modeling of Comorbidity and Heterotypic Continuity (Nagin and Tremblay, 2001; Nagin (2005) Panel A-Conventional Approach Behavior X: X1 X 2 X3 ……………… XT Comorbidity Behavior Z: Behavior X: Z1 X1 Z2 X 2 Z3 X3 ……………… ……………… ZT XT Heterotypic Continuity Behavior Z: ZT ZT+1 Zt+3 ……………… ZT+K Panel B-Dual Trajectory Approach Behavior X: X1 X Behavior Z: Z1 Z2 Z3 X X3 2 X3 ……………… XT Comorbidity Behavior X: X1 2 ……………… ……………… ZT XT Heterotypic Continuity Behavior Z: ZT ZT+1 Zt+3 ……………… ZT+K Modeling the Linkage Between Trajectories of Physical Aggression in Childhood and Trajectories of Violent Delinquency in Adolescence Trajectories of Adolescent Violent Delinqunecy from Age 13 to 17 4 3 Low 2 Desisting 1 High 0 6 8 10 Age 12 Rate Physical Aggression Trajectories of Childhood Physical Aggression from Age 6 to 13 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Low 1 Low 2 Declining Rising Chronic 13 14 15 Age 16 17 Transition Probabilities Linking Trajectories in Adolescent to Childhood Trajectories Trajectory in Adolescence Trajectory in Childhood Low 1&2 Rising Declining Chronic .889 .092 .019 .000 Declining .707 .136 .128 .029 High .215 .206 .158 Low .422 The Dual-Trajectory Model Generalized to Include Predictors of Conditional Probabilities Are drug use and family break-up at age 12 predict the conditional probabilities linking childhood physical aggression trajectories with adolescent violent delinquency trajectories? Answer: yes for drug use but no family break-up Conditional probabilities specified to follow a “constrained” multinomial logit function (see section 8.7 of Nagin) Probability of Transition to Chronic Trajectory Depending on Drug Use at Age 12 and Childhood Physical Aggression Trajectory Drug Use at age 12 None 75th Percentile Low Moderate High Physical Physical Physical Aggression Aggression Aggression .00 .02 .12 .00 .18 .46 Multi-Trajectory Modeling Linking Trajectories to Later Out Comes— Trajectories of Physical Aggression from 6 to 15 and Sexual Partners at 16 .4 Adding Subject Attrition to the Model .1 .2 .3 Probability of Death by Trajectory Group 0 2 1 40.2% 4 Time (weeks) 2 45.7% 6 8 3 14.1%