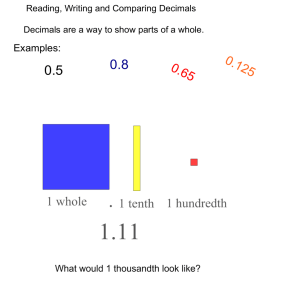
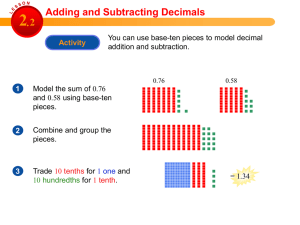
Weeks One and Two: Decimals and Exponents
advertisement

Welcome to +h 6 Grade Ma+h Day….. 1 – Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers 2 – Multiplying Decimals by Decimals 3 – Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers 4 - Dividing Decimals by Decimals 5 – Exploring Multiplying and Dividing Decimals 6 - Multiplying decimals by Powers of 10 7 – Dividing decimals by Powers of 10 8 - Exploring Powers of 10 9 – Exponents and Chapter Review Chapter 1 Multiply and Divide Decimals Day 1 Bell Work The Steven’s Family drove 258 miles a day for 3 days. How many miles did the drive in all? Justify your answer. If they continued to travel at this rate, how many miles would they drive in a week? I Can…… Estimate the product of decimals and judge the reasonableness of the results. Vocabulary • Estimate – a reasonable guess • Compatible number- numbers that are easily multiplied or divided mentally. • Decimal - a representation of a real number using the base ten and decimal notation, such as 201.4, 3.89, or 0.0006. • Round-Off Error – the difference between an approximation of a number used in computation and it’s exact value Let’s Review • Place Value Estimate Products • Essential Understanding: To estimate the product of decimals, round to the nearest whole number or compatible number before multiplying. Guided Practice: Complete Problems a, b, c on page 25 Self-Check # 1 Independent Practice: Complete Problems 7-8 on page 27 I Can…. Multiply decimals by whole numbers. Multiply Decimals by Whole Numbers • Essential Understanding: Use the basic rules of multiplication when multiplying a decimal by a whole number or other decimal. To place the decimal in the product, find the sum of decimals places in each factor. Example: 3 x .02 = .06 Guided Practice: Complete Problems 1-8 on page 30 Self-Check # 2 Independent Practice: Complete Problems 9-17 on page 31 Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Station Work Day 2 Bell Work Louisa walked her dog 0.4 miles a day on Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, and Friday. Find the total distance she walked all week. Justify your answer. If Louisa continued to walk her dog at this rate how far would she walk in 4 weeks? I Can…… Multiply decimals by decimals. Vocabulary • • • • No New Vocabulary Estimate – a reasonable guess Compatible number- numbers that are easily multiplied or divided mentally. Decimal - a representation of a real number using the base ten and decimal notation, such as 201.4, 3.89, or 0.0006. Round-Off Error – the difference between an approximation of a number used in computation and it’s exact value Multiplying Decimals by Decimals • Essential Understanding: Use the basic rules of multiplication when mulitpling a decimal by a whole number or other decimal. To place the decimal in the product, find the sum of decimals places in each factor. Example: 1 .5 x 1.5 = 2.25 Guided Practice: Complete Problems a-f on pages 38-39 Self-Check # 3 Independent Practice: Complete Problems 2-10 even on page 39 Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Station Work Day 3 Bell Work Junnie walked for 2.5 hours at a speed of 2.3 miles per hour. Maurice walked for 1.8 hours at a speed of 4.1 miles per hour. Who walked farther? Justify your answer. (Hint: Distance = speed x time) How much farther did Junnie Walk? I can….. Estimate the quotient of decimals and judge the reasonableness of the results. Vocabulary • • • • No New Vocabulary Estimate – a reasonable guess Compatible number- numbers that are easily multiplied or divided mentally. Decimal - a representation of a real number using the base ten and decimal notation, such as 201.4, 3.89, or 0.0006. Round-Off Error – the difference between an approximation of a number used in computation and it’s exact value Let’s Review • Long Division • Quick Check: Complete Problems 10-14 on page 24 • Self Check # 4 Estimate Quotients • Essential Understanding: To estimate the quotient of decimals, round to the nearest compatible number before dividing. Guided Practice: Complete Problems a-d on page 42 Self-Check # 5 Independent Practice: Complete Problems 2-4 on page 43 I Can…. Divide decimals by whole numbers. Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers • Essential Understanding: Use the basic rules of division. To divide by decimals, change the divisor into a whole number by multiplying it by some power of 10. Then multiply the quotient by the same power of 10. Finally, bring the decimal up and divide as usual. Guided Practice: Complete Problems 1-4 on page 48 Self-Check # 6 Independent Practice: Complete Problems a-f on pages 49-50 Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Station Work Day 4 Bell Work Ryan and his brother are sharing the cost of a video game. The game cost $28.60. How much does each brother have to pay? Justify your answer. If Ryan saves $20 for the game, how much money will he have left? I Can…… Divide decimals by decimals. Vocabulary • • • • No New Vocabulary Estimate – a reasonable guess Compatible number- numbers that are easily multiplied or divided mentally. Decimal - a representation of a real number using the base ten and decimal notation, such as 201.4, 3.89, or 0.0006. Round-Off Error – the difference between an approximation of a number used in computation and it’s exact value Dividing Decimals by Decimals • Essential Understanding: Use the basic rules of division. To divide by decimals, change the divisor into a whole number by multiplying it by some power of 10. Then multiply the quotient by the same power of 10. Finally, bring the decimal up and divide as usual. Guided Practice: Complete Problems 1-6 on pages 54-55 Self-Check # 7 Independent Practice: Complete Problems 19-25 on page 58 Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Station Work Day 5 Bell Work The longest vehicle tunnel in the world is the Laerdal Tunnel in Norway with a length of 15.2 miles long. How many vehicles could fit in the tunnel, bumper to bumper, if the average vehicle’s length is 0.004 mile? Justify your answer. Vocabulary • • • • No New Vocabulary Estimate – a reasonable guess Compatible number- numbers that are easily multiplied or divided mentally. Decimal - a representation of a real number using the base ten and decimal notation, such as 201.4, 3.89, or 0.0006. Round-Off Error – the difference between an approximation of a number used in computation and it’s exact value Explore Lab Day Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Station Work Day 6 Bell Work A necklace is being made with beads that are 1.25 centimeters in diameter. The necklace is 30 centimeters long. How many beads are needed? Justify your answer. How many beads are needed to make 20 necklaces? I Can…… Multiply decimals mentally by powers of 10. Vocabulary • Base – the number used as a factor in a power . • Exponent – in a power, the number that tells how many times the base is used as a factor. • Powers – numbers expressed using exponents. • Power of 10 – numbers such as 10; 100; 1,000; 10,000 and so on. Multiplying Decimals by Powers of 10 Essential Understanding: • To multiply a decimal by a power of 10 greater than 1, move the decimal to the right one place for every zero in the power of 10. Example: 1.8565 x 100 = 185.65 • To multiply a decimal by a power of 10 that is between 0 and 1, move the decimal to the left one place for every decimal place in the power of 10. Example: 34.5 x 0.001 = 0.0345 Guided Practice: Complete Problems a-f on pages 66-67 Self-Check # 8 Independent Practice: Complete Problems 12-24 even on page 68 Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Station Work Day 7 Bell Work 4.8x .01 = .048 13.4 x 10 = 134 3.6 x 100= 360 7742.3 x .001 = 7.7423 0.0063 x 1000 = 6.3 I Can…… Divide decimals mentally by powers of 10. Vocabulary No New Vocabulary • Base – the number used as a factor in a power Exponent – in a power, the number that tells how many times the base is used as a factor. • Powers – numbers expressed using exponents. • Power of 10 – numbers such as 10; 100; 1,000; 10,000 and so on. Dividing Decimals by Powers of 10 Essential Understanding: To divide a decimal by a power of 10 greater than 1, move the decimal the left one place for every zero in the power of ten. Example: 421.2 ÷ 10 = 42.12 To divide a decimal by a power of 10 that is between 0 and 1, move the decimal the right one place for every decimal place in the power of 10. Example: 3.172 ÷ 0.01 = 317.2 Guided Practice: Complete Problems a-e on pages 70-71 Self-Check # 9 Independent Practice: Complete Problems 8-18 even on page 72 Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Station Work Day 8 Bell Work Mrs. Ewen’s class has collected $578.92 in pennies to donate to charity. A penny is equal to $0.01. How many pennies did the students collect? Justify your answer. If Mrs. Ewen’s class collected the same amount of money in dimes, how many dimes would they have? (hint a dime is equal to $0.10) Vocabulary No New Vocabulary • Base – the number used as a factor in a power Exponent – in a power, the number that tells how many times the base is used as a factor. • Powers – numbers expressed using exponents. • Power of 10 – numbers such as 10; 100; 1,000; 10,000 and so on. I Can…… Represent numbers using exponents. Using Exponents to Represent Repeating Factors Essential Understanding: • To write a product using an exponent: Count the number of times the base is used is used as a factor. Example: 5 x 5 x 5 x 5 = 54 Guided Practice: Complete Problems a-e on pages 62-63 Self-Check # 10 Independent Practice: Complete Problems 14-32 on page 64 Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Station Work Day 9 Bell Work Annie wants to buy 2 pairs of capris for $34.99 each and 3 pairs of flip flops for $7.99 each. Does she need to save $150, or is $100 enough? Justify your answer. How much change will she have left, after her purchase? Vocabulary • • • • • • • • No New Vocabulary Estimate – a reasonable guess Compatible number- numbers that are easily multiplied or divided mentally. Decimal - a representation of a real number using the base ten and decimal notation, such as 201.4, 3.89, or 0.0006. Round-Off Error – the difference between an approximation of a number used in computation and it’s exact value Base – the number used as a factor in a power . Exponent – in a power, the number that tells how many times the base is used as a factor. Powers – numbers expressed using exponents. Power of 10 – numbers such as 10; 100; 1,000; 10,000 and so on. Review and Assess Please Take out your Study Guides Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Station Work Self Check # 1 A - 20 B - 12 C – 1,400 Self Check # 2 1 – 0.9 2 – 0.8 3 – 0.08 4 – 0.05 5 – 1.5 6 – 2.4 7 - 0.16 8 - 0.32 Self Check #3 A – 15.96 B – 0.206 C – 0.0518 D – 0.0128 E – 0.0533 F – 0.0798 Self Check # 4 10 – 14 11 – 34 12 – 49 13 – 41 14 – 4 million Self Check # 5 A – 49 ÷ 7 = 7 B – 100 ÷ 25 = 4 C – 54 ÷ 9 = 6 D – 99 ÷ 11 = 9 Self Check # 6 1 – 1.7 2 – 1.4 3 – 1.4 4 – 0.45 Self Check # 7 1–4 2–3 3–3 4 – 0.4 5 – 0.7 6 - 0.5 Self Check # 8 A – 2,720 B – 59,800 C – 3,900,000 D – 1,390,000 E – 9.36 F - 0.00784 Self Check # 9 A – 0.06743 B – 3.142 C – 73 students D – 15,800 E – 0.2 Self Check # 10 A – 74 B – 97 C – 100,00 D – 4.41 E – 2,187 gallons