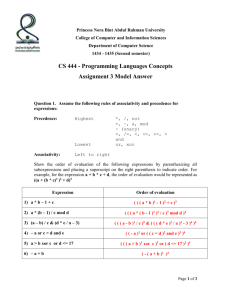
指针与引用的对比
advertisement

C++ Programming
Lecture 13
Wei Liu (刘威)
Dept. of Electronics and Information Eng.
Huazhong University of Science and Technology
Feb. 2014
Lecture 13
Chapter 15. Introduction to C++
15.1 Introduction
15.2 First Program
15.3 Sum up two numbers
15.4 Reference
15.5 More about functions
-2-
First Program
Comments(注释)
//, /* */
Function body
(函数体)
Preprocessor directive
(预处理器指令)#include
Function
return
type
Function
name
with()
Header file(头文
件)
<iostream>
Keyword(关键字)
int, return
Statement;
(语句)
std::cout, output object, print the text message
Indicate the end of program
-3-
Basic structure of source code
Comments: can be any line, started with //
Preprocessor directive: end without ;
Statement: end with ;
main() function body
keywords
-4-
C++ output with cout
std::cout
-5-
Lecture 13
Chapter 15. Introduction to C++
15.1 Introduction
15.2 First Program
15.3 Sum up two numbers
15.4 Reference
15.5 More about functions
-6-
Another Program
Variables
declarations
Input object
std::cin
Arithmetic
calculation
-7-
Experiment
编写程序,对两个数求和,使用C++的语法
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int sum( int, int);
int main (void)
{
cout << " [main] begin! " << endl;
int sum1;
sum1 = sum( 5, 10);
cout << " [main] sum1 = " << sum1 << endl;
return 0;
}
-8-
Lecture 13
Chapter 15. Introduction to C++
15.1 Introduction
15.2 First Program
15.3 Sum up two numbers
15.4 Reference
15.5 More about functions
-9-
指针使用上可能出现的问题
指针也是变量,也应“声明-初始化-使用”。
在使用前一定要初始化,否则将导致程序内存
错误
int a = 1;
int *p ;
* p = 10;
// 指针被声明时,可以不初始化
// 此处操作的是一个随机地址的数据
-10-
指针使用上可能出现的问题
指针的赋值一定要类型匹配,即与该指针类型
相符合的变量或者常量的地址
指针的算术运算最好在数组连续区中进行,一
旦数组越界将导致程序内存错误
-11-
“引用”的引入
为了克服C语言指针的这些问题,C++语言引入了
“引用”(References)的概念
被声明为引用的变量(References variable)
引用变量可以作为其它变量的别名(aliase)
引用变量在声明时必须被初始化,运行时不允许重新赋值
当引用变量被声明为某个原变量的别名后,操作引用变量
等效于操作原变量
-12-
-13-
-14-
指针与引用的对比
定义 Definition 的对比
引用Reference不是一种独立的数据类型,而是已经存
在的某变量或者对象的别名,例如“侧门”
指针Pointer是一种独立的数据类型,其存储空间大小
与所指向的变量或者对象大小有关,例如“钥匙”
声明 Declaration 的对比
引用
int a = 1;
int &r = a;
// 引用被声明时必须初始化,&为引用声明符
指针
int a = 1;
int *p ;
p = &a;
// 指针被声明时,可以不初始化
// &为取地址符
-15-
指针与引用的对比
使用 Usage 的对比
引用
int &r = a;
r += 1;
// 用引用名直接访问变量
void fun1(int & x) {
x += 3;
// 用引用名直接访问变量
}
指针
int *p = &a;
*p += 1;
// 指针用*间接引用符访问变量
void fun2(int * x) {
*x += 3;
// 指针用*间接引用符访问变量
}
-16-
15.7 References and Reference
Parameters
Two ways to passing variable to function
Passing by value
值传递
Passing by reference
引用传递
-17-
15.7 References
Pass-by-reference 引用传递
the caller gives the called function the ability to access
the caller’s data directly, and to modify that data. 可以
直接操作和修改变量的值
A reference parameter is an alias for its corresponding
argument in a function call. 引用形参可以视为原实参
的一个“别名”
How to indicate a reference 引用的声明
Follow the parameter’s type in the function prototype
by an ampersand (&)
Use the same convention when listing the parameter’s
type in the function header.
-18-
-19-
-20-
Sample
指针或者引用作为函数的形参
-21-
指针或者引用作为函数的返回值
-22-
Experiment
编写四个函数,对两个数求和,分别使用指针/引用作为
函数参数和返回值,演示它们的调用
-23-
小结:指针与引用
指针 vs. 引用
引用的功能类似于指针常量,引用能够实现的功
能,指针都可以实现
C++ 引入“引用”的概念,主要意图是将引用作为函
数的形式参数,扩充函数传递数据的功能,增强可
读性、避免指针的误操作
但是引用不能完成指针的全部功能
所指向的对象会发生改变时
函数指针
数组指针
-24-
Lecture 13
Chapter 15. Introduction to C++
15.1 Introduction
15.2 First Program
15.3 Sum up two numbers
15.4 Reference
15.5 More about functions
15.6 Inline Functions
15.9 Default Arguments
15.11 Function Overloading
15.12 Function Templates
-25-
Inline Functions 内联函数
C++ provides inline functions to help reduce function
call overhead—especially for small functions. 降低函数
调用开销,适用于小规模的函数
Placing the qualifier in-line before a function’s return
type in the function definition “advises” the compiler to
generate a copy of the function’s code in place (when
appropriate) to avoid a function call. 由编译器产生替换
代码
The complete function definition must appear before
the code is inlined so that the compiler knows how to
expand a function call into its inlined code.
-26-
-27-
15.9 Default Arguments 默认实参
默认实参
在函数原型中指定实参的默认值
示例:
sum函数完成四个数相加的功能 int sum(a,b,c,d); 如果该
函数的定义符合需求,但是调用时不想输入所有参数
-28-
15.11 Function Overloading函数重载
函数重载
同名的函数但具有不同的形参,被称为函数重载
编译器通过函数的签名(函数名、形参类型)来区分
示例
sum函数完成四个数相加的功能 int sum(a,b,c,d); 如果
该函数的定义满足不了新的需求,需要考虑其他的参数
列表和返回值,且函数体有可能不同
-29-
15.12 Function Templates函数模板
函数模板
函数重载的特例,对不同类型的形参操作都相同时可以采用函数
模板
示例
sum函数完成四个数相加的功能 int sum(a,b,c,d); 如果该函数的定
义满足不了新的需求,但只是形式参数类型不同,参数的个数和
函数体都相同
-30-
谢谢!
刘威 副教授
互联网技术与工程研究中心
华中科技大学电子与信息工程系
电话:13986224922
Email: liuwei@hust.edu.cn
网址:http://itec.hust.edu.cn