Kepler`s laws - Bishop Moore High School
advertisement
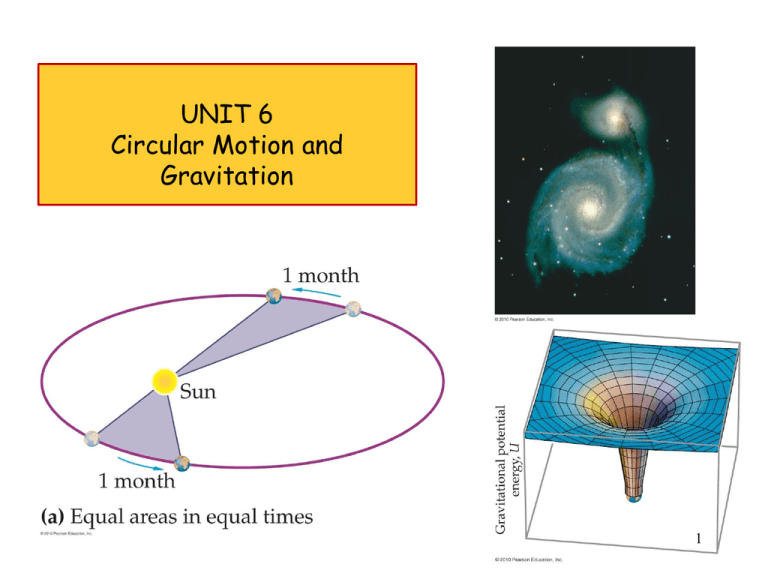
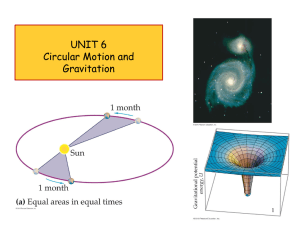
UNIT 6 Circular Motion and Gravitation 1 ConcepTest 12.4 Averting Disaster 1) It’s in Earth’s gravitational field The Moon does not crash into Earth because: 2) The net force on it is zero 3) It is beyond the main pull of Earth’s gravity 4) It’s being pulled by the Sun as well as by Earth 5) none of the above ConcepTest 12.4 Averting Disaster 1) It’s in Earth’s gravitational field The Moon does not crash into Earth because: 2) The net force on it is zero 3) It is beyond the main pull of Earth’s gravity 4) It’s being pulled by the Sun as well as by Earth 5) none of the above The Moon does not crash into Earth because of its high speed. If it stopped moving, it would, of course, fall directly into Earth. With its high speed, the Moon would fly off into space if it weren’t for gravity providing the centripetal force. Follow-up: What happens to a satellite orbiting Earth as it slows? ConcepTest 12.5 In the Space Shuttle 1) They are so far from Earth that Earth’s gravity doesn’t act any more. Astronauts in the space shuttle float because: 2) Gravity’s force pulling them inward is cancelled by the centripetal force pushing them outward. 3) While gravity is trying to pull them inward, they are trying to continue on a straight-line path. 4) Their weight is reduced in space so the force of gravity is much weaker. ConcepTest 12.5 In the Space Shuttle 1) They are so far from Earth that Earth’s gravity doesn’t act any more. Astronauts in the space shuttle float because: 2) Gravity’s force pulling them inward is cancelled by the centripetal force pushing them outward. 3) While gravity is trying to pull them inward, they are trying to continue on a straight-line path. 4) Their weight is reduced in space so the force of gravity is much weaker. Astronauts in the space shuttle float because they are in “free fall” around Earth, just like a satellite or the Moon. Again, it is gravity that provides the centripetal force that keeps them in circular motion. Follow-up: How weak is the value of g at an altitude of 300 km? Units of Chapter 7 Kinematics of Uniform Circular Motion Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation Kepler’s Laws and Newton’s Synthesis Torque and Newton’s Laws of Motion 6 Kepler’s Laws and Newton's Synthesis Kepler’s laws describe planetary motion. • All planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one of the focal points. • A line drawn from the Sun to any planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals. • The square of the orbital period of any planet is proportional to cube of the average distance from the Sun to the planet. Kepler’s Laws and Newton's Synthesis • Based on observations made by Tycho Brahe • Newton later demonstrated that these laws were consequences of the gravitational force between any two objects together with Newton’s laws of motion Kepler’s 1st Law • All planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus. – Any object bound to another by an inverse square law will move in an elliptical path – Second focus is empty Kepler’s 2nd Law • A line drawn from the Sun to any planet will sweep out equal areas in equal times – Area from A to B and C to D are the same Kepler’s 3rd Law • The square of the orbital period of any planet is proportional to cube of the average distance from the Sun to the planet. 𝐓 2 = 𝐊 s 𝒓3 • For orbit around the Sun, K = KS = 2.97x10-19 s2/m3 • K is independent of the mass of the planet in orbit K= 4𝜋2 𝐺𝐦 where m is the mass of the Sun being orbited. Kepler’s Laws and Newton's Synthesis Kepler’s laws can be derived from Newton’s laws. Irregularities in planetary motion led to the discovery of Neptune, and irregularities in stellar motion have led to the discovery of many planets outside our Solar System. Kepler’s 3rd Law Kepler’s 3rd Law leads to an equation for the period of an object in circular orbit. The speed of an object in a circular orbit depends on the same factors: 𝑟3 𝑇 = 2𝜋 𝐺𝒎 𝑣= 𝒎 𝐺 𝑟 Note that m is the mass of the central object that is being orbited. The mass of the planet or satellite that is in orbit does not effect its speed or period. The mean radius (r) is the distance between the centers of the two bodies. Kepler’s 3rd Law 𝟐 𝟒𝝅 𝑻𝟐 = 𝒓𝟑 𝑮𝒎 𝒎𝟏 𝒎𝟐 𝐅𝒈 = 𝐆 𝒓𝟐 𝒗𝟐 𝐅𝒈 = 𝐦 𝒓 𝑻= 𝟒𝝅𝟐 𝒓𝟑 𝑮𝒎 𝒎𝐬 𝒎 𝒗𝟐 𝐆 𝟐 =𝐦 𝒓 𝒓 𝒓𝟑 𝑻 = 𝟐𝝅 𝑮𝒎 𝒗= 𝒎 𝑮 𝒓 Kepler’s 3rd Law Planetary Data Period and Speed of an Orbiting Object Problem Magellan was the first planetary spacecraft to be launched from a space shuttle. During the spacecraft’s 5th orbit around Venus, Magellan traveled at a mean altitude of 361 km. If the orbit had been circular, what would Magellan’s period and speed have been? 𝒓 = 361 km + 6050 km = 6.41 x 106 m 𝑟3 = 2𝜋 𝑇 = 2𝜋 𝐺𝒎 𝑣= 𝒎 𝐺 𝑟 = 6410000m 3 6.67 𝑥 10−11 4.87 𝑥 1024 6.67 𝑥 10−11 4.87 𝑥 1024 6.41 𝑥 106 5.66 x 𝟏𝟎𝟑 𝐬 𝐦 𝟕. 𝟏𝟐 𝒙 𝟏𝟎 𝐬 𝟑 16 Torque To make an object start rotating, a force is needed; the position and direction of the force matter as well. The perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the line along which the force acts is called the lever arm (r). Torque A longer lever arm is very helpful in rotating objects. Torque Here, the lever arm for FA is the distance from the knob to the hinge; the lever arm for FD is zero; and the lever arm for FC is rC. Torque The torque is defined as: 𝝉 = 𝑭 𝐬𝐢𝐧 𝜽 𝒓 𝒐𝒓 𝝉 = 𝑭𝒓 𝐬𝐢𝐧 𝜽 Torque Equation 21 Torque Sign 22 Torque Problem A basketball is being pushed by two players during a tip-off. One player exerts an upward force of 15.0 N at a perpendicular distance of 14.0 cm from the axis of rotation. The second player applies a downward force of 11.0 N at a perpendicular distance of 7.00 cm from the axis of rotation. Find the net torque acting on the ball about its center of mass. t1 = F1d1 = (15 N)(–0.14 m) = –2.1 N•m t2 = F2d2 = (–11 N)(0.070 m) = –0.77 N•m tnet = t1 + t2 = –2.1 N•m – 0.77 N•m tnet = –2.9 N•m 23 END 24