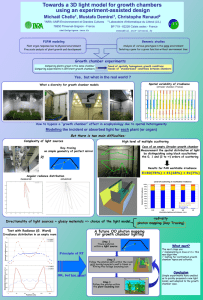
26.3 Physics 6C Energy Levels
advertisement

Physics 6C Energy Levels Bohr Model of the Atom Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB Bohr’s Model of Hydrogen •Positively charged nucleus at center •Electrons occupy circular orbits around the nucleus •Angular momentum of electrons is quantized (has to be a multiple of ħ) •Radius values and energy levels are also quantized This is the formula for calculating hydrogen energy levels. The ‘Ground State’ is n=1. This is the closest orbit and the lowest energy level. e- E 1 13 . 6 eV En rn E1 n 2 + For larger values of n, the electron is farther from the nucleus, and the energy is closer to zero. The electron is ‘free’ when its energy is zero (or positive). Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB Example: Suppose a hydrogen atom is in its ground state. If a photon is absorbed, exciting the atom to the n=3 state, what is the wavelength of the photon? Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB Example: Suppose a hydrogen atom is in its ground state. If a photon is absorbed, exciting the atom to the n=3 state, what is the wavelength of the photon? The diagram shows the photon approaching, and the electron jumping to the excited state after the photon’s energy is absorbed. n=3 n=1 + e- e- photon Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB Example: Suppose a hydrogen atom is in its ground state. If a photon is absorbed, exciting the atom to the n=3 state, what is the wavelength of the photon? The diagram shows the photon approaching, and the electron jumping to the excited state after the photon’s energy is absorbed. n=3 The photon energy is the difference between the energy levels. n=1 E photon E 3 E 1 + E3 13 . 6 eV 3 2 e- e- photon 1 . 5 eV E photon ( 1 . 5 eV ) ( 13 . 6 eV ) 12 . 1 eV Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB Example: Suppose a hydrogen atom is in its ground state. If a photon is absorbed, exciting the atom to the n=3 state, what is the wavelength of the photon? The diagram shows the photon approaching, and the electron jumping to the excited state after the photon’s energy is absorbed. n=3 The photon energy is the difference between the energy levels. n=1 E photon E 3 E 1 + E3 13 . 6 eV 3 2 e- e- photon 1 . 5 eV E photon ( 1 . 5 eV ) ( 13 . 6 eV ) 12 . 1 eV Now we can solve for the wavelength: E photon hc 12 . 1 eV ( 4 . 14 10 15 eV s )( 3 10 8 m s ) 103 nm Note that this photon is in the ultraviolet range Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB Example: Suppose a hydrogen atom is in its ground state. If a photon is absorbed, exciting the atom to the n=3 state, what is the wavelength of the photon? Now suppose the atom emits a photon and drops down to the n=2 state. What is the wavelength of this emitted photon? Again, the photon energy is the difference between the energy levels. n=3 n=2 n=1 ee- + Emitted photon Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB Example: Suppose a hydrogen atom is in its ground state. If a photon is absorbed, exciting the atom to the n=3 state, what is the wavelength of the photon? Now suppose the atom emits a photon and drops down to the n=2 state. What is the wavelength of this emitted photon? Again, the photon energy is the difference between the energy levels. n=3 n=2 n=1 ee- + Emitted photon E photon E 2 E 3 E2 13 . 6 eV 2 2 3 . 4 eV E photon ( 3 . 4 eV ) ( 1 . 5 eV ) 1 . 9 eV Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB Example: Suppose a hydrogen atom is in its ground state. If a photon is absorbed, exciting the atom to the n=3 state, what is the wavelength of the photon? Now suppose the atom emits a photon and drops down to the n=2 state. What is the wavelength of this emitted photon? Again, the photon energy is the difference between the energy levels. n=3 n=2 n=1 ee- + Emitted photon E photon E 2 E 3 E2 13 . 6 eV 2 2 3 . 4 eV E photon ( 3 . 4 eV ) ( 1 . 5 eV ) 1 . 9 eV Now we can solve for the wavelength: E photon 1 . 9 eV hc ( 4 . 14 10 15 eV s )( 3 10 8 m ) s 654 nm This one is visible, so we would see this in an emission spectrum. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB