2_Rectifiers
advertisement

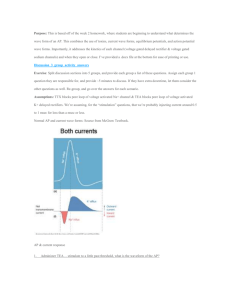
Author: Ales Havel E-mail: ales.havel@vsb.cz Phone number: 4287 Headquarters: E227 Web page: http://homen.vsb.cz/~hav278/ POWER SEMICONDUCTOR SYSTEMS I Presentation contents Main types of converters AC-DC converters Single phase rectifiers Construction possibilities, wiring Load voltage and current waveforms Mathematics Neat examples Three phase rectifiers Construction possibilities, wiring Load voltage and current waveforms Mathematics Neat examples DC-DC converters DC-AC converters AC-AC converters Power converters A power semiconductor converter is an electrical device for converting electrical energy. Division of AC/DC converters Properties of rectifiers Number of input phases Number of pulses Single phase rectifiers Three phase rectifiers n – phase rectifiers P = 1, 2, 3, 6… Possibilities of output voltage control Without control Half-controlled rectifiers Diodes + Thyristors Full-controlled rectifiers Diode rectifiers Thyristors Wiring Bridge rectifiers Node rectifiers Half-wave single phase diode rectifiers Voltage Resistive load Current Voltage Inductive load Current Half-wave single phase diode rectifiers Voltage R+L load Current R+L+D0 load Voltage Current Half-wave single phase diode rectifiers Voltage R+C load Current R+V load Voltage Current Two pulse diode rectifiers Voltage Current Two pulse thyristor controlled rectifiers Important mathematical relations The output AVG voltage of diode rectifier or thyristor rectifier with control angle α = 0°: U L0 U m p sin p The output AVG voltage of thyristor rectifier with control angle α. U L U L0 cos Condition 1: The load current must be continuous Condition 2: No parallel bypass diode on the load Output to Input phase RMS voltage ratio p[-] UL / U1 [-] 1 0.45 2 0.90 3 1.17 6 2.34 Limit of load current continuity for resistive load p[-] α[°] 3 30 6 60 Example 1- submission Calculate the output AVG voltage of the 2-pulse bridge controlled rectifier, if you know the following values: α = 60°, U1 = 230V Example 1- solution a) General calculation approach: 2 UL T 2U m U m sin(t )dt 2 sin(t )dt Um cos(t ) U m 2 U1 230 2 4 U m 1 1 U m cos cos 103.5V 3 3 2 2 b) Calculation utilizing the basic relation: U L Um p sin p cos 2 2 U1 sin 2 c) Calculation utilizing the table values: U L 0.9 U1 cos 3 0.9 230 103.5V 2 cos 3 2 U1 230 2 103.5V Example 1- question? How will change the output AVG voltage value if we use the bypass diode parallel to the load? Solution: U L BD 2U m Um 2 U m sin(t )dt sin( t ) d t cos(t ) T 2 U m U m 1 3U m 3 2 U1 3 230 2 cos cos 1 155V 3 2 2 2 2 Six pulse thyristor controlled rectifiers Six pulse thyristor controlled rectifiers Thank You for your attention