Preprocessing
advertisement

C/C++ Training
Programming C/C++ on Eclipe
Trình bày: Ths HungNM
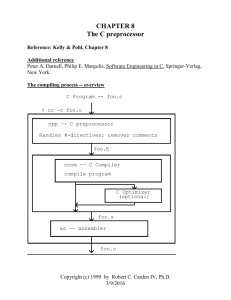
The Preprocessor
Introduction preprocessor.
Preprocessing
Logical Preprocessor Directives
Standard Preprocessing Macros
Error Generation
Using the assert() Macro
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
2
Introduction preprocessor
The preprocessor is powerful tool.
It also can be a source of hard-to-find bugs.
It can be easily be misused to create program that are
almost impossible to understand.
The preprocessor is controlled by processing directive that
begin a # character.
C Program
Modified C program
Object code
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
3
Preprocessing
Including Header Files
A header file is any external file whose contents
It use of the #include preprocessor directive.
Syntax :
• #include <standard_library_file_name>
External Variables and Functions
A program that’s made up of several source files
want to use a global variable that’s defined in another file.
Declaring the variable as external to the current file using the
extern keyword.
Syntax :
• extern datatype namevariable;
• Example : extern int number;
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
4
Preprocessing
Macro definition.
The #define directive defines a macro.
The #undefine directive remove a macro definition.
Syntax :
• #define identifer replacement-list
Example :
• #define PI 3.14159265
• #define Black White
Advance macro definition.
• It make program easier to read.
• It make program easier to modify
• It help avoid inconsistencies and topographical error.
– Example : Numerical constant like : 3.14149, but some time 3.1415
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
5
Preprocessing
Macro definition.
Advance macro definition
• Making minor changes to syntax of C program.
– Example : #define BEGIN {
– #define END }
• Renaming types.
– Exampe : #define BOOL int
• Controlling conditional compilation.
– Example : #define DEBUG
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
6
Preprocessing
Macros That Look Like Functions
Allows parameters to be specified, which may
themselves be replaced by argument values,
Syntax :
• #define identifer(x1,x2,..,xn) replacement list
Example :
• #define max(x, y) x>y ? x : y
• Call : result = myval>99 ? myval : 99;
• It mean : result = max(myval, 99);
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
7
Preprocessing
Preprocessor Directives on Multiple Lines
using the statement continuation character, \.
Example :
• #define min(x, y) \
((x)<(y) ? (x) : (y))
Strings As Macro Arguments
Example: #define MYSTR "This string"
Call : printf("%s", MYSTR);
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
8
Preprocessing
Joining Two Results of a Macro Expansion
you may wish to generate two results in a macro and
join them together
Using two characters ## serves to separate the
parameters.
Syntax :
• #define join(a, b) a##b
Example :
• strlen(join(var, 123));
• It will be result : strlen(var123);
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
9
Logical Preprocessor Directives
Conditional Compilation
Syntax :
#if defined identifier
#endif
Or
#if !defined identifier
#endif
Or
#if !defined block1
#define block1
/* Block of code you do not */
/* want to be repeated.
*/
#endif
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
10
Logical Preprocessor Directives
Directives Testing for Specific Values
Using #if directive to test the value of a constant
expression.
Syntax :
#if constant_expression
#endif
Example :
#if CPU == Pentium4
printf("\nPerformance should be good." );
#endif
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
11
Logical Preprocessor Directives
Multiple-Choice Selections
Using #if, #elseif, #else derective for excecute statements.
Syntax :
#if constant_expression
#elseif constant_expression
#elseif constant_expression
#else
#endif
Example :
#if CPU == Pentium4
printf("\nPerformance should be good." );
#else
printf("\nPerformance may not be so good." );
#endif
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
12
Standard Preprocessing Macros
Using __DATE__ macro provides a string representation of the
date.
Using __TIME__, provides a string containing the value of the
time.
Using __FILE__ , A string literal containing the name of the file
being compiled.
__LINE__ A decimal constant containing the current source line
number.
__STDC_VERSION__ : This macro expands to the C Standard's
version number.
Example :
printf("\nProgram last compiled at %s on %s", __TIME__,
__DATE__ );
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
13
Error Generation
A preprocessor error directive causes the
preprocessor to generate an error message and
causes the compilation to fail.
Syntax :
# error token-sequence
Example :
#define BUFFER_SIZE 255
#if BUFFER_SIZE < 256
#error "BUFFER_SIZE is too small." #endif
generates the error message:
BUFFER_SIZE is too small.
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
14
Using the assert() Macro
The assert() macro is defined in the standard library
header file <assert.h>.
Using #ndefine derectives for Switch on or off assertions.
#undef NDEBUG
Syntax:
#undef NDEBUG
#include <assert.h>
Example:
EcoSoftware
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int y = 5;
for(int x = 0 ; x < 20 ; x++)
{
printf("\nx = %d y = %d", x, y);
assert(x<y);
}
return 0;
}
Training C/C++
15
End
• Thank You
EcoSoftware
Training C/C++
16