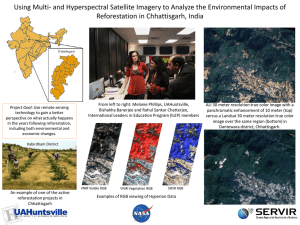
Cross-talk induced noise and influencing factors
advertisement

CROSS-TALK INDUCED NOISE AND INFLUENCING FACTORS Date: November 19th 2014 Page 1 Agenda Measurement Capabilities Demo System and process implications Simulation Capabilities Q&A Page 2 Signal Integrity requirements and Cross-talk Signal integrity requirements: - over/under-shoot - clock tCL/tCH - clock monotonic - Cross-Talk - Clock Jitter 3 Data patterns and Cross-talk RGB bars Crosstalk pattern observed with RGB bars test pattern Page 4 Menu Screen Crosstalk pattern observed with Test Menu pattern Data patterns and Cross-talk Gray Scale pattern Worst Case RGB Cross-talk test pattern Internally developed Worst-Case cross-talk pattern Crosstalk pattern observed with a Gray Scale pattern Vmin = -262 mV Page 5 Crosstalk pattern observed with A Worst-Case test pattern Vmin = -308 mV 18% increase Flex Cables and Cross-talk Cluster Type 1 – RGB signals at display pins With Shielded FFC Cluster Type 2 – RGB signals at display pins With Shielded FFC Page 6 Cluster Type 1 – RGB signals at display pins With Unshielded FFC Cluster Type 2 – RGB signals at display pins With Unshielded FFC Flex Cables and Cross-talk Cluster Type 1 - RGB bus Pinout for display Crosstalk level function of bit location GND R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0 GND Cluster Type 2 - RGB bus Pinout for display RGB data minimum voltage [mV] R1 0 -50 -100 -150 -200 -250 -300 Page 7 R3 R6 G1 G2 G3 B2 B5 B7 Cross-talk in other modules – display example Evaluate crosstalk generated on RGB lines within the display 1, by injecting a square waveform from signal generator directly into the display connector pin B2. Crosstalk on B3 line (connector) +/-165 mV Page 8 8 Johnson Controls Injected signals measured at B2 Single PCB Cross-talk Simulation Capability Manual Cross-talk evaluation using Hyperlynx 2 D Page 9 Single PCB Cross-talk Simulation Capability Perform simulations to minimize crosstalk between RGB traces Cross-talk at connector - baseline Page 10 Cross-talk at connector – optimized option Cross-talk on DDR3 data bus DDR3 noise observed during Read operation Vpk-pk avg =181mV due to random DQ4 transitions DQ0 - Measured crosstalk during data read Vpk-pk=10 mV DQ0 – Simulated crosstalk in Hyperlynx 2D due to DQ4 transitions Vpk-pk=199 mV – error under 10 % DQ0 – Simulated crosstalk in Hyperlynx 2D due to DQ4 transitions with coupling model of iMX6 between DQ0 and DQ4 (TDR) Page 11 Cross-talk on DDR3 data bus Proper simulation of crosstalk on DQ0 line during Read required use of the TDR to create an s-parameters model of coupling between DQ0 and DQ4 DQ0 DQ4 S-parameter model of coupling between DQ0 and DQ4 pins of iMX6 Solo extracted with TDR Page 12 Summary: Cross-talk sources and influencing factors Cross-talk sources and influencing factors: 1. Coupling between signals on PCB 2. Coupling between signals on interconnected PCBs 3. Coupling within cables or IC packages 4. Signal rise time Outside our “design” control 5. Data pattern 6. Cross-talk is a system level phenomenon Page 13 Cross-talk sources and influencing factors Q&A Page 14