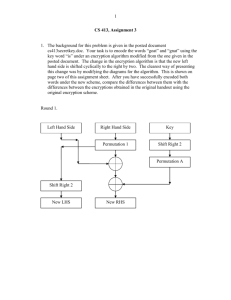
NP reductions
advertisement

Cook’s theorem and
NP-reductions
Pasi Fränti
22.10.2013
Cook’s theorem
Theorem:
Satisfiability problem (SAT) is NP-complete
Proof:
TM ≤p SAT
Satisfiability problem
f1
f2
f3
F=(X1 X2 X3) (X1 X2) (X1 X3)
x1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
x2
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
x3
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
f1
f2
f3
F
Non-deterministic algorithm
Satisfiability(F)
FOR i1 TO n DO
xi Choose{0,1};
IF F(x)=1 THEN SUCCESS;
ELSE FAIL;
T(n)=O(n) SAT NP
Notations needed
x y x y
x y x y y x
n
x
Implication
Equivalence
i
x1 xn
All are true
x
x1 xn
Some is true
i 1
n
i 1
i
n
xi xi x i x j
i 1
i 1 i , j 1
i j
n
n
At least one
is true
At most one
is true
Exactly one is true
Cook’s theorem:
Accept( x) Confic Initial Transition Final
p n n s ,t p n k s ,t
Config ai q j
t 1 s 1 i 0
s 1 j 0
p n
Cook’s theorem
Initial q01,1 ai11,1 ai22,1 ... ainn,1 a0n1,1 ... a0pn ,1
Cook’s theorem
Transit
t 1
k s ,t
s ,t
s ,t 1
q
a
a
i
i
j
s 1 i 0 j 0
p n p n m
p n p n m
a
k
t 1 s 1 i 0 j 0
s ,t
i
q
a
l
s ,t
j
r 0
s ,t 1
ir
q sjr d r ,t 1
Cook’s theorem
Final
p n
s 1
qks , p n
NP hard problems
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Satisfiability problem (SP)
Coloring problem (Color)
Exact cover problem (EC)
Traveling salesman problem (TSP)
Knapsack problem (KP)
Satisfiability to Coloring
Complete k-clique
False color
c1
c2
c2
…
ck
…
ak
c0
Connect to all but ci
Literals
a1
a1
a2
a2
a3
a3
…
ak
Choices for fi
aj
fi
fi
Connect to all but
those literals in fi
aj
SP to Coloring example
(X1 X2) (X1 X3)
Empty space for notes
Knapsack to TSP
Knapsack problem
• Input: knapsack instance {2,3,5,7,11}
• Size of the knapsack S=15.
Step 1: Create one node for every item
• Input: knapsack instance {2,3,5,7,11}
• Create a node for every knapsack element.
2
7
5
3
11
Step 2: Add start and end points
• Input: knapsack instance {2,3,5,7,11}
• Add node 0 as the home.
• Add node N+1 as the turning point.
2
7
5
0
3
n+1
11
N+2 nodes needed to represent the knapsack instance
Step 3: Create forward links
• Input: knapsack instance {2,3,5,7,11}
• Draw links from smaller nodes to bigger ones.
• Set weights according to the bigger node: w(i,j)=j.
2
7
2
7
7
7
7
5
5
0
5
n+1
5
3
3
3
11 11
11
11
11
Step 4: Create forward links for node N+1
• Input: knapsack instance {2,3,5,7,11}
• Draw links to N+1 with weights w(i,N+1)=0.
2
7
2
7
7
7
7
5
5
0
5
5
3
3
3
11 11
11
11
11
0
0
0
0
0
n+1
Step 5: Create backward links
• Input: knapsack instance {2,3,5,7,11}
• Draw backward links from bigger to smaller nodes.
• Set weight of the link as w(j,i)=0.
0
2
7
0
0
0
0
0
5
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
3
0
0
0
0
11
n+1
Solution for KP Solution for TSP
• KP = {3,5,7}
• TSP = 0-3-5-7-(N+1)-11-2-0 (S=15)
Visit the nodes in an increasing order !
2
7
0
7
0
0
5
0
n+1
5
0
3
3
11
Solution for TSP Solution for KP
• TSP = 0-3-5-7-(N+1)-11-2-0
• KP = {3,5,7} (all nodes which arrival cost > 0)
Select nodes with entrance w>0 !
2
0
7
77
0
0
0
5
55
n+1
0
3
33
11
Empty space for notes