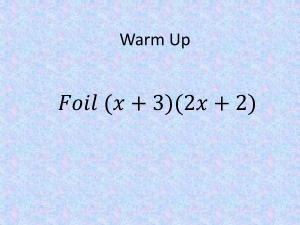OLGT: Solving Quadratic Equations
advertisement
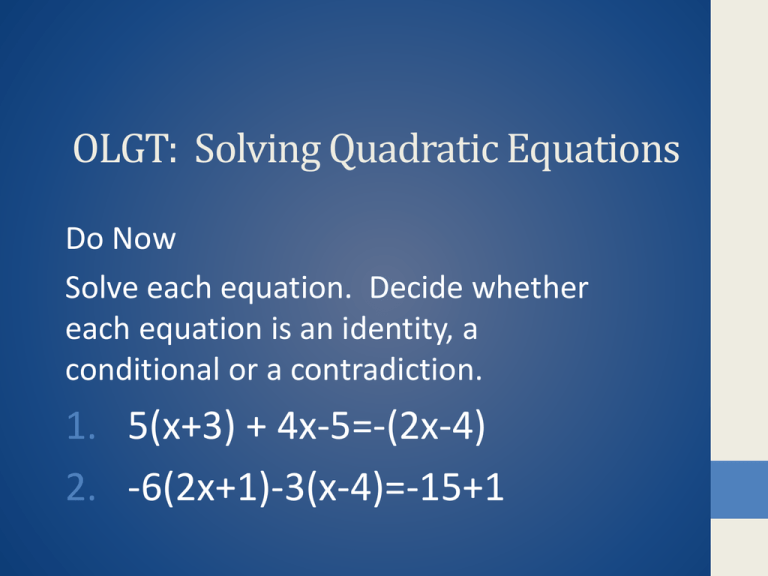
OLGT: Solving Quadratic Equations Do Now Solve each equation. Decide whether each equation is an identity, a conditional or a contradiction. 1. 5(x+3) + 4x-5=-(2x-4) 2. -6(2x+1)-3(x-4)=-15+1 Using the Zero-Factor Property • A quadratic equation written in standard form is • Ax2+bx+c = 0, where a, b, c are real numbers and a can not equal zero. • You can solve them by using one of the three methods • Zero-factor Property • Square Root Property • Quadratic Formula Zero-Factor Property • Solve 6x2+7x=3 • First put in standard form • 6x2+7x-3=0 • Then factor • (3x-1)(2x-3)=0 Zero-Factor Property • Apply the zero-factor property • 3x-1=0 or 2x+3=0 • 3x=1 2x=-3 • X=1/3 x=-3/2 • Check • 6(1/3)2+7(1/3)=3 and • 6(-3/2)2+7(-3/2)=3 Using the Square Root Property • Solve the quadratic equations x2=17 2. (x-4)2=12 X=± 17 x-4 =± 12 x=4 ± 12 x=4 ± (4)(3) x=4±2 3 Solve by the zero-property • -6x2+7x =10 • -6x2+7x -10 = 0 • -1(6x2-7x +10)=0 • -1(6x+5)(x-2) =0 • 6x-5=0 or x-2 =0 • 6x=5 • X=5/6 or x=2 Square Root Property • (x-7)2=24 • X-7 = ± 24 • X =7± 24 • X=7± (4)(6) • 7± 2 6 Homework • Page 441 # 33-44