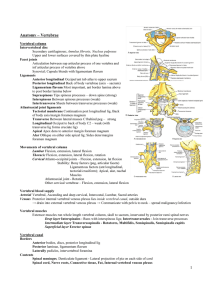
Posterior Column
advertisement

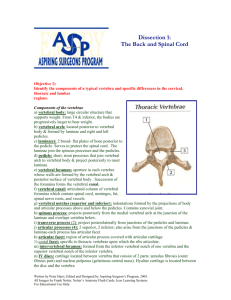
Dr. S. Nishan Silva (MBBS) At Birth The spine of a newborn is Cshaped, with one curve At About Six Months As the infant lifts his or her head during the first few months, the neck (cervical) curve and its muscles develop At About Nine Months As the infant learns to crawl and stand, the lower back (lumbar) curve and its muscles develop. Strong back muscles help give your child the strength and balance to walk and run. The spinal column The spinal column consists of individual bones called vertebrae, the building blocks, which provide support for the spine. These vertebrae are connected in the front of the spine by intervertebral discs. The spinal column consists of: •seven cervical vertebrae (C1–C7) i.e. neck •twelve thoracic vertebrae (T1–T12) i.e. upper back •five lumbar vertebrae (L1–L5) i.e. lower back •five bones (that are joined, or "fused," together in adults) to form the bony sacrum • three to five bones fused together to form the coccyx or tailbone The Back Posterior median furrow – vertical groove along the midline Spinous processes of vertebrae Spine of the scapula Medial end is opposite T3 Medial border of the scapula The Back Inferior angle of the scapula Iliac crests Supracristal line – intersects L4 Sacrum – superior to cleft in the buttocks Coccyx – posterior to the anus Surface Anatomy of the Back Figure 11.31a Surface Anatomy of the Trunk Scapulae Latissimus dorsi muscle erector spinae muscle infraspinatus muscle trapezius muscle teres major muscle posterior axillary fold triangle of auscutation 12-8 Muscles of the Back Trapezius Latissimus dorsi Erector spinae Surface Anatomy of the Back Figure 11.31b Anatomy Spinal cord ends below lower border of L1 Cauda equina is below L1 Mid dorsal spinal cord & neural canal space are of same diameter hence prone for complete lesion Mechanical injury - early ischaemia, cord edema - cord necrosis Neurological recovery unpredictable in cauda equina ie. peripheral nerves General Anatomy Lecture Anatomy Five lumbar vertebrae Five pairs (10 total) facet joints Intricate ligamentous support Anterior & posterior longitudinal Interspinous & supraspinous Anatomy Intervertebral disks Annulus fibrosus Outer zone (Sharpey’s fibers) Intermediate zone Inner zone 20 concentric collar like rings crisscrossed for strength Nucleus pulposus Fluid gradually changes to fibrocartilage Spinal Curves Posterior View Sagittal View Primary Secondary Bone Palpation Palpate L4/L5 junction (level of iliac crests) Palpate spinous processes superiorly and inferiorly S2 spinous process at level of posterior superior iliac spine Absence of any sacral and/or lumbar processes suggests spina bifida Visible or palpable step-off indicative of spondylolisthesis ANTERIOR PALPATION Soft Tissue Palpation 4 clinical zones Midline raphe Paraspinal muscles Gluteal muscles Sciatic area Anterior abdominal wall and inguinal area Vertebral arch 7 vertebral processes arise from vertebral arch 3 lever-like processes - provide attachments sites for ligaments and muscles Spinous process 2 Transverse processes 4 articular processes Arise from junction of pedicle and laminae Vertebral Arch Space enclosed by body and vertebral arch is the vertebral foramen Successive vertebral foramen form the vertebral canal Facet Joint Formed by articulation of inferior and superior processes of subsequent vertebrae Orientation in lumbar spine is toward sagittal plane, allowing flexion and extension but limiting rotation of the lumbar vertebrae Helps to prevent anterior movement of superior vertebra on inferior vertebra Articular surfaces are made up of noninnervated articular cartilage Capsule and synovial membrane are innervated with pain receptors Cervical spine anatomy Anterior column - Anterior longitudinal ligament+ Anterior annular ligament and anterior half of VB. Middle column – Posterior long. Lig. + Posterior annular ligament +Posterior half of VB. Posterior Column – Lig flavum + superior & Interspinous lig + intertransverse capsular lig + neural arch + pedicle & spinous process. Cervical Alignment Anterior vertebral body Posterior vertebral body Spinolaminal line Spinous process tips General Vertebral Anatomy Body Vertebral Arch Pedicles Laminae Vertebral Foramen Spinous Process Facets Superior Articulating Surface Inferior Articulating Surface Transverse Process Intervertebral Foramen Distinguishing Features of Cervical Vertebrae Transverse foramina C1 transverse process Spinous Processes C6 and C7 C3-C6 = bifurcate None for C1 Articulating Facets Atlas 1st Cervical Vertabrae Lack of Body Superior Articular Foveae Inferior Articulating Foveae Fovea Dentis Axis C2 Dens Rotation between skull and atlas C7 Body Spinous process Transverse Foramina Anterior element Articulations within cervical region Lateral Atlantoaxial Joints Superior facets and inferior facets of atlas Flat and in transverse plane Rotation Side toward rotation Side away from rotation Median Atlantoaxial Joints Dens of axis and anterior arch of atlas Tectorial membrane Cruciform ligament Articulation within cervical spine Atlanto-occipital Occipital condyles of skull and superior articulating surface of atlas Rotation Articulations within cervical spine Body-to-body articulation Fibrocartilogenous Intervertebral Disk Annulos fibrosis Nucleus puplosis Articulations within cervical spine Cervical facet joints Parallel to frontal plane 45 degrees to transverse plane Rotation Ligaments within cervical spine Ligamentum Nuchae Interspinous Ligament Ligamentum Flava Posterior Atlantooccipital membrane Intertransverse Ligament Curvature of cervical spine Lordotic Curve Cervical spine movement Flexion/Extension Atlanto-occipital Rotation Atlanto-axial joint Brachial Plexus Nerve Roots C5,6,7,8,T1 Trunks Upper Middle Lower Divisions Anterior Posterior Cords Lateral Posterior Medial Throat Anatomy 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic artery 4. Common carotid artery 5. Internal jugular vein 6. Superior vena cava Thoracic Vertebrae Bodies Pedicles Laminae Spinous Processes Transverse Processes Inferior & Superior Facets Distinguishing Feature Costal Fovea T1 T2-T8 T9-12 Thoracic Vertebrae and Rib Junction Functions of Thoracic Spine Costovertebral Joint Costotransverse Joint Motions All available Flexion and extension limited T7-T12 Lumbar Spine Bodies Pedicles Laminae Transverse Process Spinous Process Articular Facets Lumbar Spine Thoracolumbar Fascia Lumbar Spine Iliolumbar Ligaments Functions of Lumbar Spine Resistance of anterior translation Resisting Rotation Weight Support Motion Spinal Ligaments Anterior Longitudinal Posterior Longitudinal Ligamentum Flavum Interspinous Ligaments Supraspinous Ligaments Intertransverse Ligaments Intervertebral Disks Ratio between disk thickness and vertebral body height Disk Composition Nucleus pulposis Annulus Fibrosis Vertebral venous plexus Deep Muscles of the Back (Erector Spinae) Iliocostalis Iliocostalis lumborum Iliocostalis Thoracis IliocostalisCervicis Iliocostalis Lumborum O Common tendon origin in sacrum, iliac crest, lumber vertebrae I Lower borders ribs 6-12 N Dorsal rami of spinal nerves F Bilateral Spinal extension Maintenance of erect posture Stabilization of spine during flexion Unilateral Lateral flexion Ipsilateral rotation Iliocostalis Thoracis O Upper borders rib 6-12 I Lower borders ribs 1-6 N Dorsal rami of spinal nerves F Bilateral Same as above Unilateral Same as above Iliocostalis Cervicis O Angles ribs 1-6 I C4-6 transverse processes N Dorsal rami of spinal nerves F Same as above Longissimus Longissimus Thoracis Longissimus Cervicis Longissimus Capitus Longissimus Thoracis O Common tendon origin in sacrum, iliac crest, lumber vertebrae I T1-12 transverse processes N Dorsal rami of spinal nerves F Same as above Longissimus Cervicis O T1-5 transverse processes I C2-6 transverse processes N Dorsal rami of spinal nerves F Same as above Longissimus Capitus O T1-5 transverse processes C5-7 articular processes I Posterior mastoid process N Dorsal rami of spinal nerves F Extends and rotates head Spinalis Spinalis Thoracis Spinalis Cervicis Spinalis Capitus Spinalis Thoracis O Common tendon origin in sacrum, iliac crest, lumber vertebrae I T3-8 spinous processes N Dorsal rami pf spinal nerves F Same as above Spinalis Cervicis O C6-T12 spinous processes I C2 spinous process N Dorsal rami of spinal nerves F Same as above Spinalis Capitis O Spinous processes of lower cervical and upper thoracic I Between superiior and inferior nuchal line on occiput N Dorsal rami of spinal nerves F Same as above Transversospinal Muscles Semispinalis thoracis Semispinalis Cervicis Semispinalis Capitus Semispinalis Thoracis O T6-10 transverse processes I C6 – T4 spinous processes N Sorsal rami of spinal nerves F Same as above Semispinalis Cervicis O T1-T6 spinous processes I C2-5 spinous processes N Dorsal rami of spinal nerves F Same as above Semispinalis Capitis O C4-7 transverse processes T1-7 vertebrae I Between superior and inferior nuchal lines of occiput N Dorsal rami of spinal nerves F Same as above Multifidus O Transverse processes C4-L5 Sacrum PSIS I Spinous process of vert above origin N Spinal nerve roots F Extend and lateral flexion of vertebral column Quadratus Lumborum O Iliolumbar Ligament Iliac crest I Lower border 12th rib L1-L4 transverse processes N ventral branches of T12 and L1 to L4. F Pelvis elevation Trunk extension Trunk lateral flexion Pulls down rib 12 to fix origin of diaphragm Rotatores O Transverse processes from axis to sacrum I Laminae of vert above N Direct branches over spinal nerve roots F Spine extension Rotation to opposite side Range of Motion Flexion Extension Lateral Bending Rotation Flexion - 80º Extension - 35º Side bending - 40º each side Twisting - 3-18º Neurologic Exam: Sensory Sensory dermatomes C2-C3: Occipital area and angle of jaw C4: Supraclavicular area Axillary Nerve Patch: Lateral aspect of shoulder C5: Lateral upper arm C6: Lateral forearm, thumb, and index finger C7: Middle finger and palmar aspect of hand C8: Small finger, ring finger, and medial portion of palmar surface Neurologic Exam: Sensory Sensory dermatomes T1: Medial side of forearm and elbow T2: Medial aspect of upper arm T3: Medial aspect of upper arm T10: Umbilicus L2: Medial mid-thigh L3: Superior aspect of medial knee (vastus medialis) L4: Knee and medial arch L5: Dorsum of the foot S1: Lateral border and lateral aspect of foot S2: Popliteal fossa Neurologic Exam: Motor C1-C2: Neck flexion C1-C2: Neck extension C3: Neck lateral flexion C4: Shoulder elevation C5: Shoulder abduction and external rotation C6: Elbow flexion and wrist extension C7: Elbow extension and wrist flexion C8: Thumb abduction and ulnar deviation Neurologic Exam: Motor T1: Finger approximation L2: Hip flexion L3: Knee extension L4: Dorsiflexion L5: Great toe extension, ankle dorsiflexion, ankle eversion S1: Plantarflexion S2: Knee flexion Neurologic Exam: Reflexes Biceps (C5-C6) Supinator (C5-C6) Triceps (C7-C8) Upper abdominal (T8-T10) Lower abdominal (T11-T12) Patella (L3-L4) Achilles tendon (S1-S2) Babinski Myotomes Map of Dermatomes – Anterior View Figure 14.17a Map of Dermatomes – Posterior View Figure 14.17b Cervical Read Back Pain Common Sources of LBP Somatic dysfunction Muscle in “spasm” Nerve root In somatic dysfunction, some muscles become overactive (“spasm”) and other muscles become inactive. Muscles Joint Receptors Joint receptors vasculature Blood vessels Muscle Spindles viscera Nocioceptors Pressure, temperature chemical Internal organs Connective tissues Humoral Factors circulating hormones (gender-specific response) Bones and ligaments immune proteins cortisol Disc Diseases Radicular Signs Pain radiation to buttocks – Sciatica Posterior thigh pain Parasthesia – nerve root impringement Lower Spinal conditions Spondylolysthesis Spondylolysthesis Spondylolysis Facet joint pain Spinal injuries Watch video Atlas Fractures Type Odontoid Treated with external orthrosis Spinal Column Injury Subaxial (C3-C7) # Whiplash injury: Traumatic injury to the soft tissue in the cervical region Hyperflexion, hyperextention No fractures or dislocations Most common automobile injury Recover 3-6 months Hangman’s Fracture