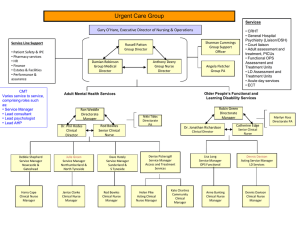
Mobility (Musculoskeletal) Health
advertisement

Review Physiological Integrity of Children Question and Answer 1. According to JCAHO, which statement is inappropriate related to pediatric restraints? A. Substitute mummy restraints for therapeutic holding in newborns undergoing IV insertion B. The restraint order must be written by the health care provider within 1 hour of applying the restraint C. No specific order is required for elbow restraints after cleft lip or palate repair D. Restraint safety must be assessed and documented at least every 2 hours 1. According to JCAHO, which statement is inappropriate related to pediatric restraints? A. Substitute mummy restraints for therapeutic holding in newborns undergoing IV insertion B. The restraint order must be written by the health care provider within 1 hour of applying the restraint C. No specific order is required for elbow restraints after cleft lip or palate repair D. Restraint safety must be assessed and documented at least every 2 hours A. Therapeutic holding is always appropriate as first line restraint if it is available and effective. 2. Why would a 3-year-old child be more likely to take 5 mL of medication from a 10 mL syringe than a 5 mL syringe if given both options? A. This child doesn’t yet comprehend the principle of conservation of mass B. The child is empowered by being given a choice C. There is more dilution when given in a larger container D. The child wants to please the nurse and chooses the larger container 2. Why would a 3-year-old child be more likely to take 5 mL of medication from a 10 mL syringe than a 5 mL syringe if given both options? A. This child doesn’t yet comprehend the principle of conservation of mass B. The child is empowered by being given a choice C. There is more dilution when given in a larger container D. The child wants to please the nurse and chooses the larger container A. Conservation of mass usually develops at school age. Before that time it looks like a smaller volume when placed in a larger container. 3. The nurse is preparing to give an IM injection to a 1 ½- yearold. Where should this be given? A. B. C. D. Deltoid Gluteus Maximus Ventrogluteus Vastus Lateralis 3. The nurse is preparing to give an IM injection to a 1 ½- yearold. Where should this be given? A. B. C. D. Deltoid Gluteus Maximus Ventrogluteus Vastus Lateralis D. This is preferred until age 2, then the ventrogluteus or deltoid may be used. The gluteus maximus should not be used until the child has been walking for at least 1 year. Physiological Integrity of Children Pediatric Safety Intramuscular 4. Which statement is true regarding the collection of blood for a CBC from a toddler? A. Since it must be arterial blood, the needle stick should be fast and the blood collected quickly B. Children fear the loss of any blood and must be reassured they will make more C. Because the pain sensors are not yet fully developed, the pain is minimal D. Bandages should not be applied as they increase the chance for infection at the blood draw site 4. Which statement is true regarding the collection of blood for a CBC from a toddler? A. Since it must be arterial blood, the needle stick should be fast and the blood collected quickly B. Children fear the loss of any blood and must be reassured they will make more C. Because the pain sensors are not yet fully developed, the pain is minimal D. Bandages should not be applied as they increase the chance for infection at the blood draw site B. Making comments about how red the blood is and how well they are making it will help reassure children. Bandages are helpful so the child will not think more will leak out. Any needle stick is painful and a CBC does not require arterial blood. 5. Which potential nursing action to assess hydration status in a child should be changed? A. Assess urine output with 35 mL/Kg/day indicating good hydration B. Obtain daily weight before breakfast C. Evaluate specific gravity by squeezing urine from the diaper on to the test strip D. Weight each diaper with each gram of urine equal to 1 mL of output 5. Which potential nursing action to assess hydration status in a child should be changed? A. Assess urine output with 35 mL/Kg/day indicating good hydration B. Obtain daily weight before breakfast C. Evaluate specific gravity by squeezing urine from the diaper on to the test strip D. Weight each diaper with each gram of urine equal to 1 mL of output A. While 1 mL/Kg/hour is what is desired, it is not possible to determine this unless the child is catheterized. 6. Which is the most serious symptom of acute dehydration? A. B. C. D. Dry mucus membranes Hypotension Capillary refill 1-2 seconds Skin color pale 6. Which is the most serious symptom of acute dehydration? A. B. C. D. Dry mucus membranes Hypotension Capillary refill 1-2 seconds Skin color pale B. Hypotension, tachycardia, and capillary refill over 3 seconds corresponds to severe dehydration with circulatory system manifestations. 7. In educating a class of school teachers about immunizations, which statement indicates the need for further clarification? A. If a child is up to date on immunizations, there is decreased risk of a chicken pox outbreak B. Immunizations are a form of passive immunity C. Passive immunity to hepatitis A is only temporary D. Natural active immunity is the longest lasting and most effective type of immunity 7. In educating a class of school teachers about immunizations, which statement indicates the need for further clarification? A. If a child is up to date on immunizations, there is decreased risk of a chicken pox outbreak B. Immunizations are a form of passive immunity C. Passive immunity to hepatitis A is only temporary D. Natural active immunity is the longest lasting and most effective type of immunity B. Immunizations are active immunity. 8. A client is exhibiting itchy eyes, bronchoconstriction and allergic rhinitis. The RN would expect which aspect of immunoglobulin to be elevated? A. B. C. D. IgA IgE IgG IgD 8. A client is exhibiting itchy eyes, bronchoconstriction and allergic rhinitis. The RN would expect which aspect of immunoglobulin to be elevated? A. B. C. D. IgA IgE IgG IgD B. IgE is related to allergic reactions. 9. A child has received a kidney transplant. Which part of the immune system needs to be suppressed? A. B. C. D. Th and Tc Ts and Th Ts and NK Ts and Tc 9. A child has received a kidney transplant. Which part of the immune system needs to be suppressed? A. B. C. D. Th and Tc Ts and Th Ts and NK Ts and Tc A. The T-helper, T-cytokins, and Natural Killer cells all need to be suppressed to prevent tissue rejection. 10. Which client does the RN assess to be most likely to benefit from immune globulin administration? A. B. C. D. Cut hand with kitchen knife and no tetanus immunization Lymphocytosis Neutrophil shift-to-the-left Congenital B-cell deficiency 10. Which client does the RN assess to be most likely to benefit from immune globulin administration? A. B. C. D. Cut hand with kitchen knife and no tetanus immunization Lymphocytosis Neutrophil shift-to-the-left Congenital B-cell deficiency D. B-cells make antibodies of which immunoglobulin is one type. A would be at little risk for tetanus and B and C are dysfunctions of WBC, not immunoglobulin deficiency. 11. Which level of prevention would the nurse perform by giving influenza vaccines in a local clinic? A. B. C. D. Primary prevention Secondary prevention Tertiary prevention All three levels of prevention 11. Which level of prevention would the nurse perform by giving influenza vaccines in a local clinic? A. B. C. D. Primary prevention Secondary prevention Tertiary prevention All three levels of prevention A. Primary prevention = health promotion and disease/injury prevention; secondary prevention = screening and early diagnosis of disease; tertiary prevention = maximizing function and minimizing effects of disabilities/chronic conditions. 12. Which immunization should a 2-month-old infant receive? A. B. C. D. Varicella vaccine Diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis vaccine (DTaP) Tetanus and diphtheria vaccine (Td) Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR) 12. Which immunization should a 2-month-old infant receive? A. B. C. D. Varicella vaccine Diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis vaccine (DTaP) Tetanus and diphtheria vaccine (Td) Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR) B. The preferred age for initial immunization for pertussis is 2 months; the pertussis vaccine is administered in combination with diphtheria and tetanus 13. What findings would the nurse anticipate when assessing a 6year-old client with possible rubella? A. B. C. D. A pinkish maculopapular rash on the head and neck A positive Kernig’s sign and nuchal rigidity Koplik's spots on the soft palate and buccal mucosa Conjunctivitis and malaise 13. What findings would the nurse anticipate when assessing a 6year-old client with possible rubella? A. B. C. D. A pinkish maculopapular rash on the head and neck A positive Kernig’s sign and nuchal rigidity Koplik's spots on the soft palate and buccal mucosa Conjunctivitis and malaise A. Choice B reflects possible meningitis, and choice C reflects possible rubeola. Conjunctivitis and malaise are part of the prodromal phase of rubeola in children, and part of the prodromal phase of rubella in adolescents and adults. 14. Which nursing diagnosis would be appropriate for the most severe (though rare) complication of Rubella in a child? A. B. C. D. Self-care deficit related to paralysis Disorganized thought processes related to increased ICP Fluid volume excess related to circulatory overload Impaired skin integrity related to skin ulceration 14. Which nursing diagnosis would be appropriate for the most severe (though rare) complication of Rubella in a child? A. B. C. D. Self-care deficit related to paralysis Disorganized thought processes related to increased ICP Fluid volume excess related to circulatory overload Impaired skin integrity related to skin ulceration B. Encephalitis has occasionally but rarely been identified after Rubella. 15. A child with Cystic Fibrosis (CF) contracts Rubeola. Which nursing intervention is most appropriate? A. Isolate the child for 2 weeks after desquamation develops B. Stress the need to keep pregnant friends/relatives from visiting C. Administer antibiotics per physician order D. Use maximum dose of antipyretic medications as fever spikes on the 1st-2nd day of the rash 15. A child with Cystic Fibrosis (CF) contracts Rubeola. Which nursing intervention is most appropriate? A. Isolate the child for 2 weeks after desquamation develops B. Stress the need to keep pregnant friends/relatives from visiting C. Administer antibiotics per physician order D. Use maximum dose of antipyretic medications as fever spikes on the 1st-2nd day of the rash C. Prophylactic antibiotics are used for high-risk children such as with a chronic disease like CF. Contagion occurs 4 days before to 5 days after rash develops. Desquamation occurs 3-4 days after onset and fever spikes on 4th to 5th day. 16. Which is the most appropriate in the plan of care for a child with mumps? A. B. C. D. Assess visual acuity every shift Isolate the child for 14 days Encourage soft foods and increased fluid intake Discourage use of underwear for the male child on bedrest 16. Which is the most appropriate in the plan of care for a child with mumps? A. B. C. D. Assess visual acuity every shift Isolate the child for 14 days Encourage soft foods and increased fluid intake Discourage use of underwear for the male child on bedrest C. Chewing often increases pain in the ear and jaw, so soft foods are encouraged. Assessing hearing is important as well as wearing underwear to support the scrotum if orchitis develops. Mumps is most contagious from just before to 4 days after onset of symptoms. 17. In teaching the parent of a child with chicken pox, which measure would the nurse suggest to relieve pruritus? A. B. C. D. Cleaning the vesicles with diluted hydrogen peroxide Applying topical calamine lotion to irritated areas Using cool saline compresses on top of the eruptions Keeping the child's fingernails short and using mittens when necessary 17. In teaching the parent of a child with chicken pox, which measure would the nurse suggest to relieve pruritus? A. B. C. D. Cleaning the vesicles with diluted hydrogen peroxide Applying topical calamine lotion to irritated areas Using cool saline compresses on top of the eruptions Keeping the child's fingernails short and using mittens when necessary B. Although answer choice D is true, it does not answer the question. To relieve pruritus, calamine lotion may prove helpful. 18. The parent of a child with chickenpox asks when the child can go back to school. Select the most appropriate response. A. B. C. D. “When the child is no longer running a fever.” “Once the blisters are all scabbed over.” “When all of the scabs on the blisters have fallen off.” “After completing antibiotics for 24 hours.” 18. The parent of a child with chickenpox asks when the child can go back to school. Select the most appropriate response. A. B. C. D. “When the child is no longer running a fever.” “Once the blisters are all scabbed over.” “When all of the scabs on the blisters have fallen off.” “After completing antibiotics for 24 hours.” B. When the open lesions are no longer draining, the disease is no longer contagious. Physiological Integrity of Children Oxygenation (Respiratory) Health Varicella (Chickenpox) 19. The parent of a child with Down Syndrome who develops Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia asks the nurse what causes cancer. Which statement by the parent indicates further discussion is needed? A. “Some cancers are caused by faulty genes.” B. “A weakened immune system can increase risk for cancer.” C. “Protooncogenes can cause normal cells to turn into cancer cells.” D. “Infection with certain viruses can lead to cancer.” 19. The parent of a child with Down Syndrome who develops Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia asks the nurse what causes cancer. Which statement by the parent indicates further discussion is needed? A. “Some cancers are caused by faulty genes.” B. “A weakened immune system can increase risk for cancer.” C. “Protooncogenes can cause normal cells to turn into cancer cells.” D. “Infection with certain viruses can lead to cancer.” C. Oncogenes can cause normal cells to transform into cancer cells. 20. The client is receiving chemotherapy with Adriamycin (doxorubicin). The nurse stops the infusion immediately and notifies the physician if which symptom(s) occur(s)? A. B. C. D. Urine turns reddish brown Nausea occurs Mouth soreness develops Redness and swelling occur at the IV site 20. The client is receiving chemotherapy with Adriamycin (doxorubicin). The nurse stops the infusion immediately and notifies the physician if which symptom(s) occur(s)? A. B. C. D. Urine turns reddish brown Nausea occurs Mouth soreness develops Redness and swelling occur at the IV site D. This type of drug may cause sclerosing and even minute amounts can cause severe cellular damage if the IV infiltrates although pain may not occur. While the other symptoms may occur, the IV is the most important problem to address immediately. 21. A 4-year-old pulls a pot of boiling soup off the stove causing burns to the left arm. What would be the best immediate intervention? A. B. C. D. Remove food particles and apply burn cream Apply an ice pack to the left arm Remove food particles and shirt sleeve Apply cool water and baking soda to the left arm 21. A 4-year-old pulls a pot of boiling soup off the stove causing burns to the left arm. What would be the best immediate intervention? A. B. C. D. Remove food particles and apply burn cream Apply an ice pack to the left arm Remove food particles and shirt sleeve Apply cool water and baking soda to the left arm C. Remove the heat source and any non-adherent clothing; apply cool water, not ice or any ointments or other agents, and transport to the emergency department. 22. A 6-year-old is playing with the mother’s “beauty equipment” and rubs hair remover cream on the legs. About 45 minutes later, the child begins to cry and say the legs burn. What should the mother be instructed to do first? A. B. C. D. Neutralize by applying water and baking soda to the legs Wipe off cream and wash legs with large amounts of water Apply burn ointment to stop the burning action of the cream Transport to the hospital without doing anything else 22. A 6-year-old is playing with the mother’s “beauty equipment” and rubs hair remover cream on the legs. About 45 minutes later, the child begins to cry and say the legs burn. What should the mother be instructed to do first? A. B. C. D. Neutralize by applying water and baking soda to the legs Wipe off cream and wash legs with large amounts of water Apply burn ointment to stop the burning action of the cream Transport to the hospital without doing anything else B. Chemicals left in contact with the skin longer than recommended will cause burns. The area should be wiped off and flushed with large amounts of water. Then transport to the hospital. 23. A construction worker accidentally touches a high voltage electric line and is thrown to the ground. What nursing diagnosis would have highest priority? A. B. C. D. Risk for increased energy field Risk for situational trauma Risk for decreased cardiac output Risk for impaired skin integrity 23. A construction worker accidentally touches a high voltage electric line and is thrown to the ground. What nursing diagnosis would have highest priority? A. B. C. D. Risk for increased energy field Risk for situational trauma Risk for decreased cardiac output Risk for impaired skin integrity C. The greatest concern with electrical situations is cardiac arrest. Physiological Integrity of Children Pediatric Safety Chemical Burns •Gently flood with water •Continue flooding while clothing is being removed •Avoid a hard blast of water, as from a hose Physiological Integrity of Children Pediatric Safety Electrical Burns •Examine for cardiac or respiratory arrest •Institute cardiopulmonary resuscitation •Apply dry sterile dressings to entry and exit wounds 24. A 4-year-old child is brought to the emergency room with a deep partial thickness burn, sustained from hot grease. Upon assessing the burn, which characteristic would a nurse expect to find? A. Dry skin surface that blanches readily to pressure and quickly refills B. Blistered, moist, mottled skin that is red or dull white C. Tough, leathery skin surface that does not blanch and refill with pressure D. Brown, tan, black, or pearly white skin with no blisters 24. A 4-year-old child is brought to the emergency room with a deep partial thickness burn, sustained from hot grease. Upon assessing the burn, which characteristic would a nurse expect to find? A. Dry skin surface that blanches readily to pressure and quickly refills B. Blistered, moist, mottled skin that is red or dull white C. Tough, leathery skin surface that does not blanch and refill with pressure D. Brown, tan, black, or pearly white skin with no blisters B. A deep partial thickness burn is a second degree burn that appears blistered, moist, and mottled and may be red, dull white, or tan Physiological Integrity of Children Pediatric Safety Deep Partial Thickness Burns 25. Which is the RN’s 1st priority after extensive deep partial thickness and full thickness burns? A. B. C. D. Obtain vascular access and start IV Provide emotional support for client and significant others Monitor for symptoms of hyperkalemia Assess for symptoms of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome 25. Which is the RN’s 1st priority after extensive deep partial thickness and full thickness burns? A. B. C. D. Obtain vascular access and start IV Provide emotional support for client and significant others Monitor for symptoms of hyperkalemia Assess for symptoms of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome A. Due to rapid massive fluid 3rd spacing after severe burns, securing airway patency and IV access are top priorities. 26. The nurse is caring for a child with circumferential full thickness burns to the right arm and trunk. Which nursing intervention has the highest priority in the plan of care? A. B. C. D. Assess radial pulses several times a day Enforce airborne infection control precautions Perform range of motion several times a day Remove blisters from the burn area 26. The nurse is caring for a child with circumferential full thickness burns to the right arm and trunk. Which nursing intervention has the highest priority in the plan of care? A. B. C. D. Assess radial pulses several times a day Enforce airborne infection control precautions Perform range of motion several times a day Remove blisters from the burn area A. Circumferential burns often produce strictures and reduce circulation causing tissue necrosis. 27. A 4-year-old child sustained full-thickness burns to the inner thighs. There is no facial, airway or upper body involvement. Which nursing diagnosis has the highest priority in the emergent phase of burn care? A. B. C. D. Diversional activity deficit Less than nutritional requirements Impaired skin integrity Dysfunctional family process 27. A 4-year-old child sustained full-thickness burns to the inner thighs. There is no facial, airway or upper body involvement. Which nursing diagnosis has the highest priority in the emergent phase of burn care? A. B. C. D. Diversional activity deficit Less than nutritional requirements Impaired skin integrity Dysfunctional family process C. Priorities include stopping the burning process, removing burned clothing if not adhering to the skin, and covering the wound. Airway is also a priority. 28. As the RN plans care for a child with 30% body surface area (BSA), partial thickness and full-thickness burns, which is the best goal to assess fluid adequacy? A. B. C. D. BP remains within normal range Urine output is maintained at 1-2 mL/Kg/hour Lung sounds remain clear Weight remains within 10% of baseline 28. As the RN plans care for a child with 30% body surface area (BSA), partial thickness and full-thickness burns, which is the best goal to assess fluid adequacy? A. B. C. D. BP remains within normal range Urine output is maintained at 1-2 mL/Kg/hour Lung sounds remain clear Weight remains within 10% of baseline B. Urine output is the best indicator of adequate fluid levels. 29. Which topical agent would be most appropriate for a client with partial thickness and deep partial thickness burns with renal insufficiency and Bactrim/Septra allergy? A. B. C. D. Betadine (providone-iodine) Sulfamylon (mafenideacetate) Silvadene (silver sulfadiazine) Garamycin (gentamycin sulfate) 29. Which topical agent would be most appropriate for a client with partial thickness and deep partial thickness burns with renal insufficiency and Bactrim/Septra allergy? A. B. C. D. Betadine (providone-iodine) Sulfamylon (mafenideacetate) Silvadene (silver sulfadiazine) Garamycin (gentamycin sulfate) A. Choices B and C are sulfa based as is Bactrim/Septa and D is nephrotoxic. 30. A client with full thickness burns to the right arm is going to hydrotherapy for escharotomy. Which intervention has the highest priority? A. B. C. D. Pain control before the procedure Psychosocial preparation for the procedure Dietary therapy to enhance healing Electrolyte replacement before the procedure 30. A client with full thickness burns to the right arm is going to hydrotherapy for escharotomy. Which intervention has the highest priority? A. B. C. D. Pain control before the procedure Psychosocial preparation for the procedure Dietary therapy to enhance healing Electrolyte replacement before the procedure A. Though full thickness burns destroy nerve endings, there are likely partial and deep partial thickness burns at the periphery of the central burn, so pain control is a priority. 31. What would be the priority action for the nurse when a client returns from surgery after split thickness skin grafts to both feet? A. Prevent movement of donor site B. Monitor donor and receiver sites for infection C. Plan activities to prevent boredom since client will be immobilized D. Maintain client on bedrest to promote graft adherence to the capillary bed 31. What would be the priority action for the nurse when a client returns from surgery after split thickness skin grafts to both feet? A. Prevent movement of donor site B. Monitor donor and receiver sites for infection C. Plan activities to prevent boredom since client will be immobilized D. Maintain client on bedrest to promote graft adherence to the capillary bed D. For this type of graft to be successful, contact between the graft and recipient “bed” must be maintained, free of bleeding and infection. 32. A hospitalized 5-year-old child with severe burns to the abdomen and legs becomes upset and combative when it is time to change the dressings and apply Sulfamylon (mafenide acetate). Select the intervention that will help this child the most. A. Allow the child to determine the time of the dressing change B. Allow the child to help with the dressing change C. Tell the child it is OK to cry but the child must lie quietly D. Explain the importance of the dressing change to the child 32. A hospitalized 5-year-old child with severe burns to the abdomen and legs becomes upset and combative when it is time to change the dressings and apply Sulfamylon (mafenide acetate). Select the intervention that will help this child the most. A. Allow the child to determine the time of the dressing change B. Allow the child to help with the dressing change C. Tell the child it is OK to cry but the child must lie quietly D. Explain the importance of the dressing change to the child B. Some control may help the child cope with the frustration of hospitalization and the discomfort of the dressing change. 33. A nurse just completed a presentation on pediculosis capitis to the local school board. What statement, overheard by the nurse, indicates the information was understood? A. “Since I'm an adult, I no longer need to worry about getting head lice.“ B. “The presence of head lice in a school indicates poor cleanliness by the school's janitorial services.“ C. “This type of problem only occurs in schools located in impoverished areas of a city.“ D. “Head lice can occur in anyone, regardless of age or socioeconomic level.“ 33. A nurse just completed a presentation on pediculosis capitis to the local school board. What statement, overheard by the nurse, indicates the information was understood? A. “Since I'm an adult, I no longer need to worry about getting head lice.“ B. “The presence of head lice in a school indicates poor cleanliness by the school's janitorial services.“ C. “This type of problem only occurs in schools located in impoverished areas of a city.“ D. “Head lice can occur in anyone, regardless of age or socioeconomic level.“ D. Anyone can have head lice (pediculosis capitis) regardless of age, cleanliness, or socioeconomic level. 34. Which intervention included in a care plan for a child with scabies needs to be revised? A. After application of Elimite (permethrin 5%), hold and comfort the child B. Bathe the child thoroughly after the Elimite has been on for 8-14 hours C. Apply Elimite beneath fingernails and toenails with a toothpick D. If itching continues after treatment, reassure that treatment does not need to be reapplied 34. Which intervention included in a care plan for a child with scabies needs to be revised? A. After application of Elimite (permethrin 5%), hold and comfort the child B. Bathe the child thoroughly after the Elimite has been on for 8-14 hours C. Apply Elimite beneath fingernails and toenails with a toothpick D. If itching continues after treatment, reassure that treatment does not need to be reapplied A. There should be minimal touching and holding after application of Elimite. If touching occurs, wash hands immediately. 35. A 24-year-old client tells the nurse she and her husband are considering starting a family soon. What teaching point would the nurse include concerning the importance of dietary folic acid? A. “Folic acid will help reduce the chance of spinal cord problems in your baby.” B. “Your baby will develop a stronger immune system due to the folic acid.” C. “One action of folic acid is to prepare your body for the pregnancy.” D. “Folic acid is needed to help form your baby’s blood components.” 35. A 24-year-old client tells the nurse she and her husband are considering starting a family soon. What teaching point would the nurse include concerning the importance of dietary folic acid? A. “Folic acid will help reduce the chance of spinal cord problems in your baby.” B. “Your baby will develop a stronger immune system due to the folic acid.” C. “One action of folic acid is to prepare your body for the pregnancy.” D. “Folic acid is needed to help form your baby’s blood components.” A. Folic acid taken prior to conception and early in pregnancy will decrease the risk of neural tube defects in the fetus. 36. After surgery for reduction of spina bifida cystica, which is the best rationale for why ventriculo-peritoneal shunt is not indicated at this time? A. The specific defect was meningocele B. Lower extremity movement is symmetrical and active after surgery C. Occipital-frontal circumference preoperative and postoperative are equal D. There is an absence of Arnold-Chiari malformation 36. After surgery for reduction of spina bifida cystica, which is the best rationale for why ventriculo-peritoneal shunt is not indicated at this time? A. The specific defect was meningocele B. Lower extremity movement is symmetrical and active after surgery C. Occipital-frontal circumference preoperative and postoperative are equal D. There is an absence of Arnold-Chiari malformation C. An increase in occipital-frontal circumference indicates hydrocephalus and the need for a shunt. Physiological Integrity of Children Sensation, Perception, and Protection Myelomeningocele 37. What response by the nurse will best help the parents of an infant with spina bifida cope with this situation? A. Encourage parents to resolve their grief as soon as possible B. Emphasize positive attributes of their infant C. Avoid talking about the infant until the parents are ready to bring up the subject D. Do not allow the parents to become too upset over the situation 37. What response by the nurse will best help the parents of an infant with spina bifida cope with this situation? A. Encourage parents to resolve their grief as soon as possible B. Emphasize positive attributes of their infant C. Avoid talking about the infant until the parents are ready to bring up the subject D. Do not allow the parents to become too upset over the situation B. Pointing out unique physical or personality traits of an infant helps parents to see their child as a unique individual 38. An infant with a myelomeningocele develops increased intracranial pressure as a result of hydrocephalus. What early sign of increased intracranial pressure would most likely be seen by the nurse? A. B. C. D. Altered pupil reactivity Papilledema Diminished response to painful stimuli High-pitched cry 38. An infant with a myelomeningocele develops increased intracranial pressure as a result of hydrocephalus. What early sign of increased intracranial pressure would most likely be seen by the nurse? A. B. C. D. Altered pupil reactivity Papilledema Diminished response to painful stimuli High-pitched cry D. Only answer choice D is considered an early sign; the other choices represent late signs of increased ICP. 39. What is a short-term preoperative goal for a 1-month-old client scheduled for ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt for congenital hydrocephalus? A. B. C. D. Keep comfortable and limit crying Feed on fixed schedule to ensure adequate hydration Protect the head from injury with thick bandage Provide wide variety of play objects for sensory stimulation 39. What is a short-term preoperative goal for a 1-month-old client scheduled for ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt for congenital hydrocephalus? A. B. C. D. Keep comfortable and limit crying Feed on fixed schedule to ensure adequate hydration Protect the head from injury with thick bandage Provide wide variety of play objects for sensory stimulation A. Crying causes increased pressure in the cranial area and blood vessels. Physiological Integrity of Children Sensation, Perception, and Protection 40. When assessing a client with nuchal rigidity, which objective finding would the RN expect? A. B. C. D. Positive Kernig’s sign Positive Babinski reflex Papilledema Decorticate posturing 40. When assessing a client with nuchal rigidity, which objective finding would the RN expect? A. B. C. D. Positive Kernig’s sign Positive Babinski reflex Papilledema Decorticate posturing A. Positive Kernig’s and Brudzinski’s signs demonstrate meningeal irritation. Normal Kernig’s sign Abnormal Kernig’s sign Normal Brudzinski’s sign Abnormal Brudzinski’s sign 41. Which would the RN expect to find in the cerebral spinal fluid of a client with bacterial meningitis? A. B. C. D. Decreased glucose, increased protein Decreased glucose, decreased protein Increased glucose, increased protein Increased glucose, decreased protein 41. Which would the RN expect to find in the cerebral spinal fluid of a client with bacterial meningitis? A. B. C. D. Decreased glucose, increased protein Decreased glucose, decreased protein Increased glucose, increased protein Increased glucose, decreased protein A. Bacteria and WBC increase the protein count and bacteria use up glucose so the glucose level decreases. 42. Which is a true statement regarding meningitis? A. Both viral and bacterial meningitis may have an associated fever B. Stiff neck is the most common symptom in infants with viral meningitis C. Headaches only occur with bacterial meningitis D. Viral meningitis is more easily detected than bacterial meningitis in children 42. Which is a true statement regarding meningitis? A. Both viral and bacterial meningitis may have an associated fever B. Stiff neck is the most common symptom in infants with viral meningitis C. Headaches only occur with bacterial meningitis D. Viral meningitis is more easily detected than bacterial meningitis in children A. Fevers may occur with both bacterial and viral meningitis. The other statements are not accurate. 43. Which statement is true concerning neuroblastoma? A. Diagnosis is easily made based on symptoms B. Tumors develop primarily along the retroperitoneal sympathetic chain C. Treatment begins with chemotherapy, then radiation and surgery D. Prognosis is best if the child is over age 2 when diagnosed 43. Which statement is true concerning neuroblastoma? A. Diagnosis is easily made based on symptoms B. Tumors develop primarily along the retroperitoneal sympathetic chain C. Treatment begins with chemotherapy, then radiation and surgery D. Prognosis is best if the child is over age 2 when diagnosed B. This is where the “silent” tumors develop. Diagnosis is difficult because there are few symptoms until the tumor has metastasized. 44. What would the RN teach when instructing a class on epilepsy? A. Generalized seizures involve tonic-clonic contractions of muscles in the lower part of the body B. Absence seizures are partial seizures C. Complex partial seizures lead to loss of consciousness D. During an absence seizure, the nurse should attempt to awaken the client 44. What would the RN teach when instructing a class on epilepsy? A. Generalized seizures involve tonic-clonic contractions of muscles in the lower part of the body B. Absence seizures are partial seizures C. Complex partial seizures lead to loss of consciousness D. During an absence seizure, the nurse should attempt to awaken the client C. Complex partial seizures occur in a focal part of the brain and there is loss of consciousness for 1-3 minutes. Generalized seizures involve the whole body. Absence are generalized seizures and last only briefly. 45. A child is seen in the clinic with a chief complaint of “Seizures”. Which finding by the RN is most indicative of absence seizure? A. Experiences 20-25 events a day lasting 5-10 seconds B. Loses muscle control and displays head dropping C. Displays repetitive muscle contractures without loss of consciousness D. Displays hyperkinesis and lack of attentiveness 45. A child is seen in the clinic with a chief complaint of “Seizures”. Which finding by the RN is most indicative of absence seizure? A. Experiences 20-25 events a day lasting 5-10 seconds B. Loses muscle control and displays head dropping C. Displays repetitive muscle contractures without loss of consciousness D. Displays hyperkinesis and lack of attentiveness A. “Petit mal” or absence seizures are generalized seizures leading to a brief loss of consciousness, onset is abrupt, and the child may drop things but seldom falls. B is atonic, C is myoclonic, and D is related to ADHD. Physiological Integrity of Children Tonic-Clonic Seizure 46. Which action is the best way for the parent of an 8-year-old client with a seizure disorder to determine if the child is assuming responsibility for adhering to the anticonvulsant medication schedule? A. B. C. D. Asking the child each day when the medication is due Having the child place a star on a calendar each day Noting if the child has seizures at any time Observing for behavioral changes in the child 46. Which action is the best way for the parent of an 8-year-old client with a seizure disorder to determine if the child is assuming responsibility for adhering to the anticonvulsant medication schedule? A. B. C. D. Asking the child each day when the medication is due Having the child place a star on a calendar each day Noting if the child has seizures at any time Observing for behavioral changes in the child B. As soon as the child is old enough, the child should assume responsibility for taking own medications. Reminders and incentives are often helpful 47. Which has highest priority for a client taking Dilantin for a seizure disorder? A. B. C. D. Assess for symptoms of aplastic anemia Maintain optimal mouth care Limit foods high in folic acid If given IV, flush the tubing with D5W before and after administration 47. Which has highest priority for a client taking Dilantin for a seizure disorder? A. B. C. D. Assess for symptoms of aplastic anemia Maintain optimal mouth care Limit foods high in folic acid If given IV, flush the tubing with D5W before and after administration B. Aplastic anemia is not a major side effect, but gingival hyperplasia is, so good mouth care is very important. The diet should be high in folic acid and the IV should be flushed with Normal Saline. 48. Select the action that the nurse should take first when a 12year-old client, sitting in a chair, begins to have tonic-clonic seizure movements? A. Restrain the child to prevent injury to arms and legs B. Pad the environment around the chair C. Quickly insert an oral airway in the mouth to keep the airway patent D. Move the client to a flat surface, positioning the client on right or left side 48. Select the action that the nurse should take first when a 12year-old client, sitting in a chair, begins to have tonic-clonic seizure movements? A. Restrain the child to prevent injury to arms and legs B. Pad the environment around the chair C. Quickly insert an oral airway in the mouth to keep the airway patent D. Move the client to a flat surface, positioning the client on right or left side D. This is the only correct choice. Inserting an airway during tonic-clonic movements can cause injury. The child should be protected from injury, but not restrained. A flat, sidelying position will protect the airway and promote blood flow to the brain. 49. A nurse is caring for a 6-year-old child who suddenly falls to the floor and begins to have a generalized tonic-clonic seizure. How can the nurse best insure the child’s safety? A. B. C. D. Place a pillow under the head Insert a plastic bite stick into the mouth Hold the extremities in an extended alignment Wrap the child’s trunk in a sheet 49. A nurse is caring for a 6-year-old child who suddenly falls to the floor and begins to have a generalized tonic-clonic seizure. How can the nurse best insure the child’s safety? A. B. C. D. Place a pillow under the head Insert a plastic bite stick into the mouth Hold the extremities in an extended alignment Wrap the child’s trunk in a sheet A. This will prevent injury to the head and possible skull fracture during the clonic stage of the seizure. 50. A 6-year-old experienced a grand mal seizure, has been incontinent of urine, and is difficult to arouse. Identify the most appropriate nursing action. A. Ask the child’s parent if the child has a history of urinary problems B. Attempt to waken the child completely and assess level of consciousness C. Place the child in a side-lying position, stay with the child, and allow to sleep D. Perform a complete neurologic check and repeat it every three to five minutes 50. A 6-year-old experienced a grand mal seizure, has been incontinent of urine, and is difficult to arouse. Identify the most appropriate nursing action. A. Ask the child’s parent if the child has a history of urinary problems B. Attempt to waken the child completely and assess level of consciousness C. Place the child in a side-lying position, stay with the child, and allow to sleep D. Perform a complete neurologic check and repeat it every three to five minutes C. Urinary incontinence and sleep are common during and after a seizure. The child should be allowed to sleep, and while neurologic status is important, awakening every few minutes would not be helpful. 51. What should the nurse do prior to bathing a child who has brain damage, yet is able to respond to touch, sound and some visual stimuli? A. B. C. D. Administer PRN pain medication Escort the family from the room Dim the lights in the room Explain to the child what you are going to do 51. What should the nurse do prior to bathing a child who has brain damage, yet is able to respond to touch, sound and some visual stimuli? A. B. C. D. Administer PRN pain medication Escort the family from the room Dim the lights in the room Explain to the child what you are going to do D. When giving care to a client with neurological damage, always speak to the client before touching and explain in simple terms what will be done. 52. How should the parent of an infant with hypertonic cerebral palsy with scissoring of the legs be taught to carry the infant? A. B. C. D. Wrap the infant tightly in a blanket Extend the infant’s extremities Strap into a flat infant carrier Straddle on the parent’s hip 52. How should the parent of an infant with hypertonic cerebral palsy with scissoring of the legs be taught to carry the infant? A. B. C. D. Wrap the infant tightly in a blanket Extend the infant’s extremities Strap into a flat infant carrier Straddle on the parent’s hip D. This helps to control the scissoring of the legs and provides ease in supporting a child with hypertonicity. 53. The nurse is teaching the parent of a child with hemiplegia due to cerebral palsy. Which statement by the nurse refers to the purpose of positioning the child in an upright position and placing toys on the child's affected side? A. “This challenges the child to use the affected limb and may result in increased function.“ B. “Doing this provides a test of the child's visual acuity and scanning ability.“ C. “Forcing the child to obtain toys from the affected side is basically a diversional activity.“ D. “This approach is focused on increasing muscle strength in the affected limb.“ 53. The nurse is teaching the parent of a child with hemiplegia due to cerebral palsy. Which statement by the nurse refers to the purpose of positioning the child in an upright position and placing toys on the child's affected side? A. “This challenges the child to use the affected limb and may result in increased function.“ B. “Doing this provides a test of the child's visual acuity and scanning ability.“ C. “Forcing the child to obtain toys from the affected side is basically a diversional activity.“ D. “This approach is focused on increasing muscle strength in the affected limb.“ A. The purpose of this type of positioning and placement of toys is to challenge the child to use the affected limb, which may eventually lead to improved ability to use that limb. Physiological Integrity of Children Developmental Disabilities 54. A newborn has facial features including short palpebral fissures, hypoplastic philtrum, thin upper lip and hypoplastic maxilla. Which nursing diagnosis related to the medical diagnosis would need to be corrected? A. B. C. D. Risk for dysfunctional family process: alcoholism Risk for impaired parent/child attachment Risk for delayed growth and development Risk for imbalanced body temperature 54. A newborn has facial features including short palpebral fissures, hypoplastic philtrum, thin upper lip and hypoplastic maxilla. Which nursing diagnosis related to the medical diagnosis would need to be corrected? A. B. C. D. Risk for dysfunctional family process: alcoholism Risk for impaired parent/child attachment Risk for delayed growth and development Risk for imbalanced body temperature D. Fetal alcohol syndrome increases the risk for all but D. Physiological Integrity of Children Developmental Disabilities 55. A newborn is displaying symptoms of neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) and the mother is on Methadone. Which is the most appropriate intervention to plan related to this syndrome? A. Neonatal abstinence scoring system will be used to monitor baby for 1st 24 hours of life B. Lights and noises will be kept to a minimum C. Infant will be handled as infrequently as possible D. Oral opioid will be administered to decrease seizure risk 55. A newborn is displaying symptoms of neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) and the mother is on Methadone. Which is the most appropriate intervention to plan related to this syndrome? A. Neonatal abstinence scoring system will be used to monitor baby for 1st 24 hours of life B. Lights and noises will be kept to a minimum C. Infant will be handled as infrequently as possible D. Oral opioid will be administered to decrease seizure risk B. Decreasing stimulation will help to decrease irritability. Scoring should be done for 2-3 weeks because of the Methadone. Cuddling the baby helps decrease irritability. Opioid decreases diarrhea not seizures. 56. A client decides to breast feed her Down Syndrome infant. During the feeding, the mother requests help because the infant will not suck. Which action is the most appropriate nursing action? A. B. C. D. Explain the infant's feeding characteristics to the mother Tell the mother it will be easier to bottle feed Take the infant to the nursery to be fed Encourage the mother to keep trying 56. A client decides to breast feed her Down Syndrome infant. During the feeding, the mother requests help because the infant will not suck. Which action is the most appropriate nursing action? A. B. C. D. Explain the infant's feeding characteristics to the mother Tell the mother it will be easier to bottle feed Take the infant to the nursery to be fed Encourage the mother to keep trying A. The infant with Down Syndrome may have underdeveloped muscles and a large fissured tongue. These characteristics may make breast feeding more difficult. Physiological Integrity of Children Developmental Disabilities 57. Parents are having difficulty with the behavior of their hyperkinetic child who is the oldest of four siblings. Both parents express frustration about managing their child's behavior. Which health care goal is initially most important in working with the parents? A. Providing reference books on the hyperkinetic child and related problems B. Helping parents enhance their effectiveness within the limitations of the home environment C. Enlisting their assistance in identifying the child's behavioral problems in school D. Increasing their opportunities to get away from home so they can become more objective 57. Parents are having difficulty with the behavior of their hyperkinetic child who is the oldest of four siblings. Both parents express frustration about managing their child's behavior. Which health care goal is initially most important in working with the parents? A. Providing reference books on the hyperkinetic child and related problems B. Helping parents enhance their effectiveness within the limitations of the home environment C. Enlisting their assistance in identifying the child's behavioral problems in school D. Increasing their opportunities to get away from home so they can become more objective B. Learning to be effective parents involves them in a constructive task that helps them feel better about their parenting skills. 58. Parents of a child with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are discussing medication and parenting strategies with the nurse. Which statement made by the parents would indicate that further teaching is necessary? A. “Providing a regular routine for sleeping, eating, working and playing is very necessary.“ B. “Medication should be given at night so it doesn't decrease the appetite.“ C. “We will reduce distractions and external stimuli to help with concentration.“ D. “We will establish firm but reasonable limits on behavior.” 58. Parents of a child with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are discussing medication and parenting strategies with the nurse. Which statement made by the parents would indicate that further teaching is necessary? A. “Providing a regular routine for sleeping, eating, working and playing is very necessary.“ B. “Medication should be given at night so it doesn't decrease the appetite.“ C. “We will reduce distractions and external stimuli to help with concentration.“ D. “We will establish firm but reasonable limits on behavior.” B. Medications such as methylphenidate (Ritalin), pemoline (Cylert) or other stimulants may keep the child awake and should not be given at bedtime (give 6 hrs prior to HS). 59. The nurse is assessing a child with possible acute otitis media, who is exhibiting a runny nose, fever, cough and irritability. Which finding would the nurse anticipate when performing an otoscopic evaluation? A. A bulging, red tympanic membrane B. Lack of a red reflex in the affected ear C. Reddish turbinates covered with purulent drainage D. Occasional white patches on a reddish pharynx 59. The nurse is assessing a child with possible acute otitis media, who is exhibiting a runny nose, fever, cough and irritability. Which finding would the nurse anticipate when performing an otoscopic evaluation? A. A bulging, red tympanic membrane B. Lack of a red reflex in the affected ear C. Reddish turbinates covered with purulent drainage D. Occasional white patches on a reddish pharynx A. With otitis media, the tympanic membrane of the affected ear, as observed through the otoscope, appears to be bulging and is reddish in color. Physiological Integrity of Children Sensation, Perception, and Protection 60. A child is hit with a snowball in the left eye and complains that something is in the eye. The eye appears irritated with some swelling. The child is tearing and complains of acute pain. In doing an eye examination, the school nurse sees a small piece of wood that seems to be adherent to the cornea. Which action should the nurse take immediately? A. Notify the child's parents to take child to an ophthalmologist B. Instill normal saline drops and cover the eye with a patch C. Instill anesthetic ointment to kill the pain D. Using strict aseptic techniques and a sterile forceps, remove the piece of wood 60. A child is hit with a snowball in the left eye and complains that something is in the eye. The eye appears irritated with some swelling. The child is tearing and complains of acute pain. In doing an eye examination, the school nurse sees a small piece of wood that seems to be adherent to the cornea. Which action should the nurse take immediately? A. B. C. D. Notify the child's parents to take child to an ophthalmologist Instill normal saline drops and cover the eye with a patch Instill anesthetic ointment to kill the pain Using strict aseptic techniques and a sterile forceps, remove the piece of wood A. It is imperative to get the child to the ophthalmologist as soon as possible. No treatment should be undertaken until the doctor sees the child. 61. Acute conjunctivitis is diagnosed in a 3-year-old child with erythematous conjunctiva, swollen eyelids and purulent drainage. Which physician order would be questioned by the RN? A. B. C. D. Ilotycin (erythromycin) ophthalmic ointment Pred G (prednisolone and gentamycin) ophthalmic drops Notify physician if temperature is over 100.4o F (38o C) Instill eye medication after crusts are removed with warm, moist cloth 61. Acute conjunctivitis is diagnosed in a 3-year-old child with erythematous conjunctiva, swollen eyelids and purulent drainage. Which physician order would be questioned by the RN? A. B. C. D. Ilotycin (erythromycin) ophthalmic ointment Pred G (prednisolone and gentamycin) ophthalmic drops Notify physician if temperature is over 100.4o F (38o C) Instill eye medication after crusts are removed with warm, moist cloth B. No steroidal eye drops are used as they can decrease ocular resistance to bacteria. Although ointment may blur the vision, Ilotycin is the better choice. 62. A 5-year-old has just returned from cardiac catheterization. Which assessment would be most important at this time? A. B. C. D. Vital signs Dressing Pedal pulses IV site 62. A 5-year-old has just returned from cardiac catheterization. Which assessment would be most important at this time? A. B. C. D. Vital signs Dressing Pedal pulses IV site C. Pedal pulses will indicate arterial occlusion distal to the incision. The other assessments are also important to identify bleeding or hemorrhage. 63. Which clinical finding is the nurse most likely to assess in the pediatric client with resolution of heart failure? A. Increased mucus due to formula B. Decreased respiratory effort C. Absence of peripheral edema and increase in periorbital edema D. Gallop heart rhythm 63. Which clinical finding is the nurse most likely to assess in the pediatric client with resolution of heart failure? A. Increased mucus due to formula B. Decreased respiratory effort C. Absence of peripheral edema and increase in periorbital edema D. Gallop heart rhythm B. The stem asks for a finding that indicates the heart failure has improved, or resolved. C is only partially correct – there would be no increase in periorbital edema. A and D are incorrect (D is associated with active heart failure). 64. Before administering digoxin (Lanoxin) to a 4-month-old infant, the nurse takes the apical pulse and finds it to be 120 beats per minute. Based on this information, what is the correct nursing action? A. Administer the medication and record both the administration and pulse rate B. Withhold the medication and report this to the charge nurse at the end of the shift C. Withhold the medication and call the physician D. Obtain an EKG and withhold the medication 64. Before administering digoxin (Lanoxin) to a 4-month-old infant, the nurse takes the apical pulse and finds it to be 120 beats per minute. Based on this information, what is the correct nursing action? A. Administer the medication and record both the administration and pulse rate B. Withhold the medication and report this to the charge nurse at the end of the shift C. Withhold the medication and call the physician D. Obtain an EKG and withhold the medication A. A “normal resting” heart rate for children 3 months to 2 years is 70 – 150, so administering the medication is appropriate. 65. When evaluating the nursing interventions and goal attainment for an infant with suspected atrial septal defect (ASD), which finding necessitates further assessment? A. Child is acyanotic at rest without tachypnea and tachycardia B. Child’s O2 saturation is maintained at 92% C. Child’s parents bring a tape recording of their voices for the baby to hear D. Child’s parents handle and touch the baby only briefly to allow for rest 65. When evaluating the nursing interventions and goal attainment for an infant with suspected atrial septal defect (ASD), which finding necessitates further assessment? A. Child is acyanotic at rest without tachypnea and tachycardia B. Child’s O2 saturation is maintained at 92% C. Child’s parents bring a tape recording of their voices for the baby to hear D. Child’s parents handle and touch the baby only briefly to allow for rest D. Parents need to hold, touch, talk to and look at the infant to promote bonding. The prognosis is very good unless Eisenmenger’s syndrome develops. Physiological Integrity of Children Oxygenation (Cardiovascular) Health 66. What nursing information most accurately describes the cardiac defect of VSD? A. B. C. D. Hole in the heart between the right and left atria Hole in the membrane between the right and left ventricle Narrowing of the large aorta artery just above the heart Short tube that connects the aorta to the pulmonary artery 66. What nursing information most accurately describes the cardiac defect of VSD? A. B. C. D. Hole in the heart between the right and left atria Hole in the membrane between the right and left ventricle Narrowing of the large aorta artery just above the heart Short tube that connects the aorta to the pulmonary artery B. This is the definition of VSD. Physiological Integrity of Children Oxygenation (Cardiovascular) Health 67. At a routine pediatrician’s visit, a 4-week-old baby is found to have a murmur, and on further investigation, bounding pulses and a widened pulse pressure are discovered. What can the nurse expect to be done for this child? A. Coils will be placed in the patient ductus during cardiac catheterization B. Child will be watched for a year to see if the cardiac defect resolves C. Child will be scheduled for open heart surgery to repair the atrial defect D. A prostaglandin inhibitor indomethacin (Indocin) will be administered 67. At a routine pediatrician’s visit, a 4-week-old baby is found to have a murmur, and on further investigation, bounding pulses and a widened pulse pressure are discovered. What can the nurse expect to be done for this child? A. Coils will be placed in the patient ductus during cardiac catheterization B. Child will be watched for a year to see if the cardiac defect resolves C. Child will be scheduled for open heart surgery to repair the atrial defect D. A prostaglandin inhibitor indomethacin (Indocin) will be administered A. These symptoms are indicative of a patent ductus arteriosus. At this age, indomethacin will not be effective, but the child is likely to be treated with insertion of coils to occlude the opening. Physiological Integrity of Children Oxygenation (Cardiovascular) Health 68. Identify the assessment that would lead the nurse to conclude that an infant has coarctation of the aorta. A. Loud machinery murmur at the left sternal boarder B. Growth retardation and lack of energy C. Stronger upper extremity compared to lower extremity pulses D. Widened pulse pressure and increased pulse rate 68. Identify the assessment that would lead the nurse to conclude that an infant has coarctation of the aorta. A. Loud machinery murmur at the left sternal boarder B. Growth retardation and lack of energy C. Stronger upper extremity compared to lower extremity pulses D. Widened pulse pressure and increased pulse rate C. The stricture in the aorta causes an increased blood supply to the upper part of the body while reducing the supply to the lower part of the body. Physiological Integrity of Children Oxygenation (Cardiovascular) Health 69. A child with tetralogy of Fallot starts crying, screaming and visibly shaking when a laboratory technician attempts to draw blood. The child becomes cyanotic and the respiratory rate increases to 40 breaths per minute. Choose the priority action of the nurse. A. B. C. D. Ask the physician for a sedative for the child Explain to the child the importance of the blood tests Place the child in a knee-to-chest position Auscultate for an irregular heartbeat 69. A child with tetralogy of Fallot starts crying, screaming and visibly shaking when a laboratory technician attempts to draw blood. The child becomes cyanotic and the respiratory rate increases to 40 breaths per minute. Choose the priority action of the nurse. A. B. C. D. Ask the physician for a sedative for the child Explain to the child the importance of the blood tests Place the child in a knee-to-chest position Auscultate for an irregular heartbeat C. Flexing the legs reduces venous flow back to the heart, decreasing the volume of blood moving through the areas of defect. Physiological Integrity of Children Oxygenation (Cardiovascular) Health Tetralogy of Fallot 70. How would the nurse best respond to a request by a parent to describe the Blalock-Taussig procedure for tetralogy of Fallot? A. Ask the physician to give an explanation the next time rounds are made B. It is a surgical procedure to increase the blood flow to the brain C. The subclavian artery is connected to the pulmonary artery D. Blood is diverted to the other side of the heart using a prosthetic material 70. How would the nurse best respond to a request by a parent to describe the Blalock-Taussig procedure for tetralogy of Fallot? A. Ask the physician to give an explanation the next time rounds are made B. It is a surgical procedure to increase the blood flow to the brain C. The subclavian artery is connected to the pulmonary artery D. Blood is diverted to the other side of the heart using a prosthetic material C. This procedure is used palliatively for tetralogy of Fallot to increase oxygen levels in the blood by circulating more blood through the lungs. 71. After corrective surgery for tetralogy of Fallot, the nurse monitors the child for decreased cardiac output. Select the findings that would indicate low cardiac output. A. Altered level of consciousness, warm extremities, and pallor B. Bounding pulses and mottled skin on extremities C. Altered level of consciousness, thready pulse, and cool extremities D. Capillary refill two seconds and blood pressure 90/60 mm Hg 71. After corrective surgery for tetralogy of Fallot, the nurse monitors the child for decreased cardiac output. Select the findings that would indicate low cardiac output. A. Altered level of consciousness, warm extremities, and pallor B. Bounding pulses and mottled skin on extremities C. Altered level of consciousness, thready pulse, and cool extremities D. Capillary refill two seconds and blood pressure 90/60 mm Hg C. Clinical signs of low cardiac output are pale, cool extremities, weak thready pulses, delayed capillary refill and altered consciousness. 72. A newborn has been diagnosed with transposition of the great vessels. What will the parents be told about this condition? A. There is very little that can be done for this child at this time B. The mortality rate following surgery is very high for all children C. The child will have surgery to repair the circulation in a week D. There will be a high risk of heart failure later in life 72. A newborn has been diagnosed with transposition of the great vessels. What will the parents be told about this condition? A. There is very little that can be done for this child at this time B. The mortality rate following surgery is very high for all children C. The child will have surgery to repair the circulation in a week D. There will be a high risk of heart failure later in life C. The surgical procedure to repair circulation has a mortality rate of about 5-10% and is done early in life. Physiological Integrity of Children Oxygenation (Cardiovascular) Health 73. Which assessment finding is unexpected in a child with probable Kawasaki Disease? A. B. C. D. Temperature 102.0o F (38.89o C) Conjunctivitis without exudates Crackles bilaterally lower lobes Desquamation of hands and feet 73. Which assessment finding is unexpected in a child with probable Kawasaki Disease? A. B. C. D. Temperature 102.0o F (38.89o C) Conjunctivitis without exudates Crackles bilaterally lower lobes Desquamation of hands and feet C. Lung involvement is not a common characteristic of Kawasaki Disease. 74. Primary prevention of rheumatic fever includes which measure? A. Teaching parents to complete 10-14 day antibiotic therapy for strep throat B. Teaching the parents the symptoms of rheumatic fever C. Encouraging rest when the child has an upper respiratory infection D. Encouraging the child to stay in bed 74. Primary prevention of rheumatic fever includes which measure? A. Teaching parents to complete 10-14 day antibiotic therapy for strep throat B. Teaching the parents the symptoms of rheumatic fever C. Encouraging rest when the child has an upper respiratory infection D. Encouraging the child to stay in bed A. After a positive culture for hemolytic streptococci, the child is placed on antibiotics for 10 to 14 days. The full course of medication is very important. 75. If an infant with prolonged bleeding after circumcision has hemophilia, which blood test will be abnormal? A. B. C. D. Bleeding time Platelet count Clot retraction time Partial thromboplastin time 75. If an infant with prolonged bleeding after circumcision has hemophilia, which blood test will be abnormal? A. B. C. D. Bleeding time Platelet count Clot retraction time Partial thromboplastin time D. Partial thromboplastin time measures the activity of thromboplastin which is dependent on intrinsic clotting factors (like factor VIII). Bleeding time, platelet count and clot retraction tests measure platelet function and will be normal in someone with hemophilia. 76. An 8-year-old child with hemophilia A is admitted to a unit with a severe bleeding episode. What is most important in planning care with the child? A. Explore the emotional aspects of this disease with the child and the parents B. Make sure the parents and child understand home management of this disease C. Help the child keep up with school work D. Institute measures to control the bleeding episode 76. An 8-year-old child with hemophilia A is admitted to a unit with a severe bleeding episode. What is most important in planning care with the child? A. Explore the emotional aspects of this disease with the child and the parents B. Make sure the parents and child understand home management of this disease C. Help the child keep up with school work D. Institute measures to control the bleeding episode D. The most immediate concern is control of bleeding, which must be stopped before moving to other aspects of managing hemophilia. 77. When making rounds, the nurse discovers a client with a nosebleed. Which intervention is appropriate? A. Position the client with the head back and apply an ice bag directly to the nose B. Have the client lean forward and apply direct pressure to the nose C. Position the client in the Fowler’s position and place packing in the nose D. Have the client pinch the nares together and spit out any blood in the mouth 77. When making rounds, the nurse discovers a client with a nosebleed. Which intervention is appropriate? A. Position the client with the head back and apply an ice bag directly to the nose B. Have the client lean forward and apply direct pressure to the nose C. Position the client in the Fowler’s position and place packing in the nose D. Have the client pinch the nares together and spit out any blood in the mouth B. This is the appropriate first aid treatment for nosebleeds. Keeping the head downward will prevent swallowing or aspiration of blood. 78. In considering care planning for the sickle cell crisis client, what would the nurse anticipate in addition to pain relief measures? A. B. C. D. Antispasmodics and ambulation TID Cold packs to affected area and oxygen Gene therapy and Factor VIII replacement Hydration and electrolyte replacement 78. In considering care planning for the sickle cell crisis client, what would the nurse anticipate in addition to pain relief measures? A. B. C. D. Antispasmodics and ambulation TID Cold packs to affected area and oxygen Gene therapy and Factor VIII replacement Hydration and electrolyte replacement D. Bedrest is important to minimize use of oxygen and energy expenditure. Cold packs promote sickling and vasoconstriction. Electrolyte replacement is important to combat metabolic acidosis (from hypoxia) which promotes more sickling. 79. What should be stressed to help parents decrease the risk of vaso-occlusive crises in a child with sickle cell disease? A. B. C. D. Frequent hand washing Diet high in iron-rich foods Avoid use of mothballs in the home Limit or closely monitor milk intake 79. What should be stressed to help parents decrease the risk of vaso-occlusive crises in a child with sickle cell disease? A. B. C. D. Frequent hand washing Diet high in iron-rich foods Avoid use of mothballs in the home Limit or closely monitor milk intake A. Crises are often associated with infection, dehydration, acidosis, or exposure to cold. Many infections, especially respiratory, are largely spread by fomites, through hand-tonose or eye contact. 80. What is the highest priority for a child with sickle cell disease admitted with vaso-occlusive crisis? A. B. C. D. Pain control and hydration Psychological and emotional support Genetic counseling and bedrest Transfusion of packed red blood cells and Factor VIII 80. What is the highest priority for a child with sickle cell disease admitted with vaso-occlusive crisis? A. B. C. D. Pain control and hydration Psychological and emotional support Genetic counseling and bedrest Transfusion of packed red blood cells and Factor VIII A. Hydration is absolutely necessary to prevent clumping of blood cells and pain is a stressor that needs to be eliminated. These are physiological measures and have higher priority than emotional measures. 81. What would the nurse include when educating parents of a child with leukemia about the cause of the anemia? A. B. C. D. Inadequate iron intake, which is common in children Decreased red blood cell production by bone marrow Increased destruction of red blood cells by lymphocytes Progressive replacement of bone marrow with inefficient blood producing cells 81. What would the nurse include when educating parents of a child with leukemia about the cause of the anemia? A. B. C. D. Inadequate iron intake, which is common in children Decreased red blood cell production by bone marrow Increased destruction of red blood cells by lymphocytes Progressive replacement of bone marrow with inefficient blood producing cells B. Bone marrow overproduces white blood cells at the expense of producing red blood cells and platelets. 82. What information does the nurse give a 10-year-old client and parents prior to a bone morrow aspiration? A. Will be put to sleep and not feel anything B. Will need to stay in bed for 24 hours after the procedure C. Will feel a sharp, stabbing pain at the site for the first 24 hours D. Will feel pressure at the site during the procedure 82. What information does the nurse give a 10-year-old client and parents prior to a bone morrow aspiration? A. Will be put to sleep and not feel anything B. Will need to stay in bed for 24 hours after the procedure C. Will feel a sharp, stabbing pain at the site for the first 24 hours D. Will feel pressure at the site during the procedure D. It is important for the client to know what type of pain to expect. 83. When caring for a child with leukemia, the RN notes blood on the pillowcase and the child’s pajamas. Which parameter of the child’s laboratory report would the nurse check? A. B. C. D. Platelet count Uric acid level Prothrombin time Red blood cell count 83. When caring for a child with leukemia, the RN notes blood on the pillowcase and the child’s pajamas. Which parameter of the child’s laboratory report would the nurse check? A. B. C. D. Platelet count Uric acid level Prothrombin time Red blood cell count A. Leukemia causes decreased platelet count. Uric acid level affects urinary output, not blood clotting. Prothrombin time is influenced by vitamin K factors, not platelets. RBC would not explain the cause for bleeding. 84. After a prolonged course of mercaptopurine (Purinethol) and methotrexate (Amethopterin), an 8-year-old child has an absolute neutrophil count of 400. What would be the primary nursing action? A. B. C. D. Initiate droplet infection control precautions Consult with physician Increase fluid intake Restrict staff and visitors 84. After a prolonged course of mercaptopurine (Purinethol) and methotrexate (Amethopterin), an 8-year-old child has an absolute neutrophil count of 400. What would be the primary nursing action? A. B. C. D. Initiate droplet infection control precautions Consult with physician Increase fluid intake Restrict staff and visitors D. The child will be placed in protective isolation and staff and visitors with signs and symptoms of active infection will not be allowed in the child’s room. 85. At the time of discharge, the sibling of a 7-year-old with leukemia develops chicken pox. What information does the nurse give to the family in planning discharge? A. Chicken pox can be fatal to clients with leukemia B. Clients receiving prednisone are immune to chicken pox C. Immunization prior to discharge will protect the child from acquiring the disease D. Discharge is planned if the client avoids contact with the sibling with chicken pox 85. At the time of discharge, the sibling of a 7-year-old with leukemia develops chicken pox. What information does the nurse give to the family in planning discharge? A. Chicken pox can be fatal to clients with leukemia B. Clients receiving prednisone are immune to chicken pox C. Immunization prior to discharge will protect the child from acquiring the disease D. Discharge is planned if the client avoids contact with the sibling with chicken pox A. The virus cannot be combated by the child with leukemia and might be fatal. 86. Which nursing care measure would the nurse identify as a teaching priority for the child newly diagnosed with leukemia and the family? A. B. C. D. Comfort measures Nutritional supplements Injury prevention Anticipatory grieving 86. Which nursing care measure would the nurse identify as a teaching priority for the child newly diagnosed with leukemia and the family? A. B. C. D. Comfort measures Nutritional supplements Injury prevention Anticipatory grieving D. The family will be overwhelmed by the diagnosis. Other diagnoses are pertinent but would not be priority with the new diagnosis. 87. A child with leukemia is being discharged from the hospital on several antineoplastic medications after intrathecal administration of methotrexate. What must discharge instructions to the parents include? A. Limit contact with friends B. Schedule routine laboratory testing to evaluate response to medication C. Withhold medication when nausea occurs D. Prepare the child for occasional blood transfusions 87. A child with leukemia is being discharged from the hospital on several antineoplastic medications after intrathecal administration of methotrexate. What must discharge instructions to the parents include? A. Limit contact with friends B. Schedule routine laboratory testing to evaluate response to medication C. Withhold medication when nausea occurs D. Prepare the child for occasional blood transfusions B. If WBC drops dramatically, therapy may be stopped temporarily. Prolonged therapy contraindicates isolation from peers, nausea is common and not a cause for medication discontinuation, and blood transfusions are not expected. 88. How can the nurse best help a 6-year-old client diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia cope with the fear of dying? A. Avoid discussions related to the illness B. Distract the child by playing games and watching television C. Refer the child’s questions to the physician or to the parents D. Answer the questions in an open and honest manner 88. How can the nurse best help a 6-year-old client diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia cope with the fear of dying? A. Avoid discussions related to the illness B. Distract the child by playing games and watching television C. Refer the child’s questions to the physician or to the parents D. Answer the questions in an open and honest manner D. This helps the client deal directly and realistically with the problem. A and B ignore the problem and C shifts responsibility. 89. Which child should be evaluated first? A. A 20-month-old with bronchiiolitis who has crackles bilaterally and has been in 23% oxygen all night B. A 6-month-old who has a croupy cough and some inspiratory stridor with activity C. A 4-year-old with bronchial asthma who required PRN respiratory treatment of albuterol (Ventolin) for wheezes two hours ago D. A 3-year-old with cystic fibrosis with right lower lobe pneumonia, crackles bilaterally, and in 21% oxygen 89. Which child should be evaluated first? A. A 20-month-old with bronchiiolitis who has crackles bilaterally and has been in 23% oxygen all night B. A 6-month-old who has a croupy cough and some inspiratory stridor with activity C. A 4-year-old with bronchial asthma who required PRN respiratory treatment of albuterol (Ventolin) for wheezes two hours ago D. A 3-year-old with cystic fibrosis with right lower lobe pneumonia, crackles bilaterally, and in 21% oxygen C. This client’s respiratory status is the most unstable and needs to be re-evaluated first since the child required a PRN respiratory treatment 2 hours ago. 90. A 2-week-old infant is admitted with symptoms of respiratory distress related to upper respiratory infection. Which nursing diagnosis has the highest priority? A. B. C. D. Activity intolerance related to fatigue Ineffective airway clearance related to secretions Ineffective breathing pattern related to respiratory distress Risk for altered parenting related to hospitalization 90. A 2-week-old infant is admitted with symptoms of respiratory distress related to upper respiratory infection. Which nursing diagnosis has the highest priority? A. B. C. D. Activity intolerance related to fatigue Ineffective airway clearance related to secretions Ineffective breathing pattern related to respiratory distress Risk for altered parenting related to hospitalization B. Airway clearance comes before breathing. 91. A couple who has recently lost a child to sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) suddenly joins the SIDS Foundation. Which explanation shows the best understanding regarding their action? A. B. C. D. The desire to obtain answers regarding why SIDS occurred Using the organization to obtain education regarding SIDS Providing information that will prevent SIDS in others Seeking the support of others who have experienced SIDS 91. A couple who has recently lost a child to sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) suddenly joins the SIDS Foundation. Which explanation shows the best understanding regarding their action? A. B. C. D. The desire to obtain answers regarding why SIDS occurred Using the organization to obtain education regarding SIDS Providing information that will prevent SIDS in others Seeking the support of others who have experienced SIDS D. Losing a child, particularly when death is unexplainable, e.g. SIDS, requires a lot of emotional support. Only another person who has experienced the same phenomenon can truly understand and give the needed support. 92. Which child has signs and symptoms most suggestive of bronchiolitis? A. A 2-month-old with a respiratory rate of 68, heart rate of 175, and expiratory wheeze B. A 12-month-old with a respiratory rate of 50, heart rate of 140, and mild expiratory stridor C. A 6-month-old with a respiratory rate of 70, heart rate of 180, and a prolonged inspiratory phase D. An 8-month-old with a respiratory rate of 50, heart rate of 140, and inspiratory wheeze 92. Which child has signs and symptoms most suggestive of bronchiolitis? A. A 2-month-old with a respiratory rate of 68, heart rate of 175, and expiratory wheeze B. A 12-month-old with a respiratory rate of 50, heart rate of 140, and mild expiratory stridor C. A 6-month-old with a respiratory rate of 70, heart rate of 180, and a prolonged inspiratory phase D. An 8-month-old with a respiratory rate of 50, heart rate of 140, and inspiratory wheeze A. Bronchiolitis results in a narrowing of the bronchial passages on expiration which results in expiratory wheezes. Tachycardia and respiratory rate greater than 50 per minute are common with bronchiolitis. 93. A hospitalized infant with acute bronchiolitis is NPO and receiving IV fluids. Which statement explains the rationale for eliminating feedings? A. “The baby doesn’t need as many calories right now.” B. “There is an increased risk of fluid overload.” C. “Feeding would be too much of an effort for the baby right now.” D. “The baby’s digestive system is sluggish because of the infection.” 93. A hospitalized infant with acute bronchiolitis is NPO and receiving IV fluids. Which statement explains the rationale for eliminating feedings? A. “The baby doesn’t need as many calories right now.” B. “There is an increased risk of fluid overload.” C. “Feeding would be too much of an effort for the baby right now.” D. “The baby’s digestive system is sluggish because of the infection.” C. Oral feeding during the acute phase of the illness will increase hypoxemia and the effort expended during feeding may result in tachypnea, weakness and fatigue. Caloric needs will increase because of accelerated metabolism, over hydrating is not the reason why the child is NPO, and there is no reason why peristalsis should decrease. 94. A 2 ½ -year-old child with acute asthma is short of breath, has a pulse of 100 and a respiratory rate of 54. What blood gas values will the nurse expect to find? A. B. C. D. pH of 7.32 PO2 of 95 mm Hg HCO3 of 26 mEq/L PCO2 of 40 mm Hg 94. A 2 ½ -year-old child with acute asthma is short of breath, has a pulse of 100 and a respiratory rate of 54. What blood gas values will the nurse expect to find? A. B. C. D. pH of 7.32 PO2 of 95 mm Hg HCO3 of 26 mEq/L PCO2 of 40 mm Hg A. Hypoxia causes hypercapnia which leads to a decreased pH (normal 7.35-7.45). B is within normal range (80-100), C is within normal range (21-28), and D is within normal range (35-45). 95. A 7-year-old child is brought to the clinic with an acute asthma attack. The parent states the child has had an upper respiratory infection with a frequent dry cough for several days. What is the priority nursing action? A. B. C. D. Obtain a complete history from the parent Obtain STAT arterial blood gases Determine what medications the child takes regularly Auscultate lung bases for air movement 95. A 7-year-old child is brought to the clinic with an acute asthma attack. The parent states the child has had an upper respiratory infection with a frequent dry cough for several days. What is the priority nursing action? A. B. C. D. Obtain a complete history from the parent Obtain STAT arterial blood gases Determine what medications the child takes regularly Auscultate lung bases for air movement D. Since an acute asthma attack results in airway obstruction, the nurse needs to ascultate the lungs to evaluate the severity of the obstruction and degree of airflow compromise. 96. Which suggestion by the nurse would be most appropriate when discussing with parents measures to prevent their child's asthma attacks? A. Maintain a high humidity (>70%) environment inside the house B. Encourage the child to sleep with the window open at night C. Use an antimold agent in cleaning showers and tile areas D. Spray an aerosol disinfectant in the child's bedroom 96. Which suggestion by the nurse would be most appropriate when discussing with parents measures to prevent their child's asthma attacks? A. Maintain a high humidity (>70%) environment inside the house B. Encourage the child to sleep with the window open at night C. Use an antimold agent in cleaning showers and tile areas D. Spray an aerosol disinfectant in the child's bedroom C. Exposure to mold, aerosolized chemicals, and substances inhaled through an open window can all be triggers for asthma attacks. Also, it's best to maintain a low humidity environment (under 50%) to discourage house dust mites. 97. A 10-year-old client with asthma suddenly stops breathing. What is the priority nursing action? A. B. C. D. Call 911 Initiate rescue breathing with 2 breaths Begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation Check for a carotid pulse 97. A 10-year-old client with asthma suddenly stops breathing. What is the priority nursing action? A. B. C. D. Call 911 Initiate rescue breathing with 2 breaths Begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation Check for a carotid pulse B. The nurse should initiate rescue breathing with 2 breaths and continue at a rate of 12 breaths per minute. 98. An 8-year-old child is receiving both intravenous aminophylline (Aminophyllin) and hydrocortisone (Solu-Medrol). During the morning assessment, the child vomits breakfast and is very irritable. Assessment reveals a heart rate of 116 beats per minute, but other vital signs are within normal ranges. Breath sounds are equal with a faint expiratory wheeze. What should be the priority nursing action? A. Re-evaluate vital signs and irritability again in 30 minutes and document results B. Notify the physician immediately as these are signs of theophylline toxicity C. Call the physician to increase the aminophylline dose since wheezes are still present D. Continue with the prescribed dosages as these are normal side effects of the medication 98. An 8-year-old child is receiving both intravenous aminophylline (Aminophyllin) and hydrocortisone (Solu-Medrol). During the morning assessment, the child vomits breakfast and is very irritable. Assessment reveals a heart rate of 116 beats per minute, but other vital signs are within normal ranges. Breath sounds are equal with a faint expiratory wheeze. What should be the priority nursing action? A. Re-evaluate vital signs and irritability again in 30 minutes and document results B. Notify the physician immediately as these are signs of theophylline toxicity C. Call the physician to increase the aminophylline dose since wheezes are still present D. Continue with the prescribed dosages as these are normal side effects of the medication B. Vomiting, irritability and elevated heart rate are signs of theophylline toxicity. 99. What is the first action the nurse should take when a child is admitted with status asthmaticus? A. B. C. D. Monitor vital signs every two to four hours Place upright in a sitting position Administer large amounts of IV fluids for hydration Perform chest physiotherapy and postural drainage 99. What is the first action the nurse should take when a child is admitted with status asthmaticus? A. B. C. D. Monitor vital signs every two to four hours Place upright in a sitting position Administer large amounts of IV fluids for hydration Perform chest physiotherapy and postural drainage B. This position will make breathing easier and help increase oxygenation. 100. Which diagnosis suggests that a nurse may obtain inaccurate readings from a pulse oximeter that is attached to the finger of a 5-year-old with croup? A. B. C. D. Activity intolerance Decreased tissue perfusion Fluid volume excess Ineffective airway clearance 100. Which diagnosis suggests that a nurse may obtain inaccurate readings from a pulse oximeter that is attached to the finger of a 5-year-old with croup? A. B. C. D. Activity intolerance Decreased tissue perfusion Fluid volume excess Ineffective airway clearance B. Poor tissue perfusion will decrease circulation to the finger and interfere with accurate readings. Ineffective airway clearance would make the pulse oximetry readings low, but they would be accurate. 101. What intervention is most important when providing care to a 4-year-old child with croup? A. Monitor respiratory function to maintain a patent airway B. Force non-caffeinated fluids to liquefy pulmonary secretions C. Maintain a semi-Fowler’s position to decrease chest pain D. Increase oxygen supply to prevent subcutaneous skin breakdown 101. What intervention is most important when providing care to a 4-year-old child with croup? A. Monitor respiratory function to maintain a patent airway B. Force non-caffeinated fluids to liquefy pulmonary secretions C. Maintain a semi-Fowler’s position to decrease chest pain D. Increase oxygen supply to prevent subcutaneous skin breakdown A. Maintaining an airway is the most important of the respiratory interventions listed. 102. The client with which symptoms needs the most immediate attention? A. Barking cough, oxygen saturation of 93 in room air, and occasional inspiratory stridor B. Tympanic temperature of 102.2o F (39o C), green nasal drainage, and pulling at the ears C. Harsh paroxysmal cough, audible expiratory wheeze and mild retractions D. Sore throat, tongue slightly protruding, drooling, expiratory stridor and tachypnea 102. The client with which symptoms needs the most immediate attention? A. Barking cough, oxygen saturation of 93 in room air, and occasional inspiratory stridor B. Tympanic temperature of 102.2o F (39o C), green nasal drainage, and pulling at the ears C. Harsh paroxysmal cough, audible expiratory wheeze and mild retractions D. Sore throat, tongue slightly protruding, drooling, expiratory stridor and tachypnea D. The assessment data suggest this child is experiencing acute epiglottitis which can result in acute respiratory distress secondary to airway obstruction. 103. A 5-year-old child is found to have a cough, fever, and chest pain following an upper respiratory infection. A chest X-ray indicates pneumonia is likely. What will the nurse expect to happen next? A. B. C. D. An IV with intense antibiotic therapy Supportive care with oxygen and cool mist Antipyretics and IV fluid administration Sputum culture to determine causative organism 103. A 5-year-old child is found to have a cough, fever, and chest pain following an upper respiratory infection. A chest X-ray indicates pneumonia is likely. What will the nurse expect to happen next? A. B. C. D. An IV with intense antibiotic therapy Supportive care with oxygen and cool mist Antipyretics and IV fluid administration Sputum culture to determine causative organism D. While all of the listed treatments may be done, the first thing is to determine whether the pneumonia is viral or bacterial so appropriate treatment can be started. 104. An adolescent has had a “cold” for a week and suddenly develops a high fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. The diagnosis is staphylococcal pneumonia. What is the complication likely to occur with this diagnosis? A. B. C. D. Empyema Otitis media Appendicitis Tonsillitis 104. An adolescent has had a “cold” for a week and suddenly develops a high fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. The diagnosis is staphylococcal pneumonia. What is the complication likely to occur with this diagnosis? A. B. C. D. Empyema Otitis media Appendicitis Tonsillitis A. This type of pneumonia is likely to cause empyema if not treated early and aggressively. Otitis media is more common in young children with other types of bacteria. 105. A 4-year-old child is admitted with a diagnosis of bronchopneumonia. Select the most appropriate expected client outcome related to the priority nursing diagnosis, “Ineffective Breathing Pattern, related to infection.” A. B. C. D. Able to tolerate food without gagging Have no symptoms of chills or coughing Able to engage in normal activities for age Exhibit no symptoms of respiratory distress 105. A 4-year-old child is admitted with a diagnosis of bronchopneumonia. Select the most appropriate expected client outcome related to the priority nursing diagnosis, “Ineffective Breathing Pattern, related to infection.” A. B. C. D. Able to tolerate food without gagging Have no symptoms of chills or coughing Able to engage in normal activities for age Exhibit no symptoms of respiratory distress D. Others may be pertinent but do not relate directly to the diagnosis. 106. The initial assessment of a 5-year-old child returning to the unit from a tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy was T-98.2o F (36.8o C), P-80, R-20, and B/P-100/60, pain rating of a 4 and some hesitancy in swallowing. Six hours later, the assessment is T98.6o F (37o C), P-100, R-18, and B/P-90/50, pain rating of 7, and frequent swallowing noted. What should be the nurse’s priority action? A. Evaluate the operative site for increased postop bleeding B. Medicate child with Tylenol with Codeine Elixir for pain C. Re-evaluate vital signs and pain rating again in 15 minutes D. Notify the physician immediately of the changes in assessment 106. The initial assessment of a 5-year-old child returning to the unit from a tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy was T-98.2o F (36.8o C), P-80, R-20, and B/P-100/60, pain rating of a 4 and some hesitancy in swallowing. Six hours later, the assessment is T98.6o F (37o C), P-100, R-18, and B/P-90/50, pain rating of 7, and frequent swallowing noted. What should be the nurse’s priority action? A. Evaluate the operative site for increased postop bleeding B. Medicate child with Tylenol with Codeine Elixir for pain C. Re-evaluate vital signs and pain rating again in 15 minutes D. Notify the physician immediately of the changes in assessment A. Frequent swallowing following a tonsillectomy/adenoidectomy is a sign of increased postop bleeding. This child went from hesitancy in swallowing to frequent swallowing which warrants further assessment of the operative site for increased bleeding. 107. An 8-year-old child has just had a tonsillectomy. The client is awake, restless, and frequently swallowing and clearing the throat. Which nursing action is most appropriate? A. Carefully insert a tongue depressor to directly observe the throat for bleeding B. Give an analgesic to promote comfort and allay restlessness C. Encourage oral intake of cool fluids such as water, crushed ice, or popsicle D. Instruct child to lie on stomach, and offer reassurance to calm child 107. An 8-year-old child has just had a tonsillectomy. The client is awake, restless, and frequently swallowing and clearing the throat. Which nursing action is most appropriate? A. Carefully insert a tongue depressor to directly observe the throat for bleeding B. Give an analgesic to promote comfort and allay restlessness C. Encourage oral intake of cool fluids such as water, crushed ice, or popsicle D. Instruct child to lie on stomach, and offer reassurance to calm child A. This child is manifesting signs of postoperative hemorrhage, and direct observation of the throat can determine the extent of bleeding 108. Of the problems listed, which makes the nurse suspect an infant has cystic fibrosis? A. B. C. D. Pneumonia Imperforate anus Meconium ileus Feeding intolerance 108. Of the problems listed, which makes the nurse suspect an infant has cystic fibrosis? A. B. C. D. Pneumonia Imperforate anus Meconium ileus Feeding intolerance C. Thick meconium blocks the lumen of the intestine and may be one of the first signs of cystic fibrosis. 109. Which rationale is the primary reason the RN includes “Decreased risk of infection exposure” in the plan of care for a child with cystic fibrosis? A. Repeated infections increase damage to the respiratory tract B. Pulmonary therapy is less effective during acute infections C. Immunocompromise caused by decreased pancreatic function increases the child’s risk of secondary infection D. Usual childhood immunizations are contraindicated in a child with cystic fibrosis 109. Which rationale is the primary reason the RN includes “Decreased risk of infection exposure” in the plan of care for a child with cystic fibrosis? A. Repeated infections increase damage to the respiratory tract B. Pulmonary therapy is less effective during acute infections C. Immunocompromise caused by decreased pancreatic function increases the child’s risk of secondary infection D. Usual childhood immunizations are contraindicated in a child with cystic fibrosis A. Pulmonary therapy is effective during infections, immunocompromise is not caused by decreased pancreatic function, and immunizations are not contraindicated in children with cystic fibrosis. 110. What factor would the nurse emphasize in discussing the administration of exogenous pancreatic enzymes with the parent of a child who has cystic fibrosis? A. B. C. D. The enzymes should be taken between meals The enzymes should be taken only at bedtime The enzymes should be taken after each loose stool The enzymes should be taken with meals and snacks 110. What factor would the nurse emphasize in discussing the administration of exogenous pancreatic enzymes with the parent of a child who has cystic fibrosis? A. B. C. D. The enzymes should be taken between meals The enzymes should be taken only at bedtime The enzymes should be taken after each loose stool The enzymes should be taken with meals and snacks D. Pancreatic enzymes should be taken every time the child eats. 111. Which meal is appropriate for an 8-year-old with cystic fibrosis? A. B. C. D. Peanut butter and jelly sandwich Hamburger and milk shake Spaghetti and meatballs Egg salad sandwich and milk 111. Which meal is appropriate for an 8-year-old with cystic fibrosis? A. B. C. D. Peanut butter and jelly sandwich Hamburger and milk shake Spaghetti and meatballs Egg salad sandwich and milk C. Fat should be reduced, however, the client should receive increased amounts of calories and protein. Peanut butter sandwich is appropriate for this age but contains too much fat. The milk and milk products are mucus-producing foods. 112. The nurse administers digestive replacement enzymes for the client with cystic fibrosis. What change indicates the enzyme is effective? A. B. C. D. Increased mucus excretion in stools Decreased fat excretion in stools Increased expectoration of mucus Weight loss 112. The nurse administers digestive replacement enzymes for the client with cystic fibrosis. What change indicates the enzyme is effective? A. B. C. D. Increased mucus excretion in stools Decreased fat excretion in stools Increased expectoration of mucus Weight loss B. This indicates the enzymes are aiding in digestion of fats and protein. 113. Parents should be taught to avoid exposing their child with cystic fibrosis to which situation to minimize the risk of complications? A. B. C. D. A dog that is shedding hair A kitten born 3 days ago A neighborhood child who has the flu A relative who has hepatitis B 113. Parents should be taught to avoid exposing their child with cystic fibrosis to which situation to minimize the risk of complications? A. B. C. D. A dog that is shedding hair A kitten born 3 days ago A neighborhood child who has the flu A relative who has hepatitis B C. Children with cystic fibrosis are very susceptible to respiratory infections. Parents should be taught to guard against exposing the child to infections to the greatest extent possible. 114. A priority for an infant born with cleft lip and palate is to receive adequate nutrition. Which intervention would need to be rewritten before the plan of care was implemented? A. B. C. D. Encourage breastfeeding if the mother chooses Use a soft bottle that can be squeezed if bottle feeding Place baby prone after feeding to help prevent aspiration If infant refuses bottle, spoon feed with rice cerealthickened formula 114. A priority for an infant born with cleft lip and palate is to receive adequate nutrition. Which intervention would need to be rewritten before the plan of care was implemented? A. B. C. D. Encourage breastfeeding if the mother chooses Use a soft bottle that can be squeezed if bottle feeding Place baby prone after feeding to help prevent aspiration If infant refuses bottle, spoon feed with rice cerealthickened formula C. Babies should not be placed on the abdomen but supine or side-lying with few exceptions. This includes babies with cleft lip and palate prior to surgery. Physiological Integrity of Children Nutritional and Metabolic Health Cleft lip and Palate Physiological Integrity of Children Nutritional and Metabolic Health Cleft lip and Palate Physiological Integrity of Children Nutritional and Metabolic Health Pre-operative Care 115. After surgery, the child with a cleft palate repair is placed on the abdomen. Why is this position the best choice? A. B. C. D. Protects the suture line Enhances cleansing procedures Facilitates drainage of secretions Decreases the infant's tendency to suck 115. After surgery, the child with a cleft palate repair is placed on the abdomen. Why is this position the best choice? A. B. C. D. Protects the suture line Enhances cleansing procedures Facilitates drainage of secretions Decreases the infant's tendency to suck C. Postoperative positioning of the infant on the abdomen is helpful in the immediate postoperative period to facilitate drainage of secretions 116. After surgery for a cleft lip repair, an infant is having difficulty breathing. Which nursing action would be most helpful in bringing relief? A. B. C. D. Raise the baby’s head Turn the baby onto the abdomen Administer oxygen per mask Exert downward pressure on the infant’s chin 116. After surgery for a cleft lip repair, an infant is having difficulty breathing. Which nursing action would be most helpful in bringing relief? A. B. C. D. Raise the baby’s head Turn the baby onto the abdomen Administer oxygen per mask Exert downward pressure on the infant’s chin D. After cleft lip repair, the infant must become accustomed to nasal breathing. If the infant is having difficulty breathing, the first thing that should be done is open the mouth. Abdominal positioning and raising the baby’s head may aggravate the breathing problem and abdominal positioning may damage the suture line. Oxygen is not necessary if opening the mouth is successful and a mask might damage the suture line. 117. An infant, born with a cleft lip and palate, is ready for discharge. Which behavior would indicate the parents are ready for the infant's homecoming? A. B. C. D. Parents appear angry about the infant's condition During infant feedings, the parents talk to the infant Mother asks the nurse to feed the infant Father refuses to touch the infant 117. An infant, born with a cleft lip and palate, is ready for discharge. Which behavior would indicate the parents are ready for the infant's homecoming? A. B. C. D. Parents appear angry about the infant's condition During infant feedings, the parents talk to the infant Mother asks the nurse to feed the infant Father refuses to touch the infant B. Talking to and stroking the infant are signs of attachment and readiness to care for the infant 118. Which physician order for a child with gastroesophageal reflux would the RN question? A. B. C. D. Small, frequent, thickened formula feedings Tagamet (cimetidine) PO Reglan (megoclopramide) PO Position supine after feedings 118. Which physician order for a child with gastroesophageal reflux would the RN question? A. B. C. D. Small, frequent, thickened formula feedings Tagamet (cimetidine) PO Reglan (megoclopramide) PO Position supine after feedings D. The child should be placed in an upright position after feedings, not flat. 119. A child with lactose intolerance is placed on a lactose-free diet and the parents are being taught about this condition. Which parent statement indicates understanding of the condition? A. “If my child has severe constipation, I will notify the physician.” B. “I should notice symptoms within 30 minutes to a few hours after eating.” C. “One common, hidden source of lactose is gluten.” D. “If my child drinks soy milk, that will contain plenty of calcium and Vitamin D.” 119. A child with lactose intolerance is placed on a lactose-free diet and the parents are being taught about this condition. Which parent statement indicates understanding of the condition? A. “If my child has severe constipation, I will notify the physician.” B. “I should notice symptoms within 30 minutes to a few hours after eating.” C. “One common, hidden source of lactose is gluten.” D. “If my child drinks soy milk, that will contain plenty of calcium and Vitamin D.” B. Constipation is not a common symptom. Soy milk contains ½ the calcium of milk and may not be fortified with Vitamin D. 120. A child with celiac disease is recovering from an appendectomy and is ready to eat regular food. Which food should be removed from the menu? A. B. C. D. Chicken rice soup Fresh fruit cup Hamburger patty Crackers 120. A child with celiac disease is recovering from an appendectomy and is ready to eat regular food. Which food should be removed from the menu? A. B. C. D. Chicken rice soup Fresh fruit cup Hamburger patty Crackers D. The diet for children with celiac disease is gluten-free and crackers contain gluten; the other listed foods do not. 121. What clinical assessment is most likely to be seen in an infant with pyloric stenosis? A. Visible peristaltic waves that move right to left in lower abdomen B. Rebound tenderness C. Palpable mass in the epigastrium to the right of the umbilicus D. Tenderness over epigastric area not relieved by heat application 121. What clinical assessment is most likely to be seen in an infant with pyloric stenosis? A. Visible peristaltic waves that move right to left in lower abdomen B. Rebound tenderness C. Palpable mass in the epigastrium to the right of the umbilicus D. Tenderness over epigastric area not relieved by heat application C. Typical sign due to the obstruction caused by pyloric stenosis. The waves typically move from left to right in the upper abdomen. 122. Identify the most classic sign of pyloric stenosis in a 6-weekold infant. A. B. C. D. Projectile vomiting after feeding Prolonged crying after feeding Persistent watery fecal discharge Painful episodes with constipation 122. Identify the most classic sign of pyloric stenosis in a 6-weekold infant. A. B. C. D. Projectile vomiting after feeding Prolonged crying after feeding Persistent watery fecal discharge Painful episodes with constipation A. Pyloric stenosis causes an obstruction at the gastric outlet. Any food which has been consumed cannot proceed into the small intestine and is usually forcefully ejected from the stomach. 123. An infant was returned to the unit about 4 hours ago after surgery to correct pyloric stenosis. Select the most important nursing intervention. A. Feed small amounts frequently and assess emesis B. Keep the infant NPO and encourage parent to perform oral care C. Monitor intake and output and administer medications D. Monitor hydration status and encourage parent to rest 123. An infant was returned to the unit about 4 hours ago after surgery to correct pyloric stenosis. Select the most important nursing intervention. A. Feed small amounts frequently and assess emesis B. Keep the infant NPO and encourage parent to perform oral care C. Monitor intake and output and administer medications D. Monitor hydration status and encourage parent to rest A. Small frequent feedings are resumed at 4-6 hours postoperatively. C and D are not as important as A. Physiological Integrity of Children Nutritional and Metabolic Health 124. An hour after admission to the nursery, the nurse observes the infant’s respirations to be 70 breaths/minute along with excessive drooling. Which action should the nurse take first? A. Continue to observe the infant closely for other symptoms B. Reposition to side-lying position and call the physician C. Suction the infant’s mouth and place in supine position with HOB elevated D. Provide supplemental oxygen when the respirations exceed 70 breaths/minute 124. An hour after admission to the nursery, the nurse observes the infant’s respirations to be 70 breaths/minute along with excessive drooling. Which action should the nurse take first? A. Continue to observe the infant closely for other symptoms B. Reposition to side-lying position and call the physician C. Suction the infant’s mouth and place in supine position with HOB elevated D. Provide supplemental oxygen when the respirations exceed 70 breaths/minute C. The data support the possibility of a tracheoesophageal fistula and placing the infant in this position decreases the risk of aspiration. With the excessive drooling, suctioning would be necessary to maintain the airway. 125. What is the reason for positioning an infant with tracheoesophageal fistula supine with head and shoulders elevated prior to surgery? A. Reduce respiratory and cardiac workload B. Alleviate pressure of distended abdominal contents on the diaphragm C. Increase pooling of secretions in bottom of upper esophageal pouch D. Reduce gastric distention by allowing air bubbles from the fistula to escape 125. What is the reason for positioning an infant with tracheoesophageal fistula supine with head and shoulders elevated prior to surgery? A. Reduce respiratory and cardiac workload B. Alleviate pressure of distended abdominal contents on the diaphragm C. Increase pooling of secretions in bottom of upper esophageal pouch D. Reduce gastric distention by allowing air bubbles from the fistula to escape C. Gravity encourages the flow of secretions with pooling in the bottom of the upper pouch where more effective removal of secretions can be accomplished by placing a catheter in this pool. Abdominal distention is a very late manifestation of TEF and there is no increased respiratory or cardiac workload caused by TEF. Physiological Integrity of Children Nutritional and Metabolic Health 126. The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with a suspected intussusception. Which test should the nurse anticipate being ordered for this client? A. B. C. D. MRI of the abdomen Water-soluble contrast enema Upper GI series Colonoscopy 126. The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with a suspected intussusception. Which test should the nurse anticipate being ordered for this client? A. B. C. D. MRI of the abdomen Water-soluble contrast enema Upper GI series Colonoscopy B. First, an abdominal X-ray to detect intraperitoneal air from a bowel perforation is obtained. If the X-ray is negative, water-soluble contrast and air pressure may be used to attempt to reduce the intussusception. Physiological Integrity of Children Nutritional and Metabolic Health 127. Which statement by a parent would be pertinent to a diagnosis of Hirschsprung’s disease? A. B. C. D. “He is constipated often.” “He sometimes gets colds.” “He sometimes spits up.” “He has a rectal temperature of 99.6o F (37.6o C).” 127. Which statement by a parent would be pertinent to a diagnosis of Hirschsprung’s disease? A. B. C. D. “He is constipated often.” “He sometimes gets colds.” “He sometimes spits up.” “He has a rectal temperature of 99.6o F (37.6o C).” A. Chronic constipation is the most consistent symptom. 128. A 4-year-old who has a colostomy due to Hirschsprung’s disease is admitted because of poor weight gain. While teaching the parents about proper diet, which food should the nurse recommend be avoided? A. B. C. D. Ripe bananas Spaghetti Cheese Apples 128. A 4-year-old who has a colostomy due to Hirschsprung’s disease is admitted because of poor weight gain. While teaching the parents about proper diet, which food should the nurse recommend be avoided? A. B. C. D. Ripe bananas Spaghetti Cheese Apples D. Colostomy clients should be on a low-residue, low-fiber diet. Raw apples contain a lot of fiber and residue. Physiological Integrity of Children Nutritional and Metabolic Health 129. Which assessment information would provide the nurse with the most accurate indication of the impact of fluid loss in an infant with gastroenteritis and diarrhea? A. B. C. D. Weight change from pre-illness to current Moistness of oral mucous membranes Hematocrit level Skin turgor 129. Which assessment information would provide the nurse with the most accurate indication of the impact of fluid loss in an infant with gastroenteritis and diarrhea? A. B. C. D. Weight change from pre-illness to current Moistness of oral mucous membranes Hematocrit level Skin turgor A. Infants are more vulnerable to fluid and electrolyte imbalances than older children or adults. Depending on the severity of the dehydration, the infant can experience a weight loss of up to 15%. 130. Select the most accurate expected client outcome related to the diagnosis of “Fluid Volume Deficit related to fluid loss caused by severe diarrhea”. A. B. C. D. Has normal bowel movements Does not have diarrhea stools for four hours Tolerates intravenous fluids well Exhibits moist mucous membranes 130. Select the most accurate expected client outcome related to the diagnosis of “Fluid Volume Deficit related to fluid loss caused by severe diarrhea”. A. B. C. D. Has normal bowel movements Does not have diarrhea stools for four hours Tolerates intravenous fluids well Exhibits moist mucous membranes D. It is the only answer that specifically focuses on the diagnosis. All other answer choices are good signs, but not specific enough. Physiological Integrity of Children Nutritional and Metabolic Health Physiological Integrity of Children Nutritional and Metabolic Health 131. A 6-year-old child is admitted with RLQ pain, nausea and vomiting for six hours. Which positive assessment is most indicative of appendicitis? A. B. C. D. Sunset sign Trousseau’s sign Ladin’s sign Rovsing’s sign 131. A 6-year-old child is admitted with RLQ pain, nausea and vomiting for six hours. Which positive assessment is most indicative of appendicitis? A. B. C. D. Sunset sign Trousseau’s sign Ladin’s sign Rovsing’s sign D. Rovsing’s is rebound tenderness, abdominal pain particular to appendicitis. Sunset indicates hydrocephalus, Trousseau’s indicates hypocalcemia, and Ladin’s is a sign of pregnancy. 132. A 13-year-old is admitted with the diagnosis of appendicitis and complains of “feeling funny” all over. Which sign or symptom would be related to something other than the sympathetic effects caused by the acute abdominal pain? A. B. C. D. Chills Tachycardia Dilated pupils Rapid breathing 132. A 13-year-old is admitted with the diagnosis of appendicitis and complains of “feeling funny” all over. Which sign or symptom would be related to something other than the sympathetic effects caused by the acute abdominal pain? A. B. C. D. Chills Tachycardia Dilated pupils Rapid breathing A. Chills are a normal physiologic response to infection and not a response of the sympathetic nervous system to pain. All other choices are sympathetic responses to pain. 133. A 9-year-old child is admitted with a tentative diagnosis of appendicitis. Which laboratory test result is most indicative that the condition is worsening? A. B. C. D. Negative C-reactive protein Hemoglobin 14.2 g/100 mL of blood Increasing erythrocyte sedimentation rate White blood cell count of 19,500/cu mm of blood 133. A 9-year-old child is admitted with a tentative diagnosis of appendicitis. Which laboratory test result is most indicative that the condition is worsening? A. B. C. D. Negative C-reactive protein Hemoglobin 14.2 g/100 mL of blood Increasing erythrocyte sedimentation rate White blood cell count of 19,500/cu mm of blood C. The sedimentation rate is another non-specific test for inflammatory disease; situation states it has been taken earlier and is now increasing; (the client is worse). 134. Which assessment would the RN do first when a child returns to the unit after an emergency appendectomy? A. B. C. D. Bladder Intravenous fluid infusion site Nasogastric tube function Dressing 134. Which assessment would the RN do first when a child returns to the unit after an emergency appendectomy? A. B. C. D. Bladder Intravenous fluid infusion site Nasogastric tube function Dressing D. Initial assessment should focus on the surgical site, then the nurse would check the IV site and determine if the child needs to urinate. There is seldom an NG tube unless there is a ruptured appendix. 135. Which symptoms would be unexpected in a client with pinworms? A. B. C. D. Rebound tenderness No symptoms Diarrhea Perianal pruritis 135. Which symptoms would be unexpected in a client with pinworms? A. B. C. D. Rebound tenderness No symptoms Diarrhea Perianal pruritis A. Rebound tenderness is associated with appendicitis, not pinworms. 136. A child is seen in the clinic with symptoms of intestinal parasite infestation. Which symptom would alert the RN that the infestation was by ascaris lumbricoides (roundworms)? A. B. C. D. Thread-like worms noted at anus Large 10-14 inch worms noted in diaper Large pale mucous stools Few symptoms except eosinophilia 136. A child is seen in the clinic with symptoms of intestinal parasite infestation. Which symptom would alert the RN that the infestation was by ascaris lumbricoides (roundworms)? A. B. C. D. Thread-like worms noted at anus Large 10-14 inch worms noted in diaper Large pale mucous stools Few symptoms except eosinophilia B. Ascaris is the largest of the intestinal helminthes, can lead to bowel perforation, obstructive jaundice, and pneumonia. Most frequently seen in children 1-4 years old and is treated with chewable Vermox (mebendazole). 137. A school-age child is seen in clinic for nocturnal enuresis. Tests for UTI and diabetes were negative. If the parent responds with punitive measures, which nursing diagnosis would be anticipated? A. B. C. D. Body Image Disturbance Ineffective Family Coping Self-esteem Disturbance Noncompliance 137. A school-age child is seen in clinic for nocturnal enuresis. Tests for UTI and diabetes were negative. If the parent responds with punitive measures, which nursing diagnosis would be anticipated? A. B. C. D. Body Image Disturbance Ineffective Family Coping Self-esteem Disturbance Noncompliance C. Self-esteem often is disturbed if parental response is harsh or punitive. 138. Which hospital roommate assignment would be most appropriate for a 3-year-old girl with nephrotic syndrome? A. B. C. D. 2-year-old girl with croup 3-year-old girl with impetigo 4-year-old boy with tonsillitis 4-year-old boy with a fractured femur 138. Which hospital roommate assignment would be most appropriate for a 3-year-old girl with nephrotic syndrome? A. B. C. D. 2-year-old girl with croup 3-year-old girl with impetigo 4-year-old boy with tonsillitis 4-year-old boy with a fractured femur D. First, the roommate must not be contagious then the developmental level is assessed. 139. A child with nephrotic syndrome is taking prednisone. What would the nurse tell the parents about the expected effects of the medication? A. B. C. D. Decreases blood pressure Decreases protein in the urine Increases sodium reabsorption Increases epithelial immunity 139. A child with nephrotic syndrome is taking prednisone. What would the nurse tell the parents about the expected effects of the medication? A. B. C. D. Decreases blood pressure Decreases protein in the urine Increases sodium reabsorption Increases epithelial immunity B. The purpose of taking prednisone is to decrease the excretion of protein from the kidney. 140. One of the nursing diagnoses included by the nurse in a care plan for a child with nephrotic syndrome is "Fluid volume excess." Choose the most appropriate intervention for this diagnosis. A. Observing strict bedrest B. Testing urine specific gravity every shift C. Monitoring hourly intake and output D. Weighing the child before breakfast 140. One of the nursing diagnoses included by the nurse in a care plan for a child with nephrotic syndrome is "Fluid volume excess." Choose the most appropriate intervention for this diagnosis. A. Observing strict bedrest B. Testing urine specific gravity every shift C. Monitoring hourly intake and output D. Weighing the child before breakfast D. Weight changes are important indicators of fluid status, especially in children. Hourly I and O is not necessary. Urine protein levels are more significant for nephrotic syndrome than specific gravity. 141. The nurse provides discharge teaching to the parents of a 4year-old with nephrotic syndrome. Which statement by a parent indicates the nurse’s teaching has been effective? A. “We will notify the physician if the protein increases in the urine.” B. “Our child can learn to check his/her own urine.” C. “We realize that cloudy urine will show a false positive.” D. “We will collect a clean catch specimen for analysis.” 141. The nurse provides discharge teaching to the parents of a 4year-old with nephrotic syndrome. Which statement by a parent indicates the nurse’s teaching has been effective? A. “We will notify the physician if the protein increases in the urine.” B. “Our child can learn to check his/her own urine.” C. “We realize that cloudy urine will show a false positive.” D. “We will collect a clean catch specimen for analysis.” A. This is an early sign of re-occurring nephrosis. Urine should be checked daily for protein with a dipstick. 142. When assessing a 4-year-old child with glomerulonephritis, which physical finding should be expected? A. B. C. D. Decreased joint mobility White lines on the nails Periorbital edema Hypotension 142. When assessing a 4-year-old child with glomerulonephritis, which physical finding should be expected? A. B. C. D. Decreased joint mobility White lines on the nails Periorbital edema Hypotension C. Excessive water accumulation and sodium retention lead to edema. A does not occur with nephritis and B and D occur more commonly in nephrotic syndrome. 143. A 14-year-old client with chronic glomerulonephritis is displaying signs of renal failure.The client is being taught to monitor daily fluid status. Which finding would probably be the first indication the client is retaining fluid? A. B. C. D. Decreased urine output Sudden weight gain Severe ankle edema Periorbital edema 143. A 14-year-old client with chronic glomerulonephritis is displaying signs of renal failure.The client is being taught to monitor daily fluid status. Which finding would probably be the first indication the client is retaining fluid? A. B. C. D. Decreased urine output Sudden weight gain Severe ankle edema Periorbital edema B. When clients are dealing with this disease in the home setting, they should be taught by the nurse to weigh themselves daily and to notify the doctor if an increase exceeds 2 lbs/day 144. Which nursing intervention has the highest priority in caring for a client with acute glomerulonephritis? A. B. C. D. Assess for dysuria Monitor blood pressure Monitor temperature Assess for jaundice 144. Which nursing intervention has the highest priority in caring for a client with acute glomerulonephritis? A. B. C. D. Assess for dysuria Monitor blood pressure Monitor temperature Assess for jaundice B. Increased blood pressure is a serious problem associated with this disorder. 145. A child with glomerulonephritis is placed on a low sodium diet. The parent has been taught the rationale for the diet and foods that can be included on the diet. The parent's selection of which food for a snack would indicate a clear understanding of the diet restrictions? A. B. C. D. Potato chips Ginger ale Plain popcorn Graham crackers 145. A child with glomerulonephritis is placed on a low sodium diet. The parent has been taught the rationale for the diet and foods that can be included on the diet. The parent's selection of which food for a snack would indicate a clear understanding of the diet restrictions? A. B. C. D. Potato chips Ginger ale Plain popcorn Graham crackers C. Unsalted, plain popcorn is commonly suggested as a snack for children on low sodium diets. 146. A 3-year-old child presents with an abdominal mass. A diagnosis of Wilms tumor is made. From knowledge of this tumor, which aspect of care does the nurse know must be enforced by the family and all who care for the child? A. B. C. D. Strict bed rest Forcing fluids Minimal handling of the abdomen Vigorous bathing in preparation for surgery 146. A 3-year-old child presents with an abdominal mass. A diagnosis of Wilms tumor is made. From knowledge of this tumor, which aspect of care does the nurse know must be enforced by the family and all who care for the child? A. B. C. D. Strict bed rest Forcing fluids Minimal handling of the abdomen Vigorous bathing in preparation for surgery C. In Wilms tumor it is important to avoid excessive handling of the abdomen to prevent rupture of the tumor capsule and possible spread of the tumor 147. The goal of care for a 6-year-old child with vesicoureteral reflux is to comply with preventive measures. Which is appropriate to make the goal measurable? A. B. C. D. Child will be encouraged to void every 2-3 hours Child will maintain appropriate hygiene Medications will be taken as ordered Child will have adequate fluid intake 147. The goal of care for a 6-year-old child with vesicoureteral reflux is to comply with preventive measures. Which is appropriate to make the goal measurable? A. B. C. D. Child will be encouraged to void every 2-3 hours Child will maintain appropriate hygiene Medications will be taken as ordered Child will have adequate fluid intake A. This is the most specific and most easily measurable. 148. The physician and parents have agreed to correct the congenital clubfoot using conservative treatment rather than surgery. Which intervention would be inappropriate? A. Teach warning signs to report (pain, edema, decreased capillary refill) B. Prepare for serial casting every few days for several weeks C. Teach parents to check capillary refill following cast application D. Reinforce that total treatment time is approximately 4-5 months 148. The physician and parents have agreed to correct the congenital clubfoot using conservative treatment rather than surgery. Which intervention would be inappropriate? A. Teach warning signs to report (pain, edema, decreased capillary refill) B. Prepare for serial casting every few days for several weeks C. Teach parents to check capillary refill following cast application D. Reinforce that total treatment time is approximately 4-5 months D. If not aligned by 8-12 weeks by X-ray evaluation, surgery would likely be indicated. Physiological Integrity of Children Mobility (Musculoskeletal) Health Physiological Integrity of Children Mobility (Musculoskeletal) Health 149. The nurse detects a positive Ortolani’s sign in a newborn. What is the nurse assessing? A. B. C. D. Broadening of the perineum Shortening of one leg Audible click on hip manipulation Unilateral droop of the hip 149. The nurse detects a positive Ortolani’s sign in a newborn. What is the nurse assessing? A. B. C. D. Broadening of the perineum Shortening of one leg Audible click on hip manipulation Unilateral droop of the hip C. This is the definition of Ortolani’s sign where there is an audible click and indicates hip dysplasia. Physiological Integrity of Children Mobility (Musculoskeletal) Health Physiological Integrity of Children Mobility (Musculoskeletal) Health 150. An assessment on a 2-day-old infant finds the presence of asymmetrical buttock folds. What does this indicate? A. B. C. D. Normal in a neonate Suspicious for fracture Breech delivery Developmental hip dysplasia 150. An assessment on a 2-day-old infant finds the presence of asymmetrical buttock folds. What does this indicate? A. B. C. D. Normal in a neonate Suspicious for fracture Breech delivery Developmental hip dysplasia D. This is a clinical sign of developmental dysplasia of the hip and includes unequal gluteal folds, restricted abduction and positive Ortolani’s sign. Physiological Integrity of Children Mobility (Musculoskeletal) Health Congenital Hip 151. A nurse would anticipate the presence of which finding in assessing a 2-month-old infant with developmental dysplasia of the hip? A. Ortolani's sign B. Positive Barlow's test C. Limited hip abduction D. Positive Trendelenburg sign 151. A nurse would anticipate the presence of which finding in assessing a 2-month-old infant with developmental dysplasia of the hip? A. Ortolani's sign B. Positive Barlow's test C. Limited hip abduction D. Positive Trendelenburg sign C. Ortolani's sign and a positive Barlow's test are seen in the newborn period of life. A positive Trendelenburg sign is seen in the weight-bearing or walking child. Physiological Integrity of Children Mobility (Musculoskeletal) Health Pavlik Harness 152. Which nursing action would be the most important for the successful treatment of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in an 11-year-old child? A. B. C. D. Diversional activities based on interests Maintenance of the client's intravenous infusion site Adequate preparation for surgery when fever subsides Relief of the severe pain that accompanies this disease 152. Which nursing action would be the most important for the successful treatment of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in an 11-year-old child? A. B. C. D. Diversional activities based on interests Maintenance of the client's intravenous infusion site Adequate preparation for surgery when fever subsides Relief of the severe pain that accompanies this disease B. Vigorous intravenous antibiotic therapy to ensure high blood levels is paramount to reduce the infection and prevent amputation. 153. When parents of a preschooler, diagnosed with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, ask for information about the disease progression, what should the nurse tell them? A. The disease will go into permanent remission in most children B. Many children have long remissions, but have severe deformities C. The disease typically progresses gradually and will become crippling as the child reaches adulthood D. Most children recover completely within a few years of diagnosis and treatment 153. When parents of a preschooler, diagnosed with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, ask for information about the disease progression, what should the nurse tell them? A. The disease will go into permanent remission in most children B. Many children have long remissions, but have severe deformities C. The disease typically progresses gradually and will become crippling as the child reaches adulthood D. Most children recover completely within a few years of diagnosis and treatment A. A majority of children achieve remission by adolescence. 154. Which statement by the parent of a child with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis indicates teaching by the nurse has been successful? A. “By putting cool compresses on the joints that hurt, I can help relieve my child's pain.“ B. “If my child performs vigorous weight-bearing exercises four times a day, that will help.“ C. “It's important to be sure my child sleeps on a soft mattress, to facilitate rest.“ D. “The use of moist heat on the painful joints will help ease my child's discomfort.“ 154. Which statement by the parent of a child with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis indicates teaching by the nurse has been successful? A. “By putting cool compresses on the joints that hurt, I can help relieve my child's pain.“ B. “If my child performs vigorous weight-bearing exercises four times a day, that will help.“ C. “It's important to be sure my child sleeps on a soft mattress, to facilitate rest.“ D. “The use of moist heat on the painful joints will help ease my child's discomfort.“ D. Moist heat on affected joints will increase circulation, resulting in decreased pain and facilitation of joint movement. Physiological Integrity of Children Mobility (Musculoskeletal) Health 155. When caring for a client with a compound fracture, the nurse is most concerned about the client’s increased risk for which occurrence? A. B. C. D. Immobility Infection Arthritis Callus formation 155. When caring for a client with a compound fracture, the nurse is most concerned about the client’s increased risk for which occurrence? A. B. C. D. Immobility Infection Arthritis Callus formation B. With a compound fracture, the skin (the body’s first line of defense) has been broken. This increases the client’s risk for infection. Physiological Integrity of Children Mobility (Musculoskeletal) Health 156. Two days following a long bone fracture, the client complains of sudden onset of difficulty breathing. Select the nurse’s priority, from a list of physician orders. A. B. C. D. Obtain arterial blood gases Obtain a chest X-ray Initiate an IV of 0.45% normal saline Administer oxygen 156. Two days following a long bone fracture, the client complains of sudden onset of difficulty breathing. Select the nurse’s priority, from a list of physician orders. A. B. C. D. Obtain arterial blood gases Obtain a chest X-ray Initiate an IV of 0.45% normal saline Administer oxygen D. Oxygen should be initiated immediately to treat hypoxia and the client’s “difficulty breathing.” It is possible that the client has a fat embolism and will need appropriate treatment. 157. The RN is evaluating a 3-year-old client’s outcomes related to 90 degree-90 degree skeletal traction. Which chart entry would alert the RN to the need to adjust the plan of care? A. B. C. D. Child actively resists pin care Weights are hanging freely Child uses trapeze independently Skin clear with no signs of redness or ecchymosis 157. The RN is evaluating a 3-year-old client’s outcomes related to 90 degree-90 degree skeletal traction. Which chart entry would alert the RN to the need to adjust the plan of care? A. B. C. D. Child actively resists pin care Weights are hanging freely Child uses trapeze independently Skin clear with no signs of redness or ecchymosis A. It is important that pin care be done as prescribed to prevent infection. Covering the pin sites may help decrease the child’s distress. 158. The nursing assistant is assigned to care for a client in Buck’s traction for a fractured hip. Which statement by the nursing assistant would indicate the RN needs to further clarify the instructions? A. B. C. D. “I need to monitor the client’s intake and output.” “I will remove the traction during meal times.” “I will encourage the client to cough and deep breathe.” “If the client has a productive cough, I need to note the color of the sputum.” 158. The nursing assistant is assigned to care for a client in Buck’s traction for a fractured hip. Which statement by the nursing assistant would indicate the RN needs to further clarify the instructions? A. B. C. D. “I need to monitor the client’s intake and output.” “I will remove the traction during meal times.” “I will encourage the client to cough and deep breathe.” “If the client has a productive cough, I need to note the color of the sputum.” B. Buck’s traction reduces muscle spasms and should remain on at all times. Traction should never be removed without a physician’s order. 159. The hips of a child in Bryant’s traction should be maintained in which position? A. B. C. D. 45o 60o 90o 180o 159. The hips of a child in Bryant’s traction should be maintained in which position? A. B. C. D. 45o 60o 90o 180o C. This is the proper alignment needed for proper healing. 160. The nurse is caring for a client in Crutchfield tongs for the treatment of a cervical vertebral fracture. Which independent nursing intervention would be effective in preventing constipation? A. Elevation of the head of the bed to 45 degrees during bedpan use B. Encouraging selections of bulk-building foods into the diet C. Administering a laxative for bowel stimulation D. Ambulating the client to increase peristalsis 160. The nurse is caring for a client in Crutchfield tongs for the treatment of a cervical vertebral fracture. Which independent nursing intervention would be effective in preventing constipation? A. Elevation of the head of the bed to 45 degrees during bedpan use B. Encouraging selections of bulk-building foods into the diet C. Administering a laxative for bowel stimulation D. Ambulating the client to increase peristalsis B. The nurse could independently provide dietary instructions as listed. A laxative could not be given without a physician’s order. Movement of the client in tongs is minimal without a halo vest, and requires physician order. Crutchfield Tongs Halo Traction 161. When providing care for a postoperative client who has had an open reduction of a fractured femur, the nurse observes a small amount of bloody drainage on the cast. What action should be taken by the nurse? A. B. C. D. Split the cast to minimize circulatory complications Circle the area of drainage and note the time Elevate the leg higher and apply an ice bag Report the drainage immediately to the physician 161. When providing care for a postoperative client who has had an open reduction of a fractured femur, the nurse observes a small amount of bloody drainage on the cast. What action should be taken by the nurse? A. B. C. D. Split the cast to minimize circulatory complications Circle the area of drainage and note the time Elevate the leg higher and apply an ice bag Report the drainage immediately to the physician B. Since the bloody drainage is described as a “small amount,” this would not be unusual for a “fresh” postoperative client. Continued observation for extension of the drainage beyond the circle would be most logical at this time. 162. What nursing intervention is appropriate for the care of a client with pruritus from a cast on the leg? A. B. C. D. Insert long slender object under the cast interface Direct cool air from hair dryer down the cast Pour water into the cast to cool the skin Attach toothbrush to wire hanger to stimulate skin under the cast 162. What nursing intervention is appropriate for the care of a client with pruritus from a cast on the leg? A. B. C. D. Insert long slender object under the cast interface Direct cool air from hair dryer down the cast Pour water into the cast to cool the skin Attach toothbrush to wire hanger to stimulate skin under the cast B. Cool air promotes drying and relieves itching. Scratching with a foreign object can cause infection. 163. The nurse is providing care for a client who has a casted left leg. Which observation would the nurse report to the physician immediately? A. B. C. D. Client complaints of pain in the left leg Edema of the left foot with inability to wear shoe Loss of appetite with constipation Client inability to feel toes of left foot 163. The nurse is providing care for a client who has a casted left leg. Which observation would the nurse report to the physician immediately? A. B. C. D. Client complaints of pain in the left leg Edema of the left foot with inability to wear shoe Loss of appetite with constipation Client inability to feel toes of left foot D. This could indicate insufficient perfusion to the left foot and, if left unreported and untreated (e.g. bivalving of plaster cast), might lead to necrosis of tissue and loss of part or all of the limb. 164. Choose the most appropriate roommate for a 16-year-old client who is in a full body cast. A. B. C. D. 12-year-old with an inguinal hernia repair 9-year-old with gastroenteritis 6-year-old with a fractured femur 15-year-old with pneumonia 164. Choose the most appropriate roommate for a 16-year-old client who is in a full body cast. A. B. C. D. 12-year-old with an inguinal hernia repair 9-year-old with gastroenteritis 6-year-old with a fractured femur 15-year-old with pneumonia A. Although this child is not the closest in age to the client in a full body cast, it is the closest choice without an active disease process present. 165. Which is likely to be associated with the most common type of scoliosis? A. B. C. D. Male client with 25% lateral curvature Client presents with severe pain Severity decreases with growth Develops after 10 years of age 165. Which is likely to be associated with the most common type of scoliosis? A. B. C. D. Male client with 25% lateral curvature Client presents with severe pain Severity decreases with growth Develops after 10 years of age D. Idiopathic scoliosis usually has onset after 10 years old through skeletal maturity. It is mostly in females, pain is not usually severe and severity does not usually increases with age if untreated. Physiological Integrity of Children Mobility (Musculoskeletal) Health Scoliosis Physiological Integrity of Children Mobility (Musculoskeletal) Health