Slides - LWW Journals
advertisement

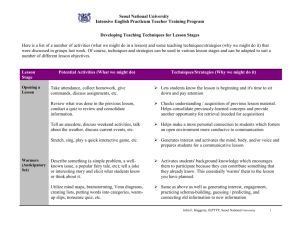
Supplemental PowerPoint Slides Reoperation Rate After Surgery for Lumbar Herniated Intervertebral Disc Disease: Nation-wide Cohort Study. Chi Heon Kim, MD, PhD1,2,3, Chun Kee Chung, MD, PhD1,2,3, Choon Seon Park, PhD4, Boram Choi, PhD4, Min Jung Kim, MS5, Byung Joo Park, MD, MPH, PhD5,6 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Hospital and Seoul National University College of Medicine; 2Neuroscience Research Institute, Seoul National University Medical Research Center; 3Clinical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea, 4Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service, 5 Medical Research Collaborating Center, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 6Department of Preventive Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine Copyright © 2012 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized commercial reproduction of this slide is prohibited Supplemental PowerPoint Slides Reoperation Rate After Surgery for Lumbar Herniated Intervertebral Disc Disease: Nation-wide Cohort Study Objective To provide a longitudinal reoperation rate after surgery for herniated intervertebral disc disease (HIVD) To compare the reoperation rate between surgical methods. Copyright © 2012 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized commercial reproduction of this slide is prohibited Supplemental PowerPoint Slides A retrospective, population-based, cohort study using Korean national health insurance data was performed and 18,590 patients were followed for at least 5 years. Reoperation was performed for 2,578 patients and more than half of the reoperations were performed within 1 year postoperatively Copyright © 2012 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized commercial reproduction of this slide is prohibited Supplemental PowerPoint Slides The primary end-point was any type of second lumbar surgery. After adjusting for confounding factors, five surgical methods (fusion, laminectomy, open discectomy, endoscopic discectomy, and nucleolysis [including mechanical nucleus decompression]) were compared. The reoperation rate at 3 months was higher for laminectomy. Rates for the other surgical methods were similar to that of open discectomy, during the entire follow-up period. Copyright © 2012 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized commercial reproduction of this slide is prohibited

![[Slogan] Proposal for Seoul Brand Idea Contest](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006838769_1-d7653e11f28783f70bcf6bf0f4022941-300x300.png)