Lecture Hand
advertisement

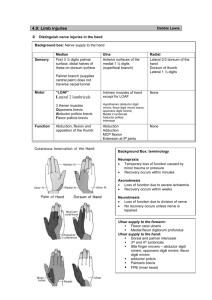
HAND Deep Fascia -Flexor retinaculum -Palmar aponeurosis -Palmaris brevis m. -fibrous digital sheaths -synovial sheaths; ulnar bursa (common flx. bursa) radial bursa (bursa of FPL) Vinculum: provide blood supply to tendons Potential spaces: can become infected (grow/widen w/infection…) Pulp space infection (felon) Flexor tendon infection Cat bite infection with ascending lymphangitis Depuyen’s contracture: contracture of flexor retinaculum. During this surgery – what is at risk? If injured what would occur? Where are they from, where do they go? Thenar mm.: Abductor thenar, Flexor thenar, opponens pollicis. Innervated by median n. Hypothenar mm.: Abductor digiti minimi, Flexor digiti minimi, Opponens digiti minimi. Lumbrical mm.: 4 of them. On digits 2 &3, innervated by median nerve. Remember: 2LOAF: 2 lumbricals and O,A,F of thenar grp. Innervated by median n. Thumb movements: Flex & Extend Abduct & Adduct Superficial Palmar Arch Arteries of the Hand Deep Palmar Arch and Dorsum Veins Ulnar Nerve Median Nerve Radial Nerve Tunnel of Guyon Bones, I can’t do this with my left hand! What nerve is injured? What muscles produce this posture? Cord levels? Dermatomes levels/nerves? Klumpke Palsy Klumpke palsy may produce several abnormal postures. Classically, it produces flexion and supination of the elbow, extension of the wrist, hyperextension of the metacarpophalangeal joints, and flexion of the interphalangeal joints with the “claw hand” posture. This presentation is rarely seen in the newborn period. Klumpke syndrome usually manifests in the newborn period as weakness restricted to or mainly involving the hand. In many occasions, there are no reflex or spontaneous movements of the intrinsic hand muscles.