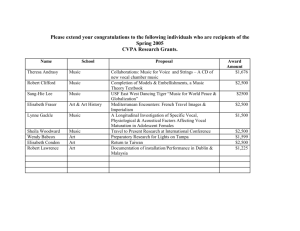
lecture 14
Laryngeal Pathology
Vocal Hyperfunction
• Misuse of laryngeal muscles
• Excessive adductory force
• Often results in laryngitis (inflammation of folds)
• Etiology:
– Excessive contraction of the lateral cricoarytenoid &
Arytenoid muscles
– Laryngeal tension from contraction of thryoarytenoid & cricothyroid
• Results in: Nodules, laryngitis, contact ulcers & vocal fatigue
Vocal Hyperfunction: Therapy
• Behavioral changes
• Vocal Hygiene
• Voice improvement through specific treatment approaches
– Easy onset speech
– Oral resonance
– Laryngeal massage
Vocal Fold Paralysis
• Loss of voluntary motor function, whereas paresis refers to weakness
• Forms or damage:
– Damage to either upper or lower motor neurons
– One side of recurrent nerve damage= unilateral
– Bilateral lower motor neuron damage= bilateral
• Adductor paralysis= Muscles of adduction paralyzed
• Abductor Paralysis= Muscles of abduction paralyzed
Vocal Fold Paralysis
• Etiology:
– Damage to nerve during thyroid surgery
– Blunt trauma (MVA)
– Cerebral vascular accident (CVA: Hemorrhage or other conditions causing loss of blood to brain)
– Aneurysm (ballooning of blood vessel)compresses laryngeal nerve causing paresis or paralysis
Vocal Fold Nodules
• Aggregates of tissue arising from abuse
– Abuses= screaming, shouting, cheerleading
– Abuse causes permanent change in vocal fold tissue
• Vocal hyperfunction- Laryngitis- Hardening of tissue- Nodule formation
• Unilateral or bilateral
• Usually arises on the anterior and middle thirds of the vocal folds (point of greatest impact)
• May need surgical removal
Puberphonia
• Normal development- children undergo voice changes
– rapid growth of thyroid cartilage & thyroarytenoid
– Pitch breaks
• thyroarytenoid is the maintenance of the childhood pitch despite having reached puberty
• Young men with falsetto quality voices
• Therapy to help achieve habitual pitch
Laryngeal Stridor
• Harsh sound produced during respiration
• Sound associated with some obstruction in the respiratory passageway
• Arise from growth in the larynx or trachea causing turbulence
• May arise from vocal folds if paralyzed in adducted position