Spinal cord, plexuses, reflexes, tracts
advertisement

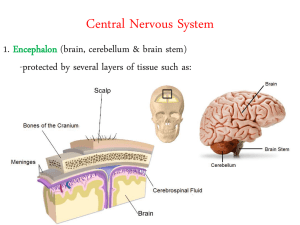
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 13-1 Spinal Cord Protection By the vertebral column, meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and vertebral ligaments. 13-2 Structures Covering the Spinal Cord • Vertebrae • Epidural space filled with fat • Dura mater – dense irregular CT tube • Subdural space filled with interstitial fluid • Arachnoid = spider web of collagen fibers • Subarachnoid space = CSF • Pia mater – thin layer covers BV – denticulate ligs hold in place 13-3 Spinal Cord Figure 13–3 The Spinal Cord and Spinal Meninges 13-4 External Anatomy of Spinal Cord • Flattened cylinder • 16-18 Inches long & 3/4 inch diameter • In adult ends at L1/L2 • In newborn ends at L4 • Growth of cord stops at age 5 13-5 Inferior End of Spinal Cord • Conus medullaris – cone-shaped end of spinal cord • Filum terminale – thread-like extension of pia mater – stabilizes spinal cord in canal • Caudae equinae (horse’s tail) – dorsal & ventral roots of lowest spinal nerves • Spinal segment – area of cord from which each pair of spinal nerves arises 13-6 Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves • Spinal nerves begin as roots • Dorsal or posterior root is incoming sensory fibers – dorsal root ganglion (swelling) = cell bodies of sensory nerves • Ventral or anterior root is outgoing motor fibers 13-7 Spinal tap or Lumbar Puncture • Technique – long needle into subarachnoid space – safe from L3 to L5 • Purpose – sampling CSF for diagnosis – injection of antibiotics, anesthetics or chemotherapy – measurement of CSF pressure 13-8 Gray Matter of the Spinal Cord Note: colors in reverse due to staining of tissue • Gray matter is shaped like the letter H or a butterfly – – – – contains neuron cell bodies, unmyelinated axons & dendrites paired dorsal and ventral gray horns lateral horns only present in thoracic spinal cord gray commissure crosses the midline • Central canal continuous with 4th ventricle of brain 13-9 White Matter of the Spinal Cord • White matter covers gray matter • Anterior median fissure deeper than Posterior median sulcus • Anterior, Lateral and Posterior White Columns contain axons that form ascending & descending tracts 13-10 Tracts of the Spinal Cord • Function of tracts – highway for sensory & motor information – sensory tracts ascend – motor tracts descend • Naming of tracts – indicates position & direction of signal – example = anterior spinothalamic tract • impulses travel from spinal cord towards brain (thalamus) • found in anterior part of spinal cord 13-11 Location of Tracts inside Cord • Motor tracts – pyramidal tract (corticospinal) – extrapyramidal tract – Sensory tracts ---spinothalamic tract ---posterior column ---spinocerebellar 13-12 Function of Spinal Tracts • Spinothalamic tract – pain, temperature, deep pressure & crude touch • Posterior columns – proprioception, discriminative touch, two-point discrimination, pressure and vibration • Direct pathways (corticospinal & corticobulbar) – precise, voluntary movements • Indirect pathways (rubrospinal, vestibulospinal) – programming automatic movements, posture & muscle tone, equilibrium & coordination of visual reflexes 13-13 Spinal Reflexes • Automatic response to change in environment • Integration center for spinal reflexes is gray matter of spinal cord • Examples – somatic reflexes result in skeletal muscle contraction – autonomic (visceral) reflexes involve smooth & cardiac muscle and glands. • heart rate, respiration, digestion, urination, etc • Note: cranial reflexes involve cranial nerves 13-14 Reflex Arc • Specific nerve impulse pathway • 5 components of reflex arc – – – – – receptor sensory neuron integrating center motor neuron effector • 4 important somatic spinal reflexes – stretch, tendon, flexor(withdrawal) & crossed extensor reflexes 13-15 Stretch Reflex (patellar reflex) • Prevents injury from over stretching because muscle contracts when it is stretched • Events of stretch reflex – muscle spindle signals stretch of muscle – motor neuron activated & muscle contracts • Reciprocal innervation (polysynaptic- interneuron) – antagonistic muscles relax as part of reflex 13-16 Illustration of the Stretch Reflex 13-17 Tendon Reflex • Controls muscle tension by causing muscle relaxation that prevents tendon damage • Golgi tendon organs in tendon – activated by stretching of tendon – inhibitory neuron is stimulated (polysynaptic) – motor neuron is hyperpolarized and muscle relaxes • Both tendon & muscle are protected • Reciprocal innervation (polysynaptic) – causes contraction of ipsilateral muscle group 13-18 Illustration of Tendon Reflex 13-19 Flexor (withdrawal) Reflex • Step on tack (pain fibers send signal to spinal cord • Interneurons branch to different spinal cord segments • Motor fibers in several segments are activated • More than one muscle group activated to lift foot off of tack 13-20 Crossed Extensor Reflex • Lifting left foot requires extension of right leg to maintain one’s balance • Pain signals cross to opposite spinal cord • Contralateral extensor muscles are stimulated by interneurons to hold up the body weight • Reciprocal innervation when extensors contract flexors relax, etc 13-21 Clinical Considerations • Checking a patient’s reflexes may help to detect disorders/injury • Plantar flexion reflex -- stroke the lateral margin of the sole – normal response is curling under the toes – abnormal response or response of children under 18 months is called Babinski sign (upward fanning of toes due to incomplete myelination in child) 13-22 The Brain Can Alter Spinal Reflexes • The Babinski Reflexes – Normal in infants – May indicate CNS damage in adults 13-23 The Brain Can Alter Spinal Reflexes Figure 13–21 The Babinski Reflexes. 13-24 Lecture 2 Spinal Nerves • 31 Pairs of spinal nerves • Named & numbered by the cord level of their origin – 8 pairs of cervical nerves (C1 to C8) – 12 pairs of thoracic nerves (T1 to T12) – 5 pairs of lumbar nerves (L1 to L5) – 5 pairs of sacral nerves (S1 to S5) – 1 pair of coccygeal nerves • Mixed sensory & motor nerves 13-25 Connective Tissue Coverings • Endoneurium = wrapping of each nerve fibers • Perineurium = surrounds group of nerve fibers forming a fascicle • Epineurium = covering of entire nerve – dura mater blends into it at intervertebral foramen 13-26 Endoneurium Perineurium Epineurium 13-27 Branching of Spinal Nerve • Spinal nerves formed from dorsal & ventral roots • Spinal nerves branch into dorsal & ventral rami – dorsal rami supply skin & muscles of back – ventral rami form plexus supply anterior trunk & limbs – meningeal branches supply meninges, vertebrae & BV 13-28 A Nerve Plexus • Joining of ventral rami of spinal nerves to form nerve networks or plexuses • Found in neck, arm, low back & sacral regions • No plexus in thoracic region – intercostal nn. innervate intercostal spaces 13-29 Spinal Nerves and Plexuses Figure 13–10 Peripheral Nerves and Nerve Plexuses. 13-30 Cervical Plexus • Ventral rami of spinal nerves (C1 to C5) • Supplies parts of head, neck & shoulders • Phrenic nerve (C3-C5) keeps diaphragm alive • Damage to cord above C3 causes respiratory arrest 13-31 Phrenic Nerve 13-32 Brachial Plexus • Ventral rami from C5 to T1 • Supplies shoulder & upper limb • Passes superior to 1st rib & under clavicle • Axillary n. = deltoid & teres m. • Musculocutaneous n. = elbow flexors • Radial n. = shoulder & elbow extensors • Median & ulnar nn. = flexors of wrist & hand 13-33 Branches off Brachial Plexus 13-34 Clinical Correlations • Radial nerve injury – improper deltoid injection or tight cast – wrist drop • Median nerve injury – numb palm & fingers; inability to pronate & flex fingers • Ulnar nerve injury (clawhand) – inability to adduct/abduct fingers, atrophy of interosseus • Long thoracic nerve injury (winged scapula) – paralysis of serratus anterior, can’t abduct above horizontal 13-35 Spinal Nerves and Plexuses Figure 13–12b The Brachial Plexus. 13-36 Spinal Nerves and Plexuses Figure 13–10 Peripheral Nerves and Nerve Plexuses. 13-37 Lumbar Plexus • Ventral rami of L1 to L4 • Supplies abdominal wall, external genitals & anterior/medial thigh • Injury to femoral nerve causes inability to extend leg & loss of sensation in thigh • Injury to obturator nerve causes paralysis of thigh adductors 13-38 Branches of Lumbar Plexus • Notice: Femoral and Obturator nerves • Found anterior and medial to hip joint 13-39 Sacral Plexus • Ventral rami of L4-L5 & S1-S4 • Anterior to the sacrum • Supplies buttocks, perineum & part of lower limb • Sciatic nerve = L4 to S4 supplies post thigh & all below knee – Peroneal nerve injury produces foot drop or numbness 13-40 Spinal Nerves and Plexuses Figure 13–13b The Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses. 13-41 Branches of Sacral Plexus • Notice: Sciatic nerve origins 13-42 Sciatic Nerve Branches • Notice: Common Peroneal nerve and Tibial nerve behind the knee • Notice: Sciatica pain extends from the buttock down the leg to the foot • may be sign of herniated disc, Spinal Subluxations, piriformis syndrome, tilted pelvis 13-43 Dermatomes & Myotomes • Each spinal nerve contains both sensory & motor nerve fibers • Dermatome – area of skin supplied by one spinal nerve – overlap prevents loss of sensation if one damaged • Skin on face supplied by Cranial Nerve V 13-44 Spinal Nerves and Plexuses Figure 13–8 Dermatomes. 13-45 Spinal Nerves and Plexuses Figure 13–9 Shingles. 13-46 Disorders • Neuritis – inflammation of nerves – caused by injury, vitamin deficiency or poison • Shingles – infection of peripheral nerve by chicken pox virus – causes pain, skin discoloration, line of skin blisters • Poliomyelitis – viral infection causing motor neuron death and possible death from cardiac failure or respiratory arrest 13-47 Sciatica • Irritation of the sciatic nerve by a subluxated vertebrae, arthritis of the spine, disc bulge or herniations, tilted pelvis, piriformis muscle, scoliosis, military spine, hyperlordosis, pes planus ( flat feet ) 13-48 • Carpal Tunnel syndrome -Median nerve, 3 ½ fingers, tinels sign, phalens test, Needle EMG, Carpal bones(floor) Flexor retinaculum (roof), transverse carpal ligament) • Thoracic outlet Syndrome – Lower end of brachial plexus and/or subclavian artery compression by: scalene muscles and/or pec minor muscle. Adson’s test, Wrights test. Numbness down the medial aspect of the forearm and the ½ of the 4th and 5th digit, diminished pulse and cold fingers. 13-49