File
advertisement

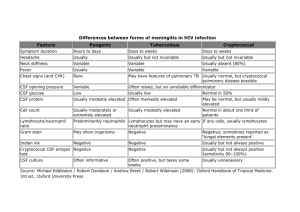
ABOUT CSF Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was first examined in the 19th century using primitive techniques (eg, sharpened bird quills). Indications of CSF examination 1. Bacterial, viral or fungal meningitis. 2. Encephalitis. 3. To investigate for Malignant infiltrates eg acute leukemia, lymphoma. Indication of CSF examination 4. Disorders with local immunoglobulin production in the CNS (multiple sclerosis). 5. Subarachnoid hemorrhage. 6. Spinal canal blockage Methods of CSF collection Lumber CSF Puncture also can be obtained from the cisterna magna by a tap below the external occipital protuberance. Lumber Puncture: uses Diagnostic and therapeutic uses 1. CSF examination [ diagnostic] 2. Therapeutic application of LP A. For spinal anesthesia, B. For introduction of radio opaque contrast media (eg, myelography), C. For injection of corticosteroids, antibiotics, and chemotherapeutic agents. LP : Instruments and procedures Which space you enter spinal canal ? LP is performed in the interspaces between the lumbar vertebrae, usually at the L4-L5, or L3-L4 level. Normal CSF values Cell count: <5 cells / cumm. mononuclears; Glucose: 60-70% of plasma levels (usually) 2.8-4.4 mmol/L Lactate: 1.2-2.8 mmol/L Protein: Full term neonate: 0.1-1.2 g/L adult: 0.15-0.45 g/L IgG/albumin ratio: <0.2 CSF Pressure Normal range is 80-180 mm H20 May Increase in Brain Abscess and encephalitis. Interpretation: acute bacterial meningitis (pyogenic). CSF appearances Cloudy Cell count Cell Type Increased >1000 cell/cumm Neutrophils Protein Normal-high Sugar Very much Reduced Gram Stain Often Positive Culture Often positive Viral meningitis CSF appearances Clear Cell count Moderate Increase Cell type Lymphocyte Protein Increased Sugar Reduced Culture Negative Fungal meningitis: Cryptococcus neoformans Meningitis [ AIDS] CSF appearances Cell count Cell type Protein Wright Giemsa/India ink Culture Clear or cloudy increased (10 -100) Lymphocytes, macrophage Increased Positive of fungus Positive Other facts In traumatic Tap = RBCs may be seen. 1. 2. 3. Physical ( macroscopic examination) Chemical Analysis Cytological Analysis Value of macroscopic Examination Pseudomonal meningitis may be associated with bright green CSF. Red Colour if contain RBC ( hemorrhage) Cob web coagulum = Tuberculosis Xanthochromia : Intracranial Bleeding The best way to distinguish RBCs related to intracranial bleeding is examination of the centrifuged supernatant CSF for xanthochromia (yellow color). N Xanthochromia Xanthochromia can persist up to several weeks following a subarachnoid hemorrhage Differential diagnosis : Xanthochromia Xanthochromia can be produced by spillover from a very high serum bilirubin level (ie, >15 mg/dL). Chemical Analysis High Protein Demyelinating Postinfectious Polyneuropathies states Low glucose Bacterial Tumor infection infiltration, and may be one of the hallmarks of meningeal carcinomatosis. Cytological Analysis Cytological examination Detection of malignant cells: Carcinoma, lymphoma or leukemia. Oligoclonal bands; Increased IgG/albumin ratio 1. Demyelinating disorders, esp- Multiple Sclerosis. 2. Guillain-Barré syndrome, Risk of LP Post–spinal tap headache Nerve root trauma (eg, previous surgery in the area, scar tissue) CNS infection (eg, immunocompromised patients) Intraspinal hematoma (eg, patients on anticoagulation therapy Tonsillar Herniation LP and CSF In summary, LP and CSF examination, while their indications have been reduced, remain indispensable tools in the armamentarium of neurologic diagnosis.