Effect of renin-angiotensin system blockade on
advertisement
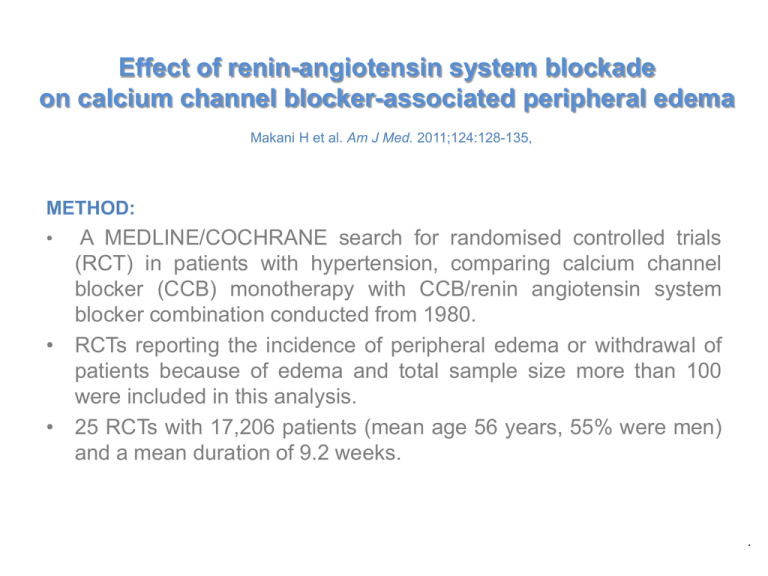
Effect of renin-angiotensin system blockade on calcium channel blocker-associated peripheral edema Makani H et al. Am J Med. 2011;124:128-135, METHOD: • A MEDLINE/COCHRANE search for randomised controlled trials (RCT) in patients with hypertension, comparing calcium channel blocker (CCB) monotherapy with CCB/renin angiotensin system blocker combination conducted from 1980. • RCTs reporting the incidence of peripheral edema or withdrawal of patients because of edema and total sample size more than 100 were included in this analysis. • 25 RCTs with 17,206 patients (mean age 56 years, 55% were men) and a mean duration of 9.2 weeks. . Percentage Combining RAAS inhibitors with CCB decreases edema incidence/withdrawal rates with CCB CCB = calcium channel blocker; RAS = renin-angiotensin system *p<0.0001 Makani H et al. Am J Med. 2011;124:128-135 ACE inhibitors are more efficacious than ARBs in reducing CCB-associated edema P=0.0001 P<0.00001 Makani H et al. Am J Med. 2011;124:128-135 Clinical significance • The combination of RAAS inhibitors with calcium channel blockers (CCB) reduces the incidence by 38% and withdrawal rate due to peripheral edema by 62% when compared with calcium channel blocker monotherapy. • ACE inhibitors were significantly more efficacious than ARBs in reducing the incidence of CCB-associated peripheral edema by 54% and 24%, respectively (P<0.0001), • Aliskiren did not show significant reduction of CCB-associated cough. Makani H et al. Am J Med. 2011;124:128-135.