Aucun titre de diapositive
advertisement

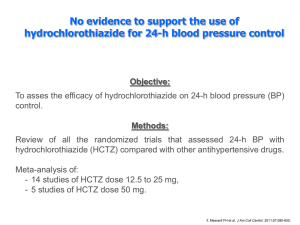
Protecting patients with hypertension How to maximize patient benefit ? Pr Roland Asmar How to maximize patient benefit 1 Goals of Antihypertensive Treatment ESH/ESC 2007 < 140/90 mmHg Hypertensive patients Diabetes Patient at high risk < 130/80 mmHg How to maximize patient benefit 2 Worldwide Blood Pressure Control in Treated Hypertensive Patients Canada 41.0 USA 53.1 Mexico 21.8 Turkey 19.8 Germany 33.6 England 29.2 Greece 49.5 Japan 55.7 China 28.8 Taiwan 18.0 Spain 38.8 Egypt 33.5 South Africa 47.6 Italy 37.5 How to maximize patient benefit Kearney et al. J Hypertens 2004; 22: 11 3 HOT: Need for Combination Therapy How to maximize patient benefit Hansson et al., Lancet 1998, 351: 1755-62 4 Percentage of Patients with Combination Treatment in Clinical Trials 100 VA HDFP ANBPS MRC-1 IPPPH MAPHY HAPPHY EWPHE COOPE STOP-1 SHEP MRC II Syst-Eur HOT Syts-China IDNT RENAAL LIFE INSIGHT CONVINCE 47 33 34 70 49 46 35 93 66 45 51 41 68 66 68 84 65 30 70 0 20 40 60 How to maximize patient benefit 80 100 % 5 ESH/ESC Guidelines - 2007 Pharmacological Rationale for Combination Therapy How to maximize patient benefit 7 Rationale for Combination Therapy •Increase Efficacy • Synergistic & additive effects on BP • Effects on several patho-physiological mechanisms of HT • Inhibition of the contra-regulation mechanisms •Decrease Side effects • Inhibition of the contra-regulation • Low dose Decrease dose-dependent side effects How to maximize patient benefit 8 Advantages of Combination Therapy Efficacy How to maximize patient benefit 9 Rationale of Combination Therapy Pathogenetic Mechanisms in Hypertension Patient A Patient B Patient C Sympathetic nervous system Renin-angiotensin system Total body sodium Waeber B. 2004 How to maximize patient benefit 11 Titration vs. Combination Diastolic BP HTZ 6.26 - HTZ 25 B10 - B40 HTZ 6.25 + B10 0 0 -1 -0,5 -2 -1 mmHg mmHg -3 -4 B10 + HTZ6.25 -3,2 -5 -6 -1,5 -1,5 -2 -2,5 -7 -3 -8 -9 -8,5 -3,5 How to maximize patient benefit -3,1 Frishman WH et al,Arch Intern Med 1994;154:1461 12 Efficacy: Up-titration vs Combination Change in SBP (mm Hg) 0 T40 T80 T40 T40 HCT12.5 V80 V160 V80 V80 HCT12.5 Ol20 Ol40 O20 Ol20 HCT12.5 -5 -6,9 -6,9 -8,2 -8,2 -10 -12,2 -12,6 -15 -16,8 -20 -15,2 -16,4 -15,2 -18,8 -20,4 -25 How to maximize patient benefit 13 Value of combination treatment: analysis of 354 randomised placebo controlled trials Effects of two different drugs on BP separately and in combination (results from 119 trials) Treatment Observed “First” drug alone “Second” drug alone Both drugs together Expected Sum of first and second drugs alone Difference between observed and expected (95% CI) SBP DBP 7.0 (0.4) 8.1 (0.3) 14.6 (0.5) 4.1 (0.3) 4.6 (0.3) 8.6 (0.4) 15.1 -0.5 (-1.4 to 0.4) 8.7 -0.1 (-1.0 to 0.8) How to maximize patient benefit Law MR BMJ 2003 14 Advantages of Combination Therapy Side Effects How to maximize patient benefit 15 Effect of ARB and HCTZ on Serum Potassium 0,2 0,1 Adjusted 0 mean D from baseline -0,1 at 8 weeks -0,2 (mEq/L) 300 100 -0,3 37.5 -0,4 0 0 6.25 12.5 ARB dose (mg/d) 25 HCTZ dose (mg/d) How to maximize patient benefit Kochar M, et al. Am J Hypertens. 1999;12:797 16 Drug related symptoms: comparison between monotherapy & combination 50 trials testing drugs of two different categories separately and in combination, SYMPTOMS Single drugs 5.2% (3. To 6.6) Two drugs 7.5% (5.8 to 9.3) Expected adding 2 drugs 10.4% How to maximize patient benefit BMJ 2003;326:1427 17 Advantages of Combination Therapy Convenience How to maximize patient benefit 18 Fixed-dose Combination Therapy Increases Compliance to Treatment Persistence (%) Persistence rates of one pill of lisinopril/HCTZ in fixed-combination vs two separate pills of lisinopril and HCTZ 100 95 90 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 Lisinopril/HCTZ (1 pill) Lisinopril and HCTZ (2 pills) 68.7 18.8% 57.8 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Dezii CM. Manag Care 2000; 9 : s2 Months Advantages of Combination Therapy Equal efficacy? How to maximize patient benefit 20 ® Blood pressure control with ARBs and in Fixed Dose Combination Protocol Endpoints Primary endpoint ■ Changes from baseline in SBP during last 6 hours of dosing interval using ABPM Secondary n=294 n=160 n=297 endpoints Changes from: ■ Baseline in DBP during the last 6 hours of dosing interval ■ Baseline in pulse pressure during the last 6 hours of dosing interval ■ Baseline in the 24-hour mean SBP and DBP Neutel JM, et al. Hypertens Res 2005;28:555 ABPM Comparison of Telmisartan HCTZ & Losartan HCTZ Parallel Group Comparison after 6 weeks Therapy Time after dosing (h) 2 6 10 14 18 Time after dosing (h) 2 22 Systolic BP Change from baseline (mmHg) 10 14 18 22 -6 -8 -12 6 Diastolic BP Telmisartan 80mg + HCTZ 12.5mg Telmisartan 40mg + HCTZ 12.5mg Losartan 50mg + HCTZ 12.5mg -8 -10 -16 -12 -20 -14 -24 -16 How to maximize patient benefit Neutel et al. Hypertens Res. 2005;28:555 22 ® Study of telMisartan On Obese/overweight Type2 diabetics with Hypertension Protocol Endpoints Primary endpoint ■ Changes from baseline in SBP during last 6 hours of dosing interval using ABPM Secondary endpoints ■ Changes in other ABPM-derived parameters ■ Changes in trough cuff SBP and DBP ■ Metabolic blood markers (e.g.cholesterol) ■ Urine markers (e.g. proteinuria) Sharma AM, et al. Cardiovascular Diabetology. 2007;6:28 Telmisartan + HCTZ vsValsartan + HCTZ Powerful 24 hr SBP reductions 0 4 Time post dose (hours) 8 12 16 20 24 SBP change from baseline (mmHg) 0 -2 -4 -6 Valsartan 160 mg + HCTZ Telmisartan 80 mg + HCTZ *** -8 -10 -12 -14 -16 -18 -20 ***p < 0.001 T + H vs V + H 24-hour and last 6-hour mean SBP How to maximize patient benefit Sharma et al. Hypertension 2005;46:898 24 Telmisartan 80mg/HCTZ 12.5 mg vs Olmesartan 20mg/HCTZ12.5 mg Systolic BP Diastolic BP How to maximize patient benefit Fogari & al Current Therapeutic Research; 2008; 69 25 ® A comparison of Telmisartan plus HCTZ with amlodipine plus HCTZ in Older patients with predominantly Systolic hypertension Protocol Endpoints Primary endpoint ■ Changes from baseline in SBP during last 6 hours of dosing interval using ABPM n=497 n=503 Secondary endpoints Changes from: ■ Baseline in DBP during the last 6 hours of dosing interval ■ Baseline in pulse pressure during the last 6 hours of dosing interval ■ Baseline in the 24-hour mean SBP and DBP Neldam S, et al. AJGC 2006;15:151-60. How to maximize patient benefit Neldam S, et al. AJGC 2006;15:151-60. 27 Telmisartan in combination HCTZ 25 mg How to maximize patient benefit 28 Comparison of Telmisartan HCTZ & Valsartan HCTZ Change in clinic trough BP from baseline after 8 weeks therapy Change from baseline (mmHg) 0 Systolic BP Diastolic BP -5 -10 -15 -20 -1.8 (-3.0, - 0.6) p<0.02 -25 Telmisartan-HCTZ 80/25mg (n=467) Valsartan-HCTZ 160/25mg (n=479) Placebo (n=120) -2.8 (-4.6, -1.0) p<0.004 How to maximize patient benefit White et al. J Hypertens Suppl. 2003;21:S9-15.29 Comparison of Telmisartan HCTZ & Valsartan HCTZ Change in clinic trough BP from baseline after 8 weeks therapy How to maximize patient benefit White W & al BP Monitoring 2008, 13:21 30 AIIA + CCB How to maximize patient benefit 31 Composed end-point comparing a fixed combination of a CCB +ACEI vs a thiazide+ACEI ACCOMPLISH Trial Incidence of eventos HR: 0,80; IC 95%: 0,72 – 0,90 Time for events How to maximize patient benefit Jamerson K et al. NEJM; 2008; 359:2417 32 ASCOT - Summary of all end points Unadjusted Hazard ratio (95% CI) 0.90 (0.79-1.02) Primary Non-fatal MI (incl silent) + fatal CHD Secondary Non-fatal MI (exc. Silent) +fatal CHD Total coronary end point Total CV event and procedures All-cause mortality Cardiovascular mortality Fatal and non-fatal stroke Fatal and non-fatal heart failure Tertiary Silent MI Unstable angina Chronic stable angina Peripheral arterial disease Life-threatening arrhythmias New-onset diabetes mellitus New-onset renal impairment 0.87 (0.76-1.00) 0.87 (0.79-0.96) 0.84 (0.78-0.90) 0.89 (0.81-0.99) 0.76 (0.65-0.90) 0.77 (0.66-0.89) 0.84 (0.66-1.05) 1.27 (0.80-2.00) 0.68 (0.51-0.92) 0.98 (0.81-1.19) 0.65 (0.52-0.81) 1.07 (0.62-1.85) 0.70 (0.63-.078) 0.85 (0.75-0.97) Post hoc Primary end point + coronary revasc procs CV death + MI + strok 0.86 (0.77-0.96) 0.84 (0.76-0.92) e 0.50 0.70 1.00 Amlodipine perindopril better 1.45 2.00 Atenolol thiazide better The area of the blue square is proportional to the amount of statistical information How to maximize patient benefit 33 Chemical structures Telmisartan and other angiotensin II antagonists Losartan ValsartanIrbesartan Candesartan Olmesartan (active form) (active form) (active form H3C N O N N CH3 C CI CO2H N CO2H N N N O N OCH2CH3 OH N COOH COOH N N N NH N N N NH N N N NH N N N NH N N N NH Telmisartan CH3 N CH3 N N O N OH CH3 How to maximize patient benefit 34 Dissociation Half-Lives of ARB’s from Human AT1 Receptors Telmisartan 95% CI 202-226 min Olmesartan 151-184 min Candesartan 121-149 min Valsartan 60-83 min Losartan 60-77 min EXP3174 73-91 min 0 50 100 150 200 250 Dissociation half-life (min) 35 How to maximize patient benefit Kakuta et al. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 2005;25:41-6. Selective Nuclear Hormone Receptor Modulation Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma (PPAR g) interaction Pioglitazone Full Agonists Rosiglitazone Telmisartan Selective Modulation Selective Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Modulators (SPPARMS) PPAR g Insulin Sensitivity NO Weight Gain NO Oedema How to maximize patient benefit Insulin Sensitivity Weight Gain Oedema 36 Difference between Thiazolodinediones & ARBs in the Interaction with PPARg Receptor Fold Activation 150 Full Agonists 100 Partial Agonist 50 0 rosiglitazone pioglitazone telmisartan How to maximize patient benefit irbesartan eprosartan Benson et al. Hypertension. 2004;43:993 37 Activation of PPARg by ARB’s 25 Telmisartan was the only ARB that activated PPARg at concentrations (1-5 mmol/l) attained in plasma with conventional oral dosing Fold Activation 20 15 10 5 0 Telmisartan Candesartan Irbesartan Olmesartan Valsartan How to maximize patient benefit EXP 3174 Eprosartan Benson et al. Hypertension. 2004;43:993. 38 Effects of Telmisartan & Losartan in Patients with metabolic syndrome FPG FPI HOMA IR HbA1c Change from baseline (%) 0 -10 P<0.05 P<0.05 P<0.06 -20 P<0.05 Telmisartan (n=20) Losartan (n=20) -30 How to maximize patient benefit Vitale et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2005;15:6. 39 Effects of Telmisartan and Amlodipine on Metabolic Parameters in Type 2 Diabetic Hypertensives HbA1c TG HOMA IR 0 120 -2 100 -6 -8 -10 -12 FPI Telmisartan Amlodipine 60 40 20 0 -20 -40 -14 -16 Adiponectin * 80 -4 % change from baseline % change from baseline FPG * ** n.s. -60 * n.s. * p<0.05 & ** p<0.01 vs amlodipine How to maximize patient benefit Negro et al. JRAA 2006:243-6. 40 Effects of telmisartan on fat distribution in individuals with metabolic syndrome Change in the Visceral Fat Area (VFA) Change in waist circumference 300 100 +10% p=0.046 +3% Waist circumference (cm) VFA cm² 250 -12% p=0.008 200 150 100 50 -5% 98 96 94 92 90 Amlodipine Telmisartan Baseline Amlodipine Telmisartan 24 wks treatment How to maximize patient benefit Shimabukuro, J Hypertens 2007;25:841 41 Comparative Cardio-Metabolic Studies with Telmisartan Trial Patients N Duration (weeks) Comparator Agent(s) BP differential Improved Insulin Sensitivity Improved Lipid Profile Anti-oxidant/ Inflammatory Action Derosa 2004a HT, T2DM 119 52 Eprosartan/Placebo No (P yes) No Yes - Derosa 2004b HT, T2DM 116 52 Nifedipine GITS No No Yes - Vitale 2005 HT, MS 40 12 Losartan Yes? Yes - - Miura 2005 HT, T2DM 18 12 Candesartan/Valsartan No Yes Yes Yes Koulouris 2005 NT, T2DM 40 12 Ramipril No No No Yes Honjo 2005 HT, T2DM 38 12 Candesartan - Yes - - HT 37 6 Nisoldipine No? Yes - - Negro 2006a HT, T2DM 40 16 Amlodipine No Yes Yes - Negro 2006b HT, obese,IR 46 26 Irbesaratn No Yes Yes - Bahadir 2007 HT, MS 42 10 Losartan No? Yes? No - Derosa 2007 HT, T2DM 188 52 Irbesartan No Yes Yes Yes Sharma 2007 HT, obese 840 10 Valsartan HCTZ Yes No No - Benndorf 2006 How to maximize patient benefit 42 Conclusions Use of more than one agent is necessary to achieve target BP in the majority of patients. Combination therapy is related with a higher BP reduction and CV protection Fixed combinations of two drugs can simplify treatment schedule and improve compliance and tolerability. A combination of two drugs should be preferred as first step treatment when initial BP is in the grade 2 or 3 range or total cardiovascular risk is high or very high Are all the combination therapies equipotent Backup How to maximize patient benefit 44 Combination Therapy Study / Drugs BP Mo- Mort STOP 2 Old/Recent ≡ ≡ BACRI ARB + HCTZ / ACEI + Verap ≡ NA INVEST BB + HCTZ / Verap + ACEI ≡ ≡ EXFORGE ARB + CCB / ACEI + HCTZ ≡ ou ≥ NA ASCOT BB + HCTZ / ACEI + CCB ≡ ≡ ou ≥ LIFE BB + HCTZ / ARB + HCTZ ≡ ≥ ACCOMPLISH ACEI + HCTZ / ACEI + CCB ≡ ≥ ONTARGET ACEI + ARB / ACEI ≥ ≡ Side effects ++ How to maximize patient benefit 45 The HOT Study: CV Risk Reduction in Diabetics major CV events/1000 patient.y 25 p < 0.005 for trend (n = 1501) 20 15 10 5 0 Target Achieved < 90 mmHg 85 mmHg < 85 mmHg 83 mmHg How to maximize patient benefit < 80 mmHg 81 mmHg 46 Hansson L, et al. Lancet 1998;351:1755–62. Management of BP for adultsJNC VII Initial drug therapy SBP* mmHg DBP mmHg Lifestyle modification <120 and <80 Encourage Prehypertension 120–139 or 80–89 Yes No antihypertensive indicated. Stage 1 Hypertension 140–159 or 90–99 Yes Thiazide-type diuretics for most. May consider ACEI, ARB, BB, CCB, or combination. Stage 2 Hypertension >160 or >100 Yes BP classification Normal †Initial ‡Treat Without compelling indication With compelling indications drug Drug(s) for compelling indications. ‡ Drug(s) for the compelling indications.‡ Other Two-drug combination for antihypertensive most† (usually thiazide-type drugs (diuretics, ACEI, diuretic and ACEI or ARB or ARB, BB, CCB) as needed. BB or CCB). combined therapy should be used cautiously in those at risk for orthostatic hypotension. patients with chronic kidney disease or diabetes to BP goal of <130/80 mmHg. How to maximize patient benefit 47 Adverse Events: HCTZ 25 mg vs ARB + HCTZ 25 mg HCTZ ARB + HCTZ Potassium Insulin Glucose Lipids Uric Acid Adverse events Impotence How to maximize patient benefit 48 Effect of Telmisartan HCTZ 25 mg Change in clinic trough BP from baseline after 8 weeks therapy How to maximize patient benefit 49 Neldam & al J Clin Hypertens 2008; 10:612 INVEST: Primary Composite Endpoint by Treatment Group 25 Calcium Antagonist Strategy (CAS) (Verap + ACEI) Non-Calcium Antagonist Strategy (NCAS) (BB + HCTZ) Cumulative % 20 RR = 0.98 (0.90 – 1.06) 15 Log-Rank P=.57 10 5 0 0 6 12 18 24 10716 10785 10512 10536 10008 10048 No. at Risk CAS NCAS 11267 10921 11309 10991 30 36 Time, mo 6612 6604 3738 3706 42 48 54 60 1568 1563 974 960 393 390 35 33 Pepine CJ, et al. JAMA. 2003;290:2805 ONTARGET – Combination ACEI + ARB vs ACE T&R Yr 2 Yr 3 Yr 4 8576 8502 7832 7740 7473 7377 7095 7023 8214 8134 0.15 0.05 0.10 Ramipril Tel. & Ram. 0.0 Cumulative Hazard Rates 0.20 0.25 R # at Risk Yr 1 0 1 2 3 4 Years of Follow-up How to maximize patient benefitThe ONTARGET Investigators N EJM 2008;358:1547 51