USER-FRIENDLY STATISTICS
advertisement

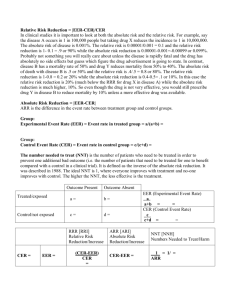
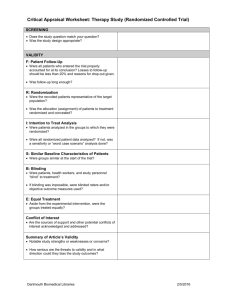
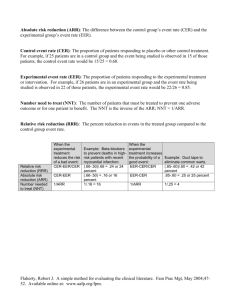
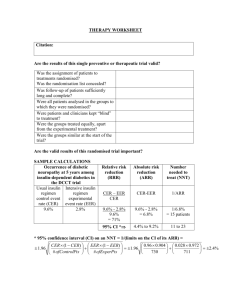
HELPDESK ANSWERS SYNTHESIZING THE EVIDENCE: Statistical Evidence OVERVIEW Learn which statistics are most helpful in relaying clinical information. Discover helpful tools in working with statistics. Convert study results into user-friendly statistics. PUTTING STATISTICS INTO ENGLISH Fictitious Case Example A now unethical RCT of sunscreen vs. placebo for melanoma shows a rate of 1/1000 = .001 for 20-year sunscreen use vs. 5/1000 = .005 for placebo in the prevention of melanoma. EER (Experimental Event Rate) = .001 “The proportion of those who developed melanoma over 20 years in the sunscreen group was 1 out of 1000.” ARR (Absolute Risk Reduction) = EER-CER = .004 “For every 1000 patients using sunscreen, 4 cases of melanoma are averted.” NNT (Number-needed-to-treat) = 1/ARR = 250 “250 patients would need to be treated with sunscreen rather than placebo for 20 years to prevent one additional case of melanoma.” RR (Relative Risk) = EER/CER = .20 “People who use sunscreens for 20 years have less than a fifth of the risk of developing melanoma of those who use a placebo. Alternatively, people who do not use sunscreens have a 5 times greater risk of developing melanoma over 20 years as compared to those who use sunscreens.” Risk remaining: “Just 20% of the original risk of developing melanoma remains for those who use sunscreen.” RRR (Relative Risk Reduction) = (EER-CER)/CER or 1 – RR = .80 “Sunscreen use decreases the risk of developing melanoma by 80% compared with no sunscreen.” Risk removed: “80% of the risk of developing melanoma is removed by using sunscreen.” USER-FRIENDLY STATISTICS We’ll focus on a few key statistics in the HelpDesk Answer Project Confidence Interval (CI) Quantifies the uncertainty in measurement. It is usually reported as a "(95% CI 5-15) which is the range of values within which we can be 95% sure that the true value for the whole population lies. For example, for an NNT of 10 with a 95% CI of 5 to 15, we would have 95% confidence that the true NNT value lies between 5 and 15. Likelihood ratio The likelihood that a given test result would be expected in a patient with the target disorder compared with the likelihood that this same result would be expected in a patient without the target disorder. Number needed to treat (NNT) The number of patients that we need to treat with a specified therapy in order to prevent one additional bad outcome. Or the NNT is the number of patients who must be treated for one patient to benefit. Calculated as the inverse of the absolute risk reduction (1/ARR). STATISTICAL EVIDENCE Convert study results into user-friendly statistics: Confidence Intervals Likelihood Ratios Number Needed to Treat/Harm Use tables to summarize or compare studies. Statistics ARE the ‘heart’ of the evidence. If the author is unsure, the reader will be unsure. If in doubt, seek experts. User-Friendly Stats 2X2 Table for Outcome of Interest + - Experimental Treatment a b Placebo/ Comparison c d a. Control Event Rate: Cer = c / c + d b. Experimental Event Rate: Eer = a / a + b c. Absolute Risk Reduction: ARR = Cer – Eer d. Relative Risk Reduction: RRR = ARR / Cer e. Relative Risk Ratio = Eer / Cer f. Number Needed to Treat: NNT = 1 / ARR http://www.cebm.net/index.aspx?o=1160 Example: User-Friendly Stats Example: User-Friendly Stats Primary End Points (first major cardiovascular events) + - Experimental treatment 142 8759 Placebo/ Comparison 251 8650 Control Event Rate: Cer = c / c + d = 251/251 + 8650 = 0.028 Experimental Event Rate: Eer = a / a + b = 142/142 + 8759 = 0.016 Absolute Risk Reduction: ARR = Cer – Eer = 0.028 – 0.016 = 0.012 Relative Risk Reduction: RRR = ARR / Cer = 0.012/0.028 = 0.43 Number Needed to Treat: NNT = 1 / ARR = 1/0.012 = 83 http://www.cebm.net/index.aspx?o=1160 Example: User-Friendly Stats Non – Fatal Myocardial Infarction Experimental treatment 22 8879 Placebo/ Comparison 62 8839 Control Event Rate: Cer = c / c + d = 62/62 + 8839 = 0.00696 Experimental Event Rate: Eer = a / a + b = 22/22 + 8879 = 0.00247 Absolute Risk Reduction: ARR = Cer – Eer = 0.00696 – 0.00247 = 0.00449 Relative Risk Reduction: RRR = 0.00449/0.00696 = 0.65 Number Needed to Treat: NNT = 1 / 0.00449 = 223 http://www.cebm.net/index.aspx?o=1160 USER-FRIENDLY STATISTICS Review the example given until you feel comfortable in following the numbers used and calculations made. Additional practice examples are available in the quiz portion of this module. Stats calculators are available throughout the web and links are available through the module home page