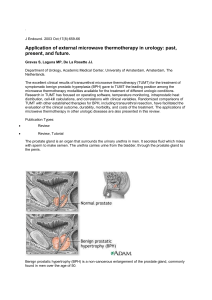
Medical management of BPH: 5-alpha reductase inhibitors and
advertisement

Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Hyperplasia Enlargement BPH Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Microscopic Proliferation of stromal (fibromuscular) and epithelial (prostate secretory glands) in the transitional zone Macroscopic “Enlarged Prostate”; DRE, TRUS, CT, MRI Static (epithelial/having a large blockage) Dynamic (increased “tone” of muscle fibers) Clinical LUTS: storage vs. voiding vs. both (nonspecific) BPH By the numbers: 14 million US men (not all seek medical attention) Annual cost of $4 billion per year BPH Incidence and Epidemiology Most common benign tumor in men Prevalence 20% in men 41-50 50% in men 51-60 Increase by 10% per 10 years Familial component likely Higher incidence in higher income & higher education Metabolic syndrome increases likelihood of BPH Anatomy BPH Evaluation: International Prostate Symptoms Score (IPSS)/AUA Symptoms Index: 0-35 points for symptoms and severity LUTS: 0-7 Mild 8-18 Moderate >18 Severe BPH Treatment Options: 1. Watchful waiting 2. Phytotherapeutics 3. Medical management Alpha blockers 5 Alpha reductase inhibitors (5 ARI’s) Phosphodiesterase inhibitors (PDE5i) Combination therapy 4. Minimally invasive techniques 5. Surgical techniques Watchful Waiting Decrease PM fluids Decrease caffeine/ETOH/bladder irritants Timed voids/double voids Review Rx list and optimize Treat constipation Phytotherapy Phytotherapeutic agents are standardized herbal preparations consisting of complex mixtures of one or more plants which contain as active ingredients plant parts or plant material in the crude or processed state. Last year, the US herbal supplement market was $7.4 billion. Phytotherapy Phytotherapeutic agents are commonly prescribed in Europe for LUTS, and in the US 30-90% of patients seen by urologists for BPH/LUTS may be taking them The US market for dietary supplements to treat LUTS or just “to keep the prostate healthy” is around $1.5 billion per year Phytotherapy Product Variability Evaluation and use of these products are complicated by variations in the plants themselves as well as the process to extract the desired components. Study (Feifer et al., 2002), showed that 3/6 samples of saw palmetto was less than 20% of the amount stated on the label and two of these had less than 5% Phytotherapy Major Issues with phytotherapy: 1. The clinical benefits of phytotherapeutic agents for BPH are still uncertain 2. Saw Palmetto is the most widely used nutraceutical for BPH 3. The mechanism of action of phytotherapeutic agents on BPH are thought to be weakly similar to finasteride, decreasing testosterone’s effects on the prostate 4. There is significant interbrand and intrabrand variability 5. The “presumed” safety of these products has never been fully confirmed Rare scientific head to head comparisons with standard treatments Phytotherapy Saw Palmetto African Plum South African Star Grass Stinging Nettle Rye-Pollen Extract Pumpkin Seeds Other: Soy, Grape Juice, Cactus Flower, Zinc, Selenium Alpha-Blockers Basis of therapy: The dynamic (increased muscle tone) part of BPH A component of BPH and bladder obstruction is mediated by alpha adrenergic receptors associated with prostatic smooth muscle. Alpha-Blockers Classification Nonselective: Phenoxybenzamine 10mg BID Alpha-1 Terazosin (Hytrin) 5 or 10mg qDay Doxazosin (Cardura) 4 or 8mg qDay Alfuzosin (Uroxatral) 10mg qDay Alpha-1a Subtype Selective Tamsulosin (Flomax) 0.4mg qDay Silodosin (Rapaflo) 8mg qDay Alpha-Blockers Typical Side Effects: Orthostatic Hypotension Dizziness Tiredness Retrograde Ejaculation Rhinitis Headache Floppy Iris Syndrome 5 Alpha Reductase Inhibitors Development Experimental studies: Testosterone production or function is inhibited in men castrated before puberty These same men were noted to have abnormal prostate development Later determined that embryonic development of the prostate is dependent on the androgen DHT, which is converted from testosterone by the enzyme, 5 alpha reductase. 5 Alpha Reductase Inhibitors 5 Alpha Reductase Inhibitors DHT Provides the major growth stimulus for prostatic tissue due to its 4-5 fold higher affinity for the prostatic androgen receptor compared to testosterone Other anti-androgenic agents have been investigated, but most lead to decreased levels of testosterone as well as DHT (think Lupron in prostate cancer) 5 Alpha Reductase Inhibitors Low testosterone (abnormal testosterone to estradiol ratios) Intolerable sexual side effects: erectile dysfunction, decreased libido Also: gynecomastia and hot flashes Thus, the development of 5 ARI’s to improve LUTS without sexual side effects associated with reduction in testosterone levels 5 Alpha Reductase Inhibitors Side Effects: Impotence Decreased libido Decreased ejacualte Breast enlargement Hot flashes 5 Alpha Reductase Inhibitors Finasteride (Proscar) Results in 80-90% reduction of type II 5 alpha reductase within the prostate. Decreased intraprostatic DHT there is reduction of epithelial (static) glandular tissue volume with resultant decrease in total gland volume (~20-30%) Note finasteride (static) vs Flomax (dynamic) 5 Alpha Reductase Inhibitors Development of dutasteride (Avodart) Hypothesis that inhibition of both Type I & Type II 5 alpha reductase may increase efficacy of tx of BPH Thus, dutasteride (second generation) that inhibits both types In comparison to finasteride, it suppresses DHT production by 93% (finasteride 70%, but objective and subjective urinary tract effects are the same. 5 Alpha Reductase Inhibitors Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial (PCPT) Results: Prostate cancer was detected in 24.4% of controls and only 18.4% of treated patients First time a treatment was shown to prevent or delay the appearance of prostate cancer However, also noted that the proportion of Gleason 7 or higher tumors was greater in the finasteride group. 5 Alpha Reductase Inhibitors REDUCE Trial Chemoprevention for prostate cancer 8,200 men 4 year trial Double-blind placebo 23% reduction in risk of prostate cancer No increased risk of aggressive tumors like PCPT. Combination Therapy Veteran’s Affairs Cooperative Study 1996 Placebo, Finasteride, Terazosin, and Combo 1229 patients, Double Blind Placebo Controlled Showed significant improvement in AUA symptom scores in terazosin and combo therapy groups. Since they had similar improvements, it was determined that the finasteride had no benefit Thus, alpha blockade (Flomax) had superiority over finasteride at 1 year. Combination Therapy Medical Therapy of Prostatic Symptoms (2001) Can medical therapy prevent or delay the progression of BPH in the long term. 5 years out: Combination of Doxazosin and Finasteride exerts a clinically relevant, positive effect on rates of disease progression. Combination Therapy Combination of Dutasteride and Tamsulosin (2003) by Barker et. al. Combo for 24 weeks, then withdrew the Tamsulosin for 12 weeks. Patients with IPSS score <20: 84% continued monotherapy without worsening of symptoms IPSS scores >20: 42% had worsening of symptoms Concluded that combo therapy allows alpha blockers to provide more rapid relief and 5 alpha reductase inhibitors for long-term treatment. Start with combo, patients with less severe symptoms can stop alpha blocker; more severe continue combo Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors Cialis 5mg daily Decreases the smooth muscle tone in the bladder, prostate and urethra (like Flomax) SE include back/muscle aches, GERD, and headaches and strengthening of erections. Good combination Rx Nice for ED, not for the patient-physicianinsurance company relationship Minimally Invasive Therapy Transurethral Microwave Procedures Microwaves are sent through a catheter to at least 111 degrees Cooling system protects the urinary tract Outpatient Reduces: frequency, urgency, straining, and intermittent flow Does NOT correct incomplete emptying Long term effects are still unknown Minimally Invasive Therapy Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA) Low-level radiofrequency energy through twin needles to burn away selected areas of the prostate Shields protect the urethra Improves urine flow and relieves symptoms Conventional Surgical Therapy Indications for surgery Urinary retention from BPH, medical refractory Gross hematuria from BPH Bladder stones UTI’s Renal Insufficiency/hydronephrosis Conventional Surgical Therapy Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) “Gold Standard” 60-90 minutes General or Spinal Wire Loop Complications: Infertility, UTI, Bladder stones, gross hematuria, retrograde ejaculation, urethral strictures or bladder neck contractures. Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Variation of TURP Instead of removing prostate tissue, small cuts are made in bladder neck Shorter operative time Good for short glands, men who have had radiation therapy and are at risk for incontinence or wish to preserve fertility Transurethral Laser Surgery Transurethral Laser Surgery Usually a side-firing laser is placed through cystoscope Holmium, Greenlight/PVP, Thullium Laser destroys/vaporizes prostatic tissue As good as a TURP with similar potential complications Conventional Surgical Therapy Surgical “Open” Prostatectomy In cases where the prostate is too large for a TURP or if the bladder has very large stones Open incision or with DaVinci Robot Opens the prostatic capsule and scoops out the prostatic tissue Other treatments UroLume urethral stent Migration, worsening irritative symptoms Encrustation and prostatic ingrowth Intraprostatic ethanol and Botox injections Performed via transrectal ultrasound Summary Diagnosis Subjective and Objective findings Medical Treatment Indications for surgery Types of Surgery Questions?