extensor pollicis brevis
advertisement

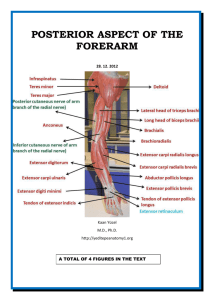
1 2 In two layers: a superficial layer a deep layer. 3 Brachioradialis Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor carpi radialis brevis Extensor carpi ulnaris Extensor digitorum Extensor digiti minimi Anconeus Lateral epicondyle of humerus Supraepicondylar ridge Supraepicondylar Lateral epicondyle ridge of humerus Lateral epicondyle of humerus Lateral epicondyle of of (common humerus extensor origin) flexion extend of and forearm abduct of humerus humerus; posterior Extends and adducts hand attriceps the wrist assists in extending (common extensor border of ulna hand at wrist Lateral surface of extends medialjoint four joint forearm origin) olecranon and at digits primarily stabilizes elbow joint; Extend and superior part of metacarpophalangeal may abduct ulnaatduring abduct hand posterior surface of at joints, secondarily Extensor pronation the wrist join ulna interphalangeal joints expansion of Extensor expansions 5th digit Lateral surface of medial four of digits distal end of radius Base of Base Base of 3rd 5th of 2nd Base of 3rd metacarpal proximal to styloid Baseof ofmetacarpal 5thmetacarpal metacarpal Base 2nd metacarpal metacarpal process Common origin from the supraepicondylar ridge and lateral epicondyle of the humerus Except for the brachioradialis and anconeus, extend as tendons 4 into the hand. Supinator Abductor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis brevis Extensor pollicis longus Extensor indicis Except for the supinator muscle, all these deep layer muscles originate from the posterior surfaces of the radius, ulna, and interosseous membrane and pass into the thumb and fingers. 5 6 Supinator Extensor carpi radialis brevis Deep branch of radial nerve Rest Posterior interosseous nerve continuation of deep branch of radial nerve 7 Radial artery Posterior interosseous artery origin: common interosseous branch of the ulnar artery recurrent interosseous artery End by joining to dorsal carpal arch of the wrist Anterior interosseous artery origin: common interosseous branch of the ulnar artery 8 Deep branch becomes posterior interosseous nerve after emerging from between 2 heads of supinator Posterior interosseous nerve passes deep to extensor pollicis longus to reach the wrist. 9 10 11 The carpal tunnel formed anteriorly at wrist by a deep arch formed by carpal bones & flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament) Flexor digitorum/superficialis Flexor pollicis longus Median nerve Pass through the carpal tunnel 12 The extensor tendons pass into the hand in six compartments defined by an extensor retinaculum: extensor digitorum & extensor indicis posterior surface of the wrist extensor carpi ulnaris & extensor digiti minimi medial side of the wrist abductor pollicis longus & extensor pollicis brevis extensor carpi radialis longus & extensor carpi radialis brevis extensor pollicis longus through three compartments on the lateral surface of the wrist. 13 A triangular condensation of deep fascia that covers the palm and is anchored to the skin in distal regions. Continuous with the palmaris longus tendon, when present; otherwise, anchored to the flexor retinaculum. 14 Tendons of the extensor digitorum extensor pollicis longus muscles expand over the proximal phalanges to form "extensor hoods" or "dorsal digital expansions". Tendons of the extensor digiti minimi, extensor indicis, extensor pollicis brevis join these hoods. 15 Palmaris brevis Thenar muscles Hypothenar muscles Adductor pollicis Lumbrical Abductor digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi Abductor pollicis brevis Opponens pollicis Flexor pollicis brevis Interossei 16 All of the intrinsic muscles of the hand by deep branch of the ulnar nerve Except three thenar & two lateral lumbrical muscles by median nerve 17 Superficial Deep palmar arch palmar arch 18 Cephalic vein originates from lateral side of dorsal venous network. Basilic vein originates from medial side of dorsal venous network. 19 Ulnar nerve medial side of the palm, medial half of the dorsum of the hand, the 5th finger, and the medial half of the 4th finger, anterior surfaces of the medial one and a half digits, Median nerve thumb,index,middle fingers,lateral side of the ring [distal parts on the dorsum of the hand] 20 Radial nerve dorsolateral side Homework: 1. Which structures pass through the carpal tunnel and their anatomical relationships with each other in the tunnel? 2. The incidence of carpal tunnel syndrome in the world and/or in Turkey? 3. The risk factors, higher in whom? Any gender disperancies in its incidence? Please send answers to yeditepeanatomy@yahoo.com 21 22