seeing beyond vision loss
Diabetic Retinopathy Basics: Objectives
Participants will learn about:
•
Anatomy of the eye
•
Diabetic retinopathy defined
•
Signs and symptoms
•
Types of diabetic retinopathy
•
Risk factors and prevention
•
Diagnostic tests
•
Treatment seeing beyond vision loss
Anatomy of the Eye
The retina – senses light & transmits images to the brain
The macula – central part of the retina used to read and see fine details clearly
The vitreous – clear gel fills the back of the eye and sits in front of the retina
Figure 1: The human eye seeing beyond vision loss
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
•
Occurs when elevated blood sugar levels cause blood vessels in the eye to swell and leak into the retina.
seeing beyond vision loss
Figure 2: Diabetic macula edema
(swelling of the retina)
Signs and Symptoms
Figure 3: Normal Vision
• Floaters
• Blurred vision
• Blank or dark areas in field of vision
• Poor night vision
• Vision loss
Figure 4: How vision may be affected by diabetic retinopathy seeing beyond vision loss
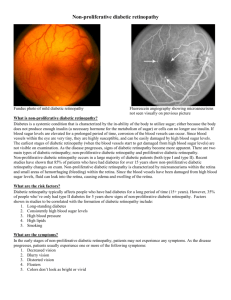
Types of Diabetic Retinopathy
Early stages:
Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR)
• Damaged blood vessels in the retina begin to leak fluid and small amounts of blood and cholesterol.
• Mild NPDR may not necessarily affect vision.
• Results of blurred vision:
Fluorescein dye leaking in macula
Figure 5: Macula edema seeing beyond vision loss
Figure 6: Fluorescein angiogram of macular edema
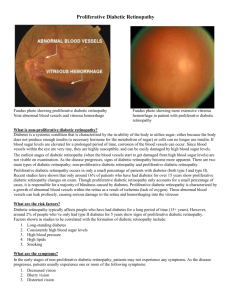
Types of Diabetic Retinopathy
Late stages:
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
•
Retinal vessels close causing significant reduction in blood flow.
•
The retina responds by growing new abnormal vessels.
•
Can affect both central and peripheral vision.
Vitreous hemorrhage
New blood vessels bleed into vitreous cavity.
Tractional retinal detachment
Scar tissue can shrink causing the retina to detach and result in vision loss. More severe vision loss occurs if the macula is detached.
Figure 7: Tractional retinal detachment seeing beyond vision loss
Risk Factors/Prevention
•
• Diabetes type
Ethinicity
• High blood sugar
• Smoking
• High blood pressure
• High cholesterol
• Obesity
Early detection via eye exams is paramount
Type 1 diabetes: within 5 years of diagnosis, then annually
Type 2 diabetes: at time of diagnosis, then annually
Gestational diabetes: within 1 st trimester seeing beyond vision loss
Diagnostic Tests
Basic assessment
• Visual acuity test
• Tonometry: Measures pressure inside the eye
• Dilated eye exam
Advanced assessment
• Fluorescein angiogram: dye is injected systemically which demonstrates retinal circulation
• Optical coherence tomography
(OCT): non-invasive imaging study that reveals retinal anatomy
Figure 8: Fluorescein angiogram
Figure 9: Optical coherence tomography (OCT) seeing beyond vision loss
Treatments
Proliferative retinopathy
Laser surgery
• Microscopic thermal laser burns are made in the retina
• Shrinks and prevents abnormal new blood vessel growth, and stops leaking of blood vessels
• Can reduce risk of further vision loss by 50%
• Also recommended to treat macular edema
Figure 10: Laser photocoagulation seeing beyond vision loss
Treatments
Proliferative retinopathy
Intraocular (anti-VEGF) injections
• Reduces swelling in the retina and causes abnormal vessels to regress
Figure 11: Intraocular injection seeing beyond vision loss
Treatments
Diabetic macular edema
Lucentis
•
Health-Canada-approved anti-VEGF treatment
•
Approved for reimbursement in Quebec only seeing beyond vision loss
Treatments
Advanced proliferative retinopathy
Vitrectomy
• Cloudy vitreous is removed and replaced with a clear solution that mimics the normal eye fluids
• Allows light rays to focus on the retina again seeing beyond vision loss
Figure 12: Pars plana vitrectomy