Unit 4: Nervous System
Lab 3: Cranial/Spinal Nerves &
Lab 4, Part 1: Introduction to the Eye
Jessica Radke-Snead, RD, MS
Bio 241 Anatomy & Physiology
Reminders
• Today’s Lab
– Cranial and spinal nerves
– Introduction to Lab 4
• Wednesday
– Human eye/vision
– Histology of the retina
– Human ear and physiological aspects of hearing
– Histology of the cochlea
– Visual acuity tests (observe on your own)
– Hearing tests (observe on your own)
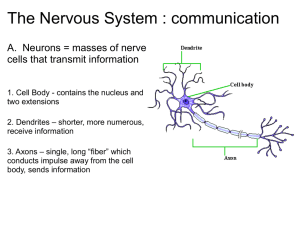
I Olfactory Nerve
Type: Sensory
Function: Smell (olfaction)
Olfactory receptors (olfactory epithelium)
extend through olfactory foramina (cribiform
plate, ethmoid bone) and collectively form the
right and left olfactory nerves and olfactory
bulbs. Axons of the olfactory tracts end in the
primary olfactory area (temporal lobe).
II Optic Nerve
Type: Sensory
Function: Vision
1. Eye, rods and cones
initiate visual signals
2. Signals relayed via optic
nerve, which merge to
form the optic chiasm
(optic foramina) and
optic tracts (posterior)
3. Axons from optic tracts
project to the primary
visual area (occipital
lobe)
III Oculomotor, IV Trochlear and
VI Abducens Nerves
Type:
Motor axons that exit the
brain stem.
Sensory axons (extrinsic
eyeball muscles) initially
travel through each of these
nerves and enter the
midbrain (V Trigeminal
nerve).
Function: Pass through Sup
Orb Fissure to control the
muscles that move the
eyeballs.
Sensory: proprioception
(non-visual perception)
III Oculomotor
“eye-mover”
• Type: Motor and Sensory
• Extends from midbrain (junction with pons)
• Somatic motor axons innervate:
– Extrinsic eyeball muscles (SR, MR, IR & IOb) Eyeball
movement
– Levator palebrae superioris raising the upper lid
• Autonomic motor axons innervate intrinsic
eyeball muscles (Ciliary) adjust the shape of
the lens and iris to adjust the size of the pupil
IV Trochlear Nerve
“pulley”
• Type: Motor and Sensory
• Posterior side of midbrain, wraps around the
pons
• Somatic motor axons innervate extrinsic
muscle (SOb) movement of the eyeball
– Trochlea: cartilage that supports the “pulley”
action of the SOb, thus nerve is called “trochlear”
VI Abducens Nerves
“Away to lead”
• Type: Motor and Sensory
• Originates in the pons
• Somatic motor axons innervate extrinsic
muscle (LR) lateral rotation of eyeball
– “ABDuction” or lateral movement of eye =
ABDucens nerve
V Trigeminal Nerve
“triple branches”
Type: Motor and Sensory
Function:
Sensory axons
• Touch, pain and temp pons
• Proprioceptors in the jaw
Motor axons supply jaw muscles for
mastication
3 Branches:
1. Ophthalmic (exits through Sup
Orb Fissure)
2.
Maxillary (exits through foramen
rotundum)
3.
Mandibular (exits through
foramen ovale)
V Trigeminal Nerve
“triple branches”
• Ophthalmic nerve
– Sensory axons from the upper eyelid, eyeball, lacrimal
glands, nasal cavity, nose, forehead and anterior scalp
• Maxillary nerve
– Sensory axons from the nose, palate, upper mouth
and lower eyelid
• Mandibular nerve
– Sensory axons from the anterior tongue (not taste),
cheek, skin over the jaw and side of the head and
lower mouth
VII Facial Nerve
Type: Motor and Sensory
Sensory axons:
• Touch, pain and temperature
from ear canal
• Proprioception from face and
scalp muscles
Motor neurons (pons) innervate
facial, scalp and neck muscles for
facial expression
Autonomic motor neurons
innervate lacrimal and salivary
glands
VIII Vestibulocochlear Nerve
“small, spiral/snail like”
VIII Vestibulocochlear Nerve
“small, spiral/snail like”
Type: Sensory
• 2 Branches
– Vestibular: impulses for equilibrium from the
semicircular canals, saccule and utricle of the
inner ear to the pons and cerebellum
– Cochlear: impulses for hearing from the spiral
organ of the inner ear to the primary auditory
area (temporal lobe)
IX Glossopharyngeal Nerve
“tongue, throat”
IX Glossopharyngeal Nerve
“tongue, throat”
Type: Motor and Sensory
Sensory axons
– Arise from taste buds (posterior tongue) and external
ear to convey touch, pain and temperature
– Proprioceptors in swallowing muscles
– Neck region: info from baroreceptors (carotid sinus) that
monitor BP and chemoreceptors (carotid bodies) that
monitor blood gas
Motor axons
– Arise in medulla oblongata, pass through the jugular
foramen to innervate muscle in pharynx for swallowing
– Autonomic axons stimulate the parotid gland (saliva)
“vagrant, wanderer”
X Vagus Nerve
X Vagus Nerve
“vagrant, wanderer”
Type: Motor and Sensory
Sensory axons arise from:
–
–
–
–
–
–
External ear: touch, pain and temperature
Taste buds (throat)
Proprioceptors in muscles of the neck and throat
Carotid sinus: monitor BP
Carotid body and aortic bodies: monitor blood gas levels
Organs (thoracic, abdominal cavities): hunger, fullness and
discomfort
Sensory axons pass through jugular foramen Medulla
oblongata
X Vagus Nerve
“vagrant, wanderer”
Type: Motor and Sensory
Motor neurons: muscles of the pharynx and
larynx for speech and swallowing
Autonomic motor neurons: lungs, heart and
smooth muscle and glands of the respiratory
passageways and GI tract
XI Accessory Nerve
“assisting”
XI Accessory Nerve
“assisting”
Type: Motor and Sensory
Motor axons
– Arise in the anterior gray horn of the spinal cord (cervical
portion)
– Exit the spinal cord laterally
– Enter the foramen magnum
– Exit through the jugular foramen (along with IX and X)
why it’s considered a cranial vs spinal nerve
Convey impulses to the SCL and trapezius muscles
coordinate head movements
XI Accessory Nerve
“assisting”
Type: Motor and Sensory
Sensory axons arise from
– Proprioceptors in the SCL and trapezius muscles
– Eventually join nerves at the cervical plexus
Enter the spinal cord Medulla oblongata
XII Hypoglossal Nerve
XII Hypoglossal Nerve
Type: Motor and Sensory
Motor neurons originate in the medulla oblongata
hypoglossal canal tongue muscles for speech
and swallowing
Sensory axons originate from proprioceptors in the
tongue muscles extend toward the brain
(hypoglossal nerve) then leave hypoglossal nerve to
join the cervical spinal nerves medulla oblongata
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
• Posterior root + Anterior root = spinal
nerve at the vertebral foramen
– Posterior root contains sensory axons
– Anterior root contains motor axons
Spinal Nerves
• Spinal cord ends near the L2 vertebrae
• Roots of the lumbar, sacral and coccygeal nerves
descend at an angle vertebral foramina (caudal
equina)
• 31 pairs of spinal nerves
– Identified by the region and level of vertebral column
from which they emerge
– 8 pairs cervical
– 12 pairs thoracic
– 5 pairs lumbar
– 5 pairs sacral
– 1 pair coccygeal
Anatomy of Spinal Nerves
• Upon passing through its
intervertebral foramen, a
spinal nerve divides into
branches (rami)
– Posterior ramus: serves the
muscles and skin of the
posterior trunk
– Anterior ramus
• Muscles and structures of
the upper and lower limbs
• Skin of the lateral and
anterior trunk
Rami communicantes
– Meningeal branch:
vertebrae, spinal cord and
meninges
– Rami communicantes:
components of the ANS
Plexuses
• Network of axons formed on both sides of the
body by joining with various numbers of axons
• Names often describe the general regions
they serve or the course they take
• Primary plexuses
– Cervical
– Brachial
– Lumbar
– Sacral
Thoracic nerves T2-T12 follow each rib laterally
and do not form plexuses
Cervical Plexus
Cervical Plexus
• Formed via C1-C4, part of C5, nerves
• Supplies:
– Skin and muscles on the head, and neck
– Superior part of the shoulders and chest
• Important nerve arising from this plexsus
– Phrenic (spinal nerves C3-C5)
• Motor nerve: Diaphragm
Brachial Plexus
• Formed by C5-C8 and T1 spinal nerves
• Provides majority of the nerve supply to the shoulders and limbs
• Complex structure: Roots Trunks Divisions Cords Branches
Brachial Plexus
• From the cords, important nerves are:
– Axillary (C5-C6)
• Motor nerve: Deltoid and Teres minor
• Sensory nerve: Lateral arm to the deltoid tuberosity
– Radial (C5-T1)
• Motor nerve: Triceps, Supinator, Brahcioradialis
• Sensory nerve: Posterior arm and forearm, medial side of posterior
hand
– Median (C5-T1)
• Motor nerve: Pronator teres and Flexor carpi radialis
• Sensory nerve: Palmar aspect of 2nd-4th fingers
– Ulnar (C8-T1)
• Motor nerve: Flexor carpi ulnaris
• Sensory nerve: Medial portion of 4th and entire 5th finger
Lumbar Plexus
• Formed by L1-L4 spinal nerves
• Supplies the
– Anterior and lateral abdominal wall
– External genitals
– Part of lower limbs
Lumbar Plexus
• Important nerves arising from
this plexus are:
– Femoral (L2-L4)
• Motor nerve: Iliacus, Pectineus,
Quadriceps femoris and Sartorius
• Sensory nerve: Skin of the lateral
anterior thigh and dorsum of the
foot
– Genitofemoral (L1-L2)
• Motor nerve: Cremaster muscle
• Sensory nerve: Skin of the medial
and anterior thigh, scrotum
(male) or labia major (female)
Sacral Plexus
Sacral Plexus
• Formed by L4-S4 spinal nerves
• Supplies the buttocks, perineum and lower limbs
• Important nerves that arise are
– Pudendal
• Motor nerve: Ischiocavernosus, Bulbospongiosus, Levator
ani and External anal sphincter
• Sensory nerve: Skin of the penis and scrotum, clitoris, labia
major and minora, vagina
– Sciatic (posterior)
• Branches into tibial and fibular nerves
• Motor nerve: Semimembranosus, Semitendinosus, Biceps
femoris, Adductor magnus
• Sensory: Lateral posterior leg, lateral aspect and plantar
surface of the foot
Introduction to the Human Eye
•
•
•
•
Surface anatomy
Extrinsic and intrinsic eye muscles
Layers forming the posterior wall of the eye
Internal anatomy of the eye
– Posterior/vitreous cavity
– Anterior cavity
Review on your own
• Extrinsic eye muscles
– Medial rectus, Superior rectus, Lateral rectus, Inferior
rectus, Superior oblique, Inferior oblique and Levator
palpebrae superioris
• Intrinsic eye muscles
– Via Oculomotor nerve (cranial)
– Circular iris muscle: (parasympathetic; bright light) pupil
constriction
– Radial iris muscle: (sympathetic; dim light, action) pupil
dilation
– Ciliary muscle: smooth muscle that changes the
tightness of zonular fibers to change shape of the lens
Surface anatomy of the Eye
Tarsal plate
Surface Anatomy of the Eye:
Eyelids
• Eyelid/Palpebrae
– Tarsal plate: elongated dense CT that forms the shape of
each palpebrae
– Levator palpebrae superioris: raises the upper lid
– Oribicularis oculi: closes the eyelid
• Superior and inferior palpebral sulci: upper and
lower lid creases
• Conjunctiva: protective mucous membrane
– Palpebral: lines each eyelid
– Bulbar: from eyelids into the anterior surface of the
eyeball and covers the sclera
Structures of the Eyeball
• Fibrous tunic (avascular outer layer)
– Cornea: admits and refracts light
– Sclera: provides shape and protection
• Vascular tunic (middle layer)
– Iris: regulates amount of light that enters the eyeball
– Ciliary body: secretes aqueous humor and alters
shape of lens for near/far vision
– Choroid: provides blood supply and absorbs scattered
light (melanin)
Structures of the Eyeball
• Retina (inner layer)
– Receives light receptor potentials and nerve impulses
– Provides output to the brain via axons (ganglion cells)
optic nerve
• Macula lutea: highly pigmented spot near the center of
the retina
• Fovea centralis: small pit that contains cones (color
vision); area of highest visual acuity (sharpness)
– Move head and eyes to place images on this point
– No rods—periphery of retina; more light sensitive—why
you can see a dim star better if you look just to the side of
it
Internal anatomy of the Eye
• Lens: refracts light and focuses images on the retina
to facilitate vision
• Posterior/vitreous cavity (lens to wall of retina)
– Vitreous body helps maintain the shape of the eyeball
and supports retinal attachment to the eyeball
• Anterior cavity (cornea to lens)
– Aqueous humor helps maintain shape of eyeball and
supplies oxygen and nutrients to lens and cornea
Objectives
• Today’s Lab 3
–
–
–
–
–
–
Cranial and spinal nerves
Surface anatomy of the eye
Intrinsic muscles of the eye
3 layers of the eye
Internal anatomy of the eye
Lacrimal apparatus (if time permits)
• Wednesday
–
–
–
–
–
–
Human eye/vision
Histology of the retina
Human ear and physiological aspects of hearing
Histology of the cochlea
Visual acuity tests (observe on your own)
Hearing tests (observe on your own)