PPT - UCLA Head and Neck Surgery
advertisement

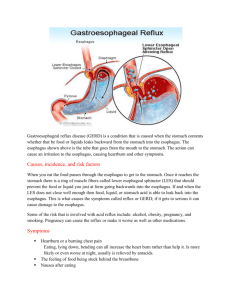
Esophagus Anatomy, Physiology, and Diseases Alan Chu March 13, 2013 Anatomy 18 – 26cm from UES to LES Esophageal wall layers Mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propia, adventitia Proximal 33% skeletal muscle, middle 35-40% mixed, distal 50-60% smooth muscle Smooth muscle innervated by CN X. Auerbach plexus: peristalsis Meissner’s plexus: afferent input Oropharyngeal dysphagia Difficulty initiating swallow followed by choking/coughing Esophageal dysphagia Anatomaic vs neuromuscular defect Solid vs solid+liquid dysphagia Dysphagia best assessed by MBSS Demonstrates presence of oropharyngeal dysfunction and aspiration Standard upper endoscope 9mm, transnasal endoscope 4mm Z line = GE junction In barrett’s squamocolumnar junction more proximal than GEJ Esophageal Motility disorder Acalasia Insufficient LES relaxation Dilated distal 2/3 esophagus with bird’s beak appearance at LES on esophagram Upper endoscopy to r/o pseudoachalasia 2/2 to GEJ tumor Tx: balloon dilation to disrupt circular muscle fibers at LES; Heller’s myotomy via laproscopic approach; Botox/CCB/nitrates Esophageal Motility Disorder Diffuse Esophageal Spasm Simultaneous and repetitive contraction in esophagus body with normal LES Cockscrew esophagus on esophagram Tx:nitrates/CCB Nutcraker esophagus High-amplitude peristalsis Ineffective esophageal motility High incidence in patients with GERD Strictures Dysphagia when <15mm Tx: dilators (Bougies, Savary dilator, balloon dilator) Risk of perforation 0.5%, higher in XRT induced strictures Goal >15mm Rings or Webs Ring Circumferential, muscle or mucosa, at distal esophagus Schatzki’s ring Eosinophilic Esophagitis (>15 eosinophils/hpf in mucosa) Web Part of lumen, mucosal, proximal esophagus Plummer Vinson GERD Chronic symptoms 2/2 abnormal reflux of gastric contents Heartburn, acid regurgitation, dysphagia, odynophagia, belching Tx: lifestyle modification, H2 blockers (60%), PPI (90%), surgery Atypical extraesophgeal symptoms: asthma, chest pain, cough, laryngitis, dental erosion Barrett’s esophagus Pale pink squamous mucosa replaced with salmon pink columnar mucosa LSBE vs SSBE (<3cm) Risk of esophageal adenoCA 0.5% per year Neoplasia AdenoCA Distal esophagus or GEJ Barrett’s SCC Mid-esopahgus and proximal esophagus Tobacco, EtOH use in AA Diverticula Zenker’s diverticulum Midesophageal diveticula Epiphrenic diverticula Intramural pseudodiverticulosis Transnasal Esophagoscopy Alan Chu March 13, 2013 Transnasal esophagoscope 3.1 – 5.1mm Performed without sedation Shorter procedure time 66% cost of transoral esophagoscope Conventional Transoral esophagoscope 10 - 12mm Performed with sedation Longer procedure time Transnasal esophagoscope Smaller biopsy size Conventional Transoral esophagoscope Indications Head and Neck SCC Replaces panendoscopy Barrett’s esophagus Surveillence Stricture dilation Balloon of Barrett’s esophagus dilation Tracheoesophageal puncture Technique Topical anesthetic and decongestant Pt’s head flexed and swallows as scope approaches cricoid level Z-line (squamocolumnar junction) visualized Retroflex view of gastric cardia