Document
advertisement
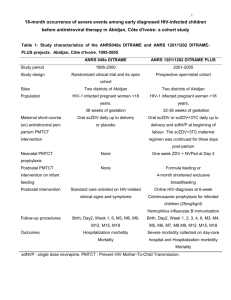
ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 trial The CAMELIA trial CAMbodian Early vs. Late Introduction of Antiretrovirals F.X. Blanc, T. Sok, D. Laureillard, L. Borand, C. Rekacewicz, E. Nerrienet, Y.Madec, O. Marcy, S. Chan, N. Prak, C. Kim, K.K. Lak, C. Hak, B. Dim, C.I. Sin, S. Sun, B. Guillard, B. Sar, S. Vong, M. Fernandez, L. Fox, J.F. Delfraissy, A.E. Goldfeld. 22nd July 2010 Late Breaker Session B-1, XVIII IAS Conference, Vienna, Austria HAART in TB-HIV: Early or late? START TB TREATMENT AND HAART SIMULTANEOUSLY START TB TREATMENT FIRST AND DELAY HAART PROS PROS Lower risk of HIV disease Avoid overlapping side effects progression or death in advanced Avoid PK interactions patients (CD4 < 50 cells/mm3) Lower pill burden Lower risk of IRIS CONS CONS Overlapping side effects PK interactions Higher pill burden Risk of immune reconstitution disease Higher risk of HIV disease progression or death in advanced patients (CD4 < 50 cells/mm3 ) Adapted from J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2007; 46: S9-S18. WHO recommendations 2003: CD4 < 200/mm3: - Start TB treatment. - Start ART as soon as TB treatment is tolerated (between 2 weeks and 2 months) - Efavirenz-containing regimens 2010: - Start ART in all HIV-infected individuals with active TB, irrespective of the CD4 cell count. Strong recommendation, low quality of evidence. - Start TB treatment first, followed by ART as soon as possible afterwards (and within the first eight weeks). Strong recommendation, moderate quality of evidence. - Use efavirenz as the preferred NNRTI in patients starting ART while on TB treatment. Strong recommendation, high quality of evidence. CAMELIA study design (2003-2004) - Prospective, randomized, open-label, two-armed trial with no placebo - Designed as a superiority trial to answer the question of the best timing for the introduction of HAART in severely immunosuppressed (CD4 ≤ 200/mm3) HIV-infected adult patients with newly diagnosed TB in Cambodia - 2 arms: late introduction of ART (reference arm: 8 weeks) vs. early (2 weeks) introduction of the same HAART - Primary endpoint: survival at the end of the trial (intent-totreat analysis) ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study CAMELIA strategy Switch D4T to AZT ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study CAMELIA key points - 2 sponsors: French ANRS and U.S. NIH/DAIDS (CIPRA) - Partnership with Cambodian Health Committee - 5 study sites (rural and urban) in Cambodia - 661 patients were AFB+ at inclusion (pulmonary or extra- pulmonary TB) with CD4 ≤ 200/mm3 - 1st patient enrolled on January 31st 2006 - 6 DSMB meetings - Last patient enrolled on May 27th 2009 - End of the study: May 2010 ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study CAMELIA recruitment 778 patients screened 661 patients randomized 332 randomized to the EARLY arm 282 38 culture + culture M.tb 12 NTM 117 patients not enrolled due to: - CD4>200 (n=78) - LFT impairment (n=24) - pregnancy (n=3) - TB treatment >1month (n=2) - CD4 >200 & LFT impairment (n=2) - death before randomization (n=2) - pregnancy & LFT impairment (n=1) - no CD4 at enrolment (n=1) - high bilirubine (n=1) - delay in blood sampling (n=1) - CD4>200 & pregnancy (n=1) - ART history & LFT impairment (n=1) 329 randomized to the LATE arm 294 31 culture + culture M.tb 4 NTM M.Tb: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; NTM: nontuberculous mycobacteria ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study Patient characteristics at enrollment Early arm (N=332) Gender Male Female Age, years Median (IQR) BMI, kg/m2 Median (IQR) Karnofsky score ≥80 50-70 ≤40 CD4, cells/mm3 Median (IQR) Viral load, log copies/mL Median (IQR) Late arm (N=329) p 0.80 215 (64.8) 117 (35.2) 210 (63.8) 119 (36.2) 0.38 35 (30 – 41) 36 (30 – 42) 0.90 16.7 (15.3 – 18.3) 16.8 (15.2 – 18.6) 0.83 43 (13.0) 259 (78.0) 30 (9.0) 44 (13.4) 251 (76.3) 34 (10.3) 0.61 25 (11 – 56) 25 (10 – 55) 0.25 5.60 (5.20 – 6.02) 5.66 (5.25 – 6.00) ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study Characteristics of tuberculosis Early arm (N=320) Location of TB Pulmonary Pulmonary & extra-pulmonary Extra-pulmonary Drug resistance None Isoniazid (INH) monoresistance Streptomycin monoresistance Rifampin monoresistance INH polydrug resistance Multidrug resistant (MDR) No DST Missing Late arm (N=325) p 0.97 221 (69.1) 71 (22.2) 28 (8.7) 222 (68.3) 73 (22.5) 30 (9.2) 0.10 217 (67.8) 23 (7.2) 17 (5.3) 3 (0.9) 16 (5.0) 6 (1.9) 37 (11.6) 1 (0.3) 240 (73.8) 10 (3.1) 10 (3.1) 4 (1.2) 24 (7.4) 7 (2.2) 30 (9.2) ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study SIGNIFICANT REDUCTION OF MORTALITY IN THE EARLY ARM N Deaths Follow-up time* Mortality rate** (95% CI) Early arm 332 59 712.4 8.28 (6.42 – 10.69) Late arm 329 90 653.7 13.77 (11.20 – 16.93) p 0.002 * expressed in person-years ** per 100 person-years 12 patients (1.8%) lost to follow-up. 8,955 protocol visits, <2% missed visits. ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study Kaplan-Meier survival curves 1.00 0.95 0.90 0.85 0.80 0.75 0.70 0.65 Log-rank p-value: p=0.0042 0.60 0 50 100 150 200 Time from TB treatment initiation (weeks) Early arm 250 Late arm Survival probability (95% CI) Early arm Late arm Log-rank p-value Week 50 86.1 (81.8 – 89.4) 80.7 (76.0 – 84.6) 0.07 Week 100 82.6 (78.0 – 86.4) 73.0 (67.7 – 77.6) 0.006 Week150 82.0 (77.2 – 85.9) 70.2 (64.5 – 75.2) 0.002 ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study Factors independently associated with mortality Multivariate analysis Adjusted HR (95% CI)* p Arm Early Late 1 1.52 (1.12 – 2.05) 0.007 BMI ≤16 16-17 17-18.5 >18.5 1.68 (1.07 – 2.63) 0.93 (0.53 – 1.60) 1 1.11 (0.66 – 1.87) 0.01 Karnofsky score ≥80 50-70 ≤40 1 1.78 (0.97 – 3.26) 4.96 (2.42 – 10.16) <0.001 TB identification and location* Pulmonary Extra-pulmonary Pulm. and extra-pulm. NTM 1 1.19 (0.68 – 2.07) 2.26 (1.62 – 3.16) 2.84 (1.13 – 7.13) <0.001 Drug resistance No** Yes Yes, MDR 1 0.98 (0.63 – 1.51) 8.02 (4.00 – 16.07) <0.001 Cox proportional hazard model * Also adjusted for site and CD4 level at baseline (stratification factors) ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study IRIS significantly more frequent in the early arm N PR/IRIS Follow-up time* Incidence** (95% CI) Early arm 332 110 2 728.5 4.03 (3.34 – 4.86) Late arm 329 48 3 333.5 1.44 (1.09 – 1.91) p <0.0001 * expressed in person-months ** per 100 person-months 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 0.00 Time aftre TBTBtreatment initiation (weeks) Time after treatment initiation (weeks) Early arm Late arm ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study >95% undetectable viral load at week 50 W26 W50 W78 W102 W126 W150 Early arm Undetectable VL VL > 250 copies/mL Not available 259 (90.2) 25 (8.7) 3 (1.1) 264 (95.6) 9 (3.3) 3 (1.1) 184 (93.0) 6 (3.0) 8 (4.0) 173 (93.5) 7 (3.8) 5 (2.7) 142 (93.4) 6 (4.0) 4 (2.6) 111 (95.7) 3 (2.6) 2 (1.7) Late arm Undetectable VL VL > 250 copies/mL Not available 241 (88.3) 25 (9.2) 7 (2.5) 237 (95.6) 9 (3.6) 2 (0.8) 145 (91.8) 8 (5.1) 5 (3.1) 143 (92.9) 5 (3.2) 9 (3.9) 126 (96.2) 3 (2.3) 2 (1.5) 96 (96.0) 1 (1.0) 3 (3.0) 0.80 0.82 0.34 0.81 0.64 0.63 p Plasma viral load (VL) measured by real time PCR for HIV-1 RNA plasmatic quantification (ANRS kit). ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study CD4 increase from baseline W26 W50 W78 W102 W126 W150 Early N Median (IQR) 283 65 (26 – 125) 273 118 (67 – 191) 189 169 (101 – 270) 180 194 (134 – 299) 148 210 (128 – 324) 115 230 (152 – 321) Late N Median (IQR) 265 59 (14 – 111) 247 112 (53 – 175) 153 165 (88 – 243) 148 177 (106 – 285) 129 187 (119 – 288) 97 201 (127 – 322) 0.11 0.22 0.81 0.19 0.57 0.51 p Week 0: median CD4+ cell count was 25/mm3 Median CD4 increase at week 50: 114/mm3 ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study CONCLUSIONS 1. Mortality was reduced by 34% when HAART was initiated 2 weeks vs. 8 weeks after onset of TB treatment. 2. Irrespective of study arm, HAART has been extremely successful, as evidenced by >95% of patients with undetectable viral load. 3. Despite extremely low CD4+ cell count at inclusion, patients enrolled in this pivotal strategic trial have been extremely adherent. 4. HAART initiation 2 weeks after onset of TB treatment could potentially save 150,000 of the 450,000 annual HIVTB deaths. ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Sponsors: ANRS and NIH/DAIDS Cambodian Health Committee Institut Pasteur du Cambodge Médecins Sans Frontières – Belgium Cambodian Ministry of Health Cambodian National TB Program (CENAT) Cambodian National AIDS Program (NCHADS) Study sites: Khmer-Soviet Friendship Hospital (Phnom Penh), Donkeo Provincial Hospital (Takeo), Calmette Hospital (Phnom Penh), Svay Rieng Provincial Hospital and Siem Reap Referral Hospital Investigators, nurses, technicians, monitors, social workers… Members of the DSMB and the Scientific Advisory Board And especially all the patients and PLWHA representatives who joined us in this challenge. ANRS 1295/12160 - CIPRA KH001/10425 study