Presentation Slides - Colorado Healthcare Associated Risk Managers
advertisement

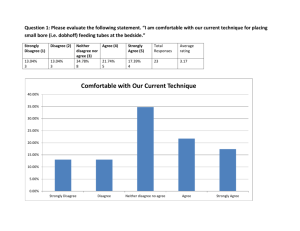
Engaging Families As A Strategy To Advance Quality & Safety Daniel Hyman, MD, MMM September 21, 2012 Family Engagement Objectives • Describe at least two best practices to engage patients/families in quality and safety in your organization • Discuss the benefits of patient/family involvement at the bedside and at system or strategic decision-making levels within your organization. • Begin to develop a plan for advancing the engagement of patients/families in quality/safety programs within 30 days, including recruitment, training and orientation. • And, do you want to talk about “risks”? Adoption of Change History of Family Engagement • From innovation…. To early adoption…. To mainstream Where are we in that arc? • Pursuing Perfection and My personal experience IHI ~2005 • Institute for Patient and Family Centered Care Polly Arango – co-founder Family Voices • MSCH/NYP • Children’s Hospital Colorado http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LkhGoIXsHQo On February 22, 2001, eighteen-month old Josie King died from medical errors. 98,000 people die every year from medical errors, making it the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. The Josie King Foundation’s mission is to prevent others from dying or being harmed by medical errors. By uniting healthcare providers and consumers, and funding innovative safety programs, we hope to create a culture of patient safety, together. www.josieking.org www.josieking.org AHRQ 2012 report AHRQ Report Summary Goal – promote patient/family engagement with tools, resources, materials, training Support the involvement of patients and family members in the safety and quality of their care. Encourage the involvement of patients and family members in improving quality and safety within the hospital setting. Facilitate the creation of partnerships between health professionals and patients/family members. Outline the steps needed to implement changes. Individual involvement • Well accepted by patients and providers Obtaining information, involvement in decision making • Less comfort with confrontational behaviors Hand washing, surgical marking e.g. • Barriers and facilitators + self efficacy, information, support/invite - fear, uncertainty, low literacy, norms Organizational context • External and influences to engaging families in quality/safety • Organizational processes and structures that enable? • Intervention strategies Influencers • Internal Serious events Business case Improvement Altruism • External “steal shamelessly” Policies/regulation Influential advocacy Public reporting Structures/Processes • No evidence that one or another structure is a barrier/enabler of patient/family engagement • Organizational ability to absorb and sustain change, strength of leadership, resource/bandwidth are relevant factors Strategies • Implementation – readiness assessment; shared vision; execution plan; staff engagement; leadership • Hospital level interventions – policies, structures; health care team level; management processes • Individual level interventions – educating, informing, activating patients and providers; facilitate communication at all levels Our story • At the bedside • Microsystem involvement • Organizational involvement Projects Committees and Councils Family Advisory Council Board level Engaging Families at the Bedside: Watchful Eye of the Parent • • At the bedside- listening to families • Family centered rounds • Intentional inclusion in decision making Speak Up!- How it can improve outcomes? • Need measurement strategy Speak Up Hand hygiene! RRTs! Patient Identification! Speak Up Falls! Pressure Injuries! Projects and Service Lines • Initial involvement may best be at project or clinical team level Partnership for Patient Safety (staff education) Hand hygiene Patient Identification Consult and team communication Ambulatory Access Speak Up! • Service Line Quality Committees What Family Advisory Councils Can Provide Hospitals • Parent voice is heard by administration • Activities that are done by active parents • Parent education Family Advisory Council Web Link(s) • MSCH FAC- • CHCO FAC Parent Partnership, Colorado FAMILY ADVISORY COUNCIL Focus Areas 2012: Family Advocacy Policy/Procedure Input Marketing of FAC/partnership opportunities Governance/Quality -Quality/Safety Committee of the Board Councils -Quality safety and Performance Improvement Council -Patient Safety Committee Service Lines, Projects/Initiatives, etc. Heart Institute QI; “Speak Up”; Hand hygiene; Patient ID; teamwork/communication/consult coordination; CF, GEDP; (others are recruiting) “HACs” New! (ADE, CLA-BSI)- Others to follow Experience at Children’s Colorado • Parent placement on multiple committees/councils and projects Selection process- especially important at the start • Recruitment strategies Family Advisory Council Programs themselves Family Relations/Risk management referrals Ad hoc contacts • Orientation documents and processes Parent orientation session- includes volunteer training Committee member orientation needed too Experience at Children’s Colorado • Overcoming resistance /concerns • Meeting management Acronyms, jargon Asking for input Managing defensiveness When people forget we have parents in the room…. • Debriefing is helpful after meetings • What we really need is an objective evaluation strategy other than that it feels good and seems like the right thing to do! “It will be easy working with families” 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% strongly disagree disagree neutral agree strongly agree Families will call out “white elephants” 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 strongly disagree disagree neutral agree strongly agree Families will express new viewpoints 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% strongly disagree disagree neutral agree strongly agree Meetings will be more effective 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% strongly disagree disagree neutral agree strongly agree Members will have legal concerns 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% not likely possibly not sure likely definitely Members will hesitate to share concerns (“dirty laundry”) 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% not likely possibly not sure likely definitely Where Hospitals are Today • Assessing Family Engagement at Children’s Hospitals in the US • 33 children’s hospitals participating in a national patient safety network • Family engagement is a goal OCHSPS - QI Assessment Survey Results for Family Engagement Parents/Families in Leadership roles re: safety 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 17 11 5 Yes No N/A Parents/Families on QI teams 20 18 18 16 14 12 10 10 8 5 6 4 2 0 Yes No N/A 10 hospitals said Yes to both questions Framework • Self assessment framework • Tools/Resources Framework Assessment Framework for assessing system level integration of family engagement Family engagement is a system level value operationalized at multiple levels within the organization AHRQ definition of Family Engagement: “A set of behaviors by patients, family members, and health professionals and a set of organizational policies and procedures that foster both the inclusion of patients and family members as active members of the health care team and collaborative partnerships with providers and provider organizations. The desired goals of patient and family engagement include improving the quality and safety of health care in a hospital setting” System Levels Experience level of care Practices used by the Health Care Team to engage families. Practices/policies used to facilitate communication between patients/families and care providers Practices used to increase patient knowledge, skills and abilities in care coordination Microsystem level Patients/families advise and engage in development of systems to engage families as part of the health care team, facilitate communication, and support care coordination Organizational level Strategies used to involve family members in management and processes within the hospital – feedback; participation in design, establishing system level priorities Examples of Practices and Processes by Organization Level Consider Family Feedback on Dignity & Respect; Information Sharing; Participation Bedside shift-to-shift report Bedside team rounds Family activated RRT Tracers – to evaluate practices Patient empowerment training Care Journals “Quiet Time” Consider Family Feedback on Participation; Collaboration Family participation in improvement teams Formal/established mechanisms to obtain participation and feedback Consider Family Feedback on Participation; Collaboration Family Advisory Board(s) Family representation as Board member or Quality Committee of the Board member Families participate in prioritization of hospital strategic initiatives Concerns and Risks • You tell me…. What are some reasons you would hesitate to engage patients/families…. In decision making and advocacy at the bedside? in quality/safety initiatives? • Breach of privacy/confidentiality? • Litigation? • Derailing meetings? How you can get started • Find early adopter parent/patient/family, staff leader • Start with a project or task force, then another….. • Discuss committee options • Develop, adapt or steal orientation materials • PDSA Cycles! • Patient/family selection strategies • Hospital staff preparation • Dealing with concerns/resistance • “Start before you’re ready” Questions and Answers