Science – Constructive and Destructive Forces
advertisement

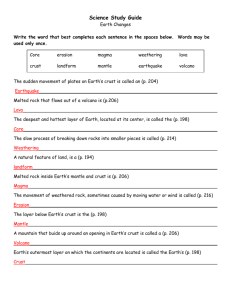
Science – Constructive and Destructive Forces The center and hottest layer of Earth • • • • • • Crust Mantle Pangea Core Erosion Plate The process of dropping sediment in a new location • • • • • • Fault Deposition Volcano Weathering Mantle Landform “Supercontinent” on Earth millions of years ago • • • • • • Mantle Pangea Mass Movement Landform Fossils Erosion Process in which soil, sand, and sediment are formed • • • • • • Fossils Weathering Lava Volcano Plate Mass movement Rigid block of crust and uppermantle rock • • • • • • Mantle Core Earthquake Crust Plate Deposition Physical Feature on Earth’s surface • • • • • • Fossils Landforms Fault Weathering Continental Drift Mass Movement Shaking of ground from energy release in the crust • • • • • • Volcano Erosion Weathering Earthquake Plate Landform Remains of traces of past life found in the crust • • • • • • Fossils Deposition Magma Continental Drift Mantle Pangea Middle layer of Earth • • • • • • Crust Fossils Core Lava Mantle Plate Hot, soft rock from the lower mantle • • • • • • Fossils Magma Weathering Core Volcano Fault Theory of how continents move over Earth’s surface • • • • • • Pangea Mass movement Earthquake Continental Drift Erosion Deposition Outer, very thin layer of Earth • • • • • • Core Crust Deposition Mantle Fault Pangea Place where pieces of the crust move • • • • • • Core Mantle Erosion Faults Magma Plate Downhill shifting of rock and soil because of gravity • • • • • • Continental drift Mass movement Pangea Magma Volcano Earthquake Opening in the crust through which lava flows • • • • • • Earthquake Continental Drift Core Volcano Deposition Landform Process of moving sediment from one place to another • • • • • • Erosion Fossils Earthquake Continental Drift Mass Movement Pangea What is the difference between constructive and destructive forces? • Constructive forces build up landforms, while destructive forces break down landforms What does a seismograph measure? • The intensity of an earthquake What happens when rocks rub against each other in running water? • They become smooth What happens when a volcano erupts? • Magma is forced out an opening in the Earth’s crust. It then becomes lava and hardens. The center of the Earth is extremely hot. Why, then, is it solid? • Because of pressure What can happen when water freezes inside the crack of a rock? • It can break the rock How can a dam prevent flooding? • By holding back and regulating the flow of water Where does the magma from volcanoes come from? • Deep inside the Earth What forces of nature can erode a rock? • Wind, rain, ice How does pollution speed up the erosion of rocks? • By causing acid rain, which dissolves rock faster What causes state or are to have a lot of earthquakes? • They are located on a fault line A new island formed in Iceland in 1963. What was most likely the cause of this island forming? • A volcano Give an example of a constructive force. • A volcano, fault lines cause a mountain to form, deposition forming a delta, etc. Give an example of a destructive force. • A volcano top blowing, landslides, mudslides, avalanches, erosion by wind, rain, or ice, etc. Why do scientists think there was originally one supercontinent that split up into the seven continents we now have? • The continents seem to fit together like a puzzle and fossils for animals from one continent have been found on other continents, suggesting they were once one. Which of the fossil layers shown is the most recent? The following pictures show the effects of wave action on a rock. Which would be the last picture if you put the pictures in order? What type of weathering is occurring in this picture? a. water weathering – water is causing erosion by moving the sand b. wind weathering – wind is causing erosion by moving the sand What type of weathering is occurring in this picture? Water is wearing away the rock by flowing over it. What do glaciers form? • Valleys (both U-shaped valleys and V-shaped valleys, depending on the size of the glacier. Explain how you could use ordinary items from your house to make a model of the Earth. • Answers will vary