18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Classification of all living Organsism:
Three Domains:
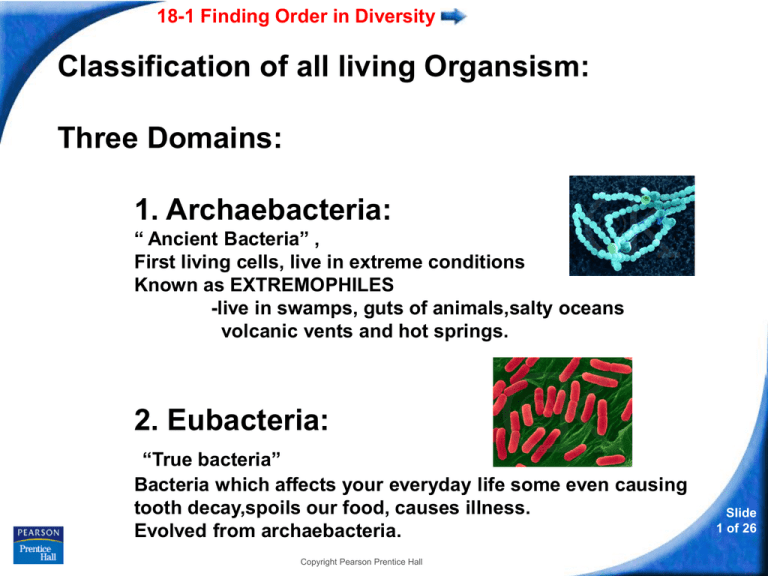
1. Archaebacteria:
“ Ancient Bacteria” ,
First living cells, live in extreme conditions
Known as EXTREMOPHILES
-live in swamps, guts of animals,salty oceans
volcanic vents and hot springs.
2. Eubacteria:
“True bacteria”
Bacteria which affects your everyday life some even causing
tooth decay,spoils our food, causes illness.
Evolved from archaebacteria.
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Slide
1 of 26
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
3. Eukarya:
“True Nucleus”,
-contains all organisms whose cells contain a nucleus:
Protista:
Eukarya
Domain is
divided
into four
Kingdoms:
Fungi:
Plantae:
Animalia:
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Slide
2 of 26
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Division of classification:
Ranges from the largest or broadest group
and keeps dividing until it reaches the most
specific group.
Broadest :
Domain
Did
Kingdom
King
Phylum
Philip
Class
Come
Order
Over
Family
For
Genus
Grape
Most specific: Species
Soda
Slide
3 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Eukarya
Domain
Grizzly Black Giant
bear
bear panda
Linnaeus's System of
Classification
Coral Sea
Red Abert
fox squirrel snake star
Broadest
Each level
is called a
taxon, or
taxonomic
category.
Most specific
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Slide
4 of 26
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Slide
5 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Species: Most specific division of classification.
Organisms of the same species can
successfully reproduce viable offspring.
Slide
6 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Every living organism is assigned a
2 word scientific name
-based on the GENUS AND
SPECIES name of that
organism.
Slide
7 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Rules for writing Scientific Names:
1. First word is the Genus and it is
always capitalized.
2. Second word is the species and it is
always lower case.
3. The entire name is underlined or
italicized.
Slide
8 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Scientific name of:
Cat:
Felis domesticus
Dog:
Canis familaris
Wolf:
Canis lupus
Polar bear:
Urus arctos
Slide
9 of 26
domesticus
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Scientific name for humans is???
Homo sapien
Slide
10 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Hybrids:
Organisms of the same genus but
different species reproduce and produce
offspring that are “usually” sterile.
Slide
11 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
LIGER
A liger is the offspring of a
lion and a tigress. It is
bigger than either parent,
10 - 12 ft in length - making
it the biggest hybrid cat
and, for many people, the
most fascinating.
Slide
12 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Tigon
A tigon is the offspring
of a tiger and a lioness.
Slide
13 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
s
Beefalo is a species
cross between Bison
(buffalo) and domestic
cattle of any breed. The
purpose of the species
cross was to blend the
outstanding qualities of
the Bison with
outstanding qualities of
the bovine breeds of the
world.
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Slide
14 of 26
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
A zebroid is a cross
between a zebra and any
other equid: essentially, a
zebra hybrid. They are
also known as zebra
mules. In general, the sire
is a zebra stallion.
Slide
15 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Zebroid: Shetland Pony and a
Zebra
Slide
16 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Polar bear + Grizzly Bear = Grolar Bear
Slide
17 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Sleeping around……
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
It's ALWAYS the kids that suffer.
His name is Zonkey
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Slide
18 of 26
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
UnicellularAutotrophic
Prokaryotic
owncell
food
Made up ofMakes
only one
Cells without
a
Photosynthesis
nucleus
Multicellular
Eukaryotic
MadeHeterotrophic
up
of many cells
Obtains
other
Cells food
withfrom
a nucleus
sources
Slide
19 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Domain
Kingdom
Archaebacteria
Eubacteria
Eukarya
Protista
Fungi
Plantae
Animalia
Name stands
for:
Autotrophic
Heterotrophic
or both
Unicellular,
Multicellular
or both
Prokaryotic or
Eukaryotic
Mobile or
nonmobile
Slide
20 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
Domain
Kingdom
Archaebacteria
Eubacteria
Eukarya
Protista
Fungi
Plantae
Animalia
Asexual,
sexual or
both types of
reproduction
Examples:
Slide
21 of 26
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall






