Lecture 24_handout
advertisement

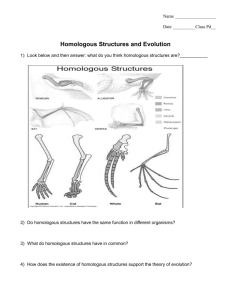
Cetacea ● ● ● Suborder Mysticeti – Baleen Whales – 4 families, 6 genera, 11 species Suborder Odontoceti – Toothed Whales – 9 families, 34 genera, 68 species Suborder †Archaeoceti – extinct (ancient) whales Mysticetes vs. Odontocetes • Baleen whales • Large body size • Feed on plankton and other small marine organisms • No echolocation (but have sound production for communication) • Toothed whales • Small, mobile, agile • Actively hunt fish and larger prey • Echolocation Odontocetes Mysticetes River Dolphins Cassens, Insa et al. (2000) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 11343-11347 Evolution of the Whale Skull • Heterodont Homodont or Edentulous • Telescoping of premax & max Posterior migration of external nares Odontocete jaws Dental adaptations Dental adaptations Dental adaptations Whale migration Echolocation in Odontocetes Echolocation in Odontocetes Baleen Mysticete feeding Skimming •Right whales •Grey wales Gulping •Rorquals Frontomandibular stay Bubble-net feeding Bottom feeding Myoglobin concentration Oxygen stores Counter-current heat exchange G. G. Simpson (1945), Principles of classification and a classification of mammals. “Ungulata” (various supraordinal ranks) has included: Cetacea: whales Artiodactyla: even-toed ungulates Perissodactyla: odd-toed ungulates Hyracoidea: hyraxes Proboscidea: elephants Sirenia: manatees & dugongs Tubulidentata: aardvarks Various fossil orders... arctocyonid condyarths artiodactyls mesonychian condyarths whales? Ambulocetus (“the walking and swimming whale”) Eocene Evolution Phylogeny “whippo” hypothesis Morphology Molecules “whippo” synapomorphies? •nearly hairless bodies •absence of sebaceous glands •thick layer of insulating fat •offspring nurse while submerged •lack of scrotal testes •general aquatic habit •vocalize/communicate underwater “Whales originated from aquatic artiodactyls in the Eocene epoch of India” Thewissen et al. 2007 “Whales originated from aquatic artiodactyls in the Eocene epoch of India” Thewissen et al. 2007 Artiocetus (“deer whale”) 47 MYA, Pakistan Nares well-forward on dorsal surface Gingerich et al., 2001, Science Rhodocetus Aquatic Webbed hands and feet Quadrupedal paddler Robust tail for undulation Artiocetus hind limb Rhodocetus Astragalus Cuboid pes Stiff webbed foot manus Protocetidae Characters of Protocetids * laterally facing orbits covered by supraorbital shield * legs shortened to streamline body * sacrum composed of four or fewer vertebrae Rodhocetus Mid. Eocene (46 mya) * P4/ larger than M1/ in occlusal outline * retention of M3/ Whales & dolphins Artiodactyls Artiodactyls Carnivorans Pangolins Perissodactyls Bats Solenodons Moles Shrews Hedgehogs Primates Treeshrews Colugos Lagomorphs Rodents Xenarthrans Golden moles Tenrecs Elephant shrews Aardvarks Dugongs & manatees Hyraxes Elephants “Cetartiodactyla”