Order Anguilliformes (Eels)
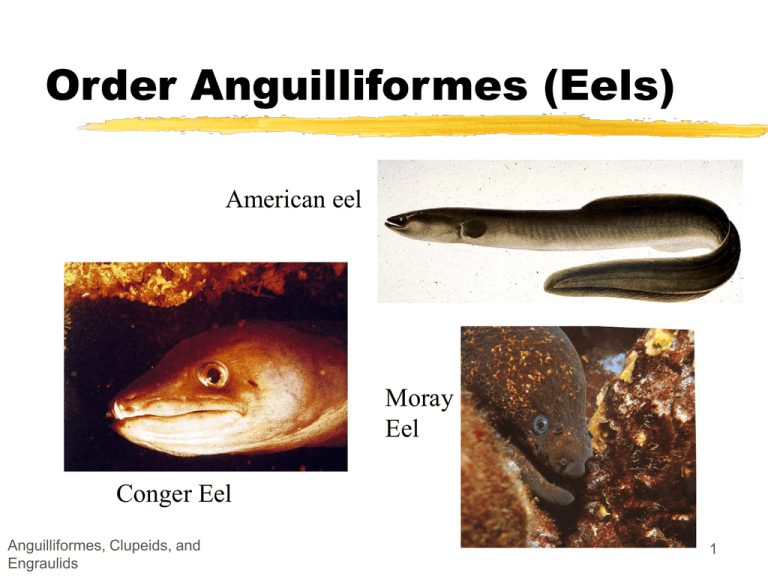
American eel
Moray
Eel
Conger Eel
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
1
Anguilliformes
Characteristics
Lack pelvic fins
Dorsal and anal fins are continuos with the
caudal fin
Embedded cycloid scales, or totally absent
Lack gill rakers
Reduced skeleton
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
2
Anguilliformes
Characteristics
All have
leptocephalus larvae
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
3
Order Anguilliformes
Freshwater Eels
Moray Eels
Conger Eels
Snake Eels
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
4
Freshwater Eels
Catadromous
Important predator in many lakes and streams
• Considered a food fish in some locals
Local species: American Eel (Anguilla rostrata)
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
5
Freshwater Eel
Reproduction
Migrate to the Sargasso Sea after 6-12 years in
freshwater habitats
• Size - 35 - 150cm.
Spawn at great depths and die
Leptocephalus larvae “migrate” to coastal waters,
and metamorphose into elvers
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
6
Spawning Sites
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
7
Moray Eels
Efficient predators on
reefs and rocky shores
• Preys on inverts and fish
Teeth are always on
display since they have to
hold their mouth open to
breathe
May exceed 9ft. rarely >
3ft.
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
8
Conger Eels
Resemble morays
• Have pectoral fins and
stout cone shaped
teeth
Most prey on inverts
Garden eels
• Feed on plankton and
often mistaken as
seagrass
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
Garden Eels
9
Snake Eels
Largest of all eel
families
Small in size
(<3ft.) and
brightly colored
Rarely seen, due
to burrowing and
nocturnal
behavior
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
10
Family Clupeidae
(Herrings)
Includes: Herrings,
Shads, Sardines, and
Menhaden
Live in well-lit surface
waters
• School
• Feed on plankton
DMF Website
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
11
Clupeidae Characteristics
Silvery scales and
compressed body
• Flexible mouth, with fine
gill rakers
Play key roles in many
food webs
• Highly abundant, ability
to feed on plankton
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
12
Clupeidae Characteristics
Concentrate in coastal waters
Many species are not harvested for direct
consumption
Important prey items for other commercially
important species
Several anadromous species
• Gizzard shad
• American Shad
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
13
Atlantic Menhaden
(Brevoortia tyrannus)
Important commercial
fishery on the East
coast
Omega protein
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
14
Purse Seine
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
15
American Shad (Alosa
sapidissima)
Anadromous species
Spawn all over the East
coast
Female spawns over
600,000 eggs
• Valuable for the roe
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
16
Common Clupeids
Atlantic Thread Herring (Opisthonema oglinum)
Round Herring (Etrumeus teres)
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
17
Family Engraulidae
Small, (<15cm.) filter
feeder
• Inhabit inshore waters
where plankton densities
are highest
Distinguished by inferior
mouth
Like Clupeids, numbers
fluctuate due to fishing
pressure and
oceanographic
conditions
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
Striped Anchovy Anchoa hepsetus
18
Family Engraulidae
Peruvian Anchoveta
• Occurr in the
upwelling currents on
the west coast of
South America
• Once one of the
worlds largest fisheries
• El Nino combined with
fishing pressure
caused a major
collapse
Anguilliformes, Clupeids, and
Engraulids
19








