Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
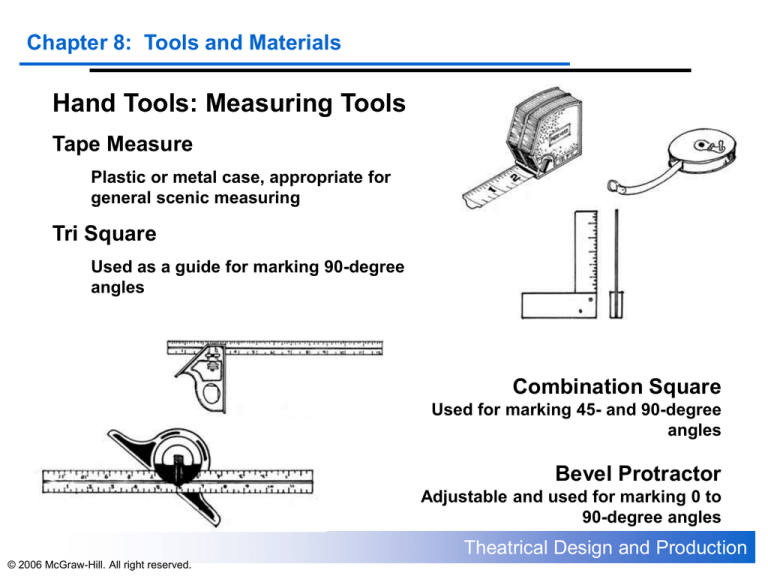
Hand Tools: Measuring Tools
Tape Measure
Plastic or metal case, appropriate for
general scenic measuring
Tri Square
Used as a guide for marking 90-degree
angles
Combination Square
Used for marking 45- and 90-degree
angles
Bevel Protractor
Adjustable and used for marking 0 to
90-degree angles
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Measuring Tools
Framing Square
Used for checking accuracy of 90-degree
corner joints in flat construction
Bevel Set
Used for transferring angles from one
piece of work to another
Carpenter’s Level
Used to determine true horizontal and
vertical angles
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Marking Tools
Pencils
Either carpenter’s pencils or number two
yellows
china markers used for marking metal
wax pencils for lighting color media
Scribe
“Scratch awl” Used for marking wood,
metal, and plastic; can also be used to
make starter holes
Chalk line
Used to mark straight lines
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Hammers
Claw Hammer
Designed for inserting and removing
nails
Rip Hammer
Can be used for prying or ripping
apart previously nailed wood
Ball Peen Hammer
Used for bending and shaping metal
and seating rivets
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Hammers
Mechanic’s Hammer
Used for shaping metal
Tack Hammer
Used for inserting tacks, the face is
magnetized to hold tacks in place
Mallet
Wooden, plastic, or metal head, they
are used for driving chisels
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Cutting Tools
Saws
Crosscut Saw
Used to cut across the grain of wood
Rip Saw
Designed to cut parallel with the grain
of the wood
Backsaw and Miter Box
Fine-toothed crosscut saw, used with
the miter box for more accurate cuts
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Cutting Tools
Saws
Keyhole Saw
Used for making curvilinear cuts in stock
lumber
Coping Saw
Used for making fine, curvilinear cuts in
thin plywood
Hacksaw
Adjustable frame saw for cutting metal
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Cutting Tools
Utility Knife
Used to trim excess muslin from the edges
of flats as well as to cut out stencils and
other lightweight cutting projects
Scissors
Used to cut papers and fabrics
Tin Snips
Used to cut thin ferrous and nonferrous
strap and sheet metals
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Cutting Tools
Wood Chisel
Used for gouging, paring, or smoothing
wood
Cold Chisel
Used for cutting through, or shearing, mild
steel and nonferrous metals
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Cutting Tools
Planes
Block Plane
Used to smooth the ends (across the
grain) of boards
Smoothing Plane
Applied parallel to the grain of the
wood
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Cutting Tools
Planes
Spoke Shave
Pulled across the surface of the work
and used to soften or round sharp
edges
Surform Tools
Not really a plane or a file, they are
pushed across the work, cross-grain
or parallel
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Cutting Tools
Files
Wood Rasp
Used for rough shaping of wood
Wood File
Used for smoothing wooden and plastic
surfaces
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Cutting Tools
Files
Rat-Tail File
Can be used with wood, plastic, and metal
Metal File
Has very fine teeth for use on metal
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Drilling Tools
Hand Drill
Used for making small-diameter holes in
wood
Brace
Used for holes larger than ¼ inch in
diameter
Push Drill
Designed for light usage, it can be useful
for making starter holes
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Drilling Tools
Bits
Twist-Drill Bits
Designed for use with either wood or
metal
Wood Bits
Designed for use in wood or soft plastic,
used with power hand drills or drill
presses
Auger Bits
Used with the brace for cutting holes in
wood
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Drilling Tools
Bits
Push-Drill Bits
Very sharp points that seem to punch
rather than drill holes in wood
Hole Saws
Used to center the saw in the work
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Clamping Tools
Carpenter’s Vice
Attached to the edge of a workbench, used
for holding wood
Machinist’s Vice
Used to clamp and hold metal
Adjustable Wood Clamp
Used in furniture construction
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Clamping Tools
Pipe Clamp
Used to clamp furniture frames, table tops, and
similar wide objects together while their glue
joints dry
Belt Clamp
Used to clamp irregularly shaped pieces
together
C Clamp
Used for holding work together while the
parts are being assembled or while glue
dries
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Clamping Tools
Pliers
Slip-Joint Pliers
Used for clamping, gripping, bending, cutting
light wire
Long-Nose Pliers
Useful for holding small objects in hard-toreach places
Adjustable Arc-Joint Pliers
Used for holding metal pipe and tubing and
other similar gripping jobs
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Clamping Tools
Pliers
Locking Pliers
“Vise Grip” Used to grasp, lock, and hold almost any object
Diagonal Cutters
Used by electricians for cutting soft wire
Wire Strippers
Used for stripping insulation for electrical wires
Wire-Crimping Tool
Used to pressure-clamp solderless connectors to electrical wire
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Clamping Tools
Wrenches
Open-End Wrench
Designed to fit nuts of specific standard or metric diameter
Box-End Wrench
Have a closed, toothed head that must be fit over the nut
Adjustable-End Wrench
“Crescent Wrench” It adapts to fit any small to medium sized
nut
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Clamping Tools
Wrenches
Monkey Wrench
Adjustable, used on large nuts and other
work too large for the crescent wrench
Pipe Wrench
Used to hold or twist metal pipes
Socket Set and Ratchet Handle
Allows you to tighten and loosen nuts
without removing the socket from the nut
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Screwdrivers
Standard Screwdriver
Available in a variety of sizes
Philips Screwdriver
Four-flanged tip allows for more rotational
force
Nut Driver
Used for tightening small hex nuts on
bolts
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Misc Hand Tools
Wrecking bars
Used to pry wood apart and remove nails
Sandpaper
Used for smoothing wood, metal, and
plastic
Nail puller
Used for extracting nails that have been
driven flush to the wood surface
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Misc Hand Tools
Grommet Set
Used to seat grommets on drops, stage draperies, and
the like
Oil Stone
Used to sharpen knives, chisels, and other cutting tools
Staple Gun
Used for attaching muslin to flat frames and fabric to
furniture
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Metalworking Hand Tools
Anvil
Used for bending metal
Conduit Bender
Used to bend thin-wall conduit
Center Punch
Used to make small indentations in metal, starter holes
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hand Tools: Metalworking Hand Tools
Bolt Cutter
Used to cut through mild-steel bolts and round stock
Pipe Cutter
Used to make clean, right-angle cuts through steel pipe
Tap and Dies
Used to cut threads on pipe and rod stock
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Power Tools: Stationary Power Saws
Table Saw
Used for ripping lumber
Radial-Arm Saw
Used for cross cutting and angle cutting, as well as for ripping lumber
Bandsaw
Used to make curvilinear cuts
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Power Tools: Power Handsaws
Circular Saw
Used for straight-line cross cutting and angle cutting, as well
as ripping
Saber Saw
Used to make curvilinear cuts
Cut Awl
Used for making curvilinear cuts and intricate cuts
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Power Tools: Power Drilling Tools
Drill Press
Used to polish and sand as well as cut mortise and tenon
joints for furniture construction
Electric Hand Drill
Used for light-duty drilling on lumber and light metals
Heavy-Duty Hand Drill
Used for heavier work, such as thick wood, thick mild
steel, and concrete
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Power Tools: Battery-Powered Tools:
Pneumatic Tools
Pneumatic Stapler
Uses air pressure to drive the staples
Pneumatic Nailer
Used for rapid assembly of platforms and similar structures
Impact Wrench
Uses air pressure to tighten or loosen nuts
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Power Tools: Metalworking: Welders
Oxyacetylene Welder
Combines oxygen and acetylene to produce a very hot
flame that burns through metal
Arc Welder
Works by creating an electrical arc that
melts the metals being welded
Mig Welder
An arc welder that focuses a flow of inert gas on the
welding zone
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Power Tools: Metalworking: Soldering Equipment
Pencil, gun, iron
Used to bond wires together
Propane Torch
Used for soldering most heavy-duty scenic jobs and heating thin-gauge
steel for bending and shaping
Power Hacksaw
Used to cut through various types of metal stock
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Power Tools: Metalworking
Cutoff Saw
Used to make either straight or angle cuts
through metal stock
Power Pipe Cutter
Used for cutting and threading metal pipes
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Power Tools: Misc
Router
Hand-held, used for shaping wood
Wood Lathe
Bench-mounted, holds and spins wood rapidly for
shaping and carving
Bench Sander
Mounted and used to bevel or smooth the surface
edges of wood and some plastics
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Power Tools: Misc
Electric Screwdriver
Magnetized tip, used with Philips screws for
assembling flats and platforms
Bench Grinder
Used for grinding and sharpening metal
Hand Power Grinder
Used for pieces too heavy or awkward for the
bench grinder
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Power Tools: Misc
Hand Power Sander
Uses a rotating disk of sandpaper to sand wood, metal,
and plastic
Belt Sander
Uses belts of sandpaper for rapid sanding of wood
Hot-Melt Glue Gun
Used for making rapid-hold glue bonds between just
about every type of material
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Wood: Stock Lumber
A Select: Free of all knots, blemishes, erratic graining and warps
B Select: Grain can be less uniform and the wood can contain more pitch
C Select: Can have a few tight knots, slightly less uniform, and still more pitch
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Wood: Stock Lumber
D Select: Can have more tight knots, an occasional pitch pocket, and some
warping
No. 1 Common: Can have knots that fall out; commonly warp and twist
No. 2 Common: Knots that fall out, bark on the edges, warped and twisted
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Wood: Molding and Trim
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Wood: Sheet Stock
Plywood
Made by laminating several layers of wood, much stronger
than solid wood
Particle Board
Composed of wood chips and sawdust mixed with a glue
binder
Heavier than plywood, but not as strong
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Wood: Sheet Stock
Wafer Board
Similar to particle board but lighter, cheaper,
and just as strong as plywood
Hardboard
Called Masonite, is manufactured from wood
pulp and used as a facing surface
Upson Board
Paper pulp and binder, fairly flexible with little
strength, used to cover fairly sharply curved
surfaces
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Wood
Sonotube
Paper tube used for forming concrete; in theatre, it can also be used to
make columns
Manufactured Wood
Woodlike construction materials made from wood by-products
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Metal: Mild Steel
Square and Rectangular Tubing
The most used and useful shapes of steel, used
for platform framing and flat framing
Tubing or Pipe
Primarily used for decorative items
Channel
Used in structures requiring significant strength, such as the framework
for large platforms and wagons
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Metal: Mild Steel
Angle
Used in those situations requiring less strength, such as lightweight
frames, braces, and stiffeners
Strap
Used to strengthen or brace existing wooden structures
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Metal: Proprietary Structural Systems
Unistrut
Consists of U-shaped channels of differing sizes
Telespar
A system of telescoping square steel tubing; can be adjusted
without cutting
Slotted Angle
Manufactured with a variety of holes and slots punched into both
faces of the stock
Aluminum
Not used as extensively as mild steel, more expensive
and more difficult to weld; mainly used for decorative
purposes
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Plastics
Acrylic
Used as a glass substitute and for making decorative baubles and
stained glass
Epoxy
Most commonly used types are those for adhesives and casting resins,
can be worked with either wood or metal cutting tools
Fluorocarbons
Teflon, makes an excellent bearing surface for turntables and for
covering skids
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Plastics: Polyesters
Saturated Polyesters
Have a variety of uses in both scenic and costume construction, such as
stage mirrors
Unsaturated Polyesters
Can be used in casting or to create fiberglass
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Plastics
Polyethylene
Available in film and foam, can be used for such things as drop cloths
and projection screens
Polystyrene
Styrofoam, used for making decorative trim
Polyvinyl Chloride
PVC pipe, can be used for a variety of decorative scenic purposes
Urethanes
Commonly used for cushions and padding in furniture
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Fasteners: Nails
Common Nail
Large head, thick shank, used for heavier general
construction
Box Nail
Narrower shaft that reduces the chance of splitting
lumber
Coated Box Nail
Even narrower shaft, coated with an adhesive that
bonds the nail to the wood
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Fasteners: Nails
Finish Nail
Slender shaft and narrow head, used for building props or furniture in
which the nail head needs to be hidden
Wire Nail and Brad
Small finish or box nails with slender shafts, used in property
construction or for attaching delicate decorative moldings to larger
scenic elements
Double-Headed Nail
Used for scaffolding or any temporary structure that needs to be
dismantled quickly
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Fasteners: Nails
Screw Nail
Threaded shank that rotates as it is driven into the wood
for more holding power
Clout Nail
Used to be used in flat construction but has since been
replaced by power-driven screws and pneumatic devices
Tack
Used for attaching fabric and for decorative
purposes
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Fasteners: Nails
Corrugated Fastener
Used to hold lightweight frames together
Staple
Come in a variety of types, used to fasten things together
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Fasteners: Screws
Flat-Head Wood Screw
Used for attaching hardware and
joining various wooden elements together
Round-Head Wood Screw
Used in those situations in which you do not want to have the top of the
screw flush with the surface of the work
Drywall Screw
Used to attach gypsum board or drywall to wooden wall and ceiling
studs
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Fasteners: Screws
Sheet-Metal Screw
Used for joining sheets of metal
Lag Screw
Very large wood screws used where the lack of access to both sides of
the work prevents the use of bolts
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Fasteners: Bolts
Carriage Bolt
Used to join either wood to wood or wood to metal
Machine Bolt
Designed to join metal to metal
Stove Bolt
Used for attaching stage hardware, hinges, and similar items that require
extra fastening strength
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Fasteners
Washers
Flat-steel disks that increase the bearing surface of the nut or bolt and
prevents the nut or bolt from cutting into the surface of the work
Nuts
Applied to threaded ends of bolts to close
and tighten the fastener
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Glues and Adhesives: Glues
Animal Glue
One of the prime ingredients of scenic glue, used to glue muslin or
canvas to flats or to construct furniture
Flexible Glue
Animal glue with glycerine, used for projects requiring flexibility
Wheat Paste
Used for hanging wallpaper, papier-mâché, and for attaching dutchman
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Glues and Adhesives: Adhesives
White Glue
Elmer’s Glue, used extensively in scenic construction
Carpenter’s Glue
Used in woodworking, dries almost clear, is stronger and dries more
quickly than white glue
Latex Cement
Used in laying carpet
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Glues and Adhesives: Adhesives
Contact Cement
Used for bonding nonporous surfaces together
Polyvinyl Glue
Resembles white glue and can be used for furniture construction and repair
and as a binder for scene paint
Cyanoacrylate Cement
Super Glue, powerful adhesives used in property construction
Epoxy Resin Adhesive
Used in the shop in situations where its strength can be an advantage,
furniture construction and property work
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Construction Hardware
Eye Bolt
Used for attaching lines or ropes to an object
Screw Eye
Similar to eye bolts but used when the extra strength or the bolt
fastener is not necessary
Screw Hook
Have a hook instead of an eye so that items hung from the hook can
be quickly removed
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Construction Hardware
U Bolt
Used to secure or fasten pipe, tube, or rod to flat surfaces
Cable Clamp
Used to hand scenery and battens
Nicopress Tool
Provides a permanent, nonremovable friction clamp for wire rope or
cable
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Construction Hardware
Thimble
Used to protect wire, rope, or cable from sharp bends or kinks
Turnbuckle
Used to lengthen or shorten a line system
Snaps
Used to provide a quick means of attaching a line to its associated load
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Construction Hardware: Hinges
Strap Hinge
Used to hinge stage doors
Butt Hinge
Used to hang stage doors
T-Strap Hinge
Used for hanging doors, gates, and box lids
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Construction Hardware: Hinges
Loose-Pin Back-Flap Hinge
Used for joining scenery, the pin can be removed in
order to break the unit apart
Tight-Pin Back-Flap Hinge
Used for joining scenery permanently
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Stage: Lashing
Lash-Line Eye
Used to attach the lash line to the flat
Lash-Line Cleat
Used to hold the rope in place so that the flats can be lashed together
Lash-Line Hook
Used to hold the rope in place so that the flats can be
lashed together; can also be used in place of a tie-off cleat
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Stage: Lashing
Tie-Off Cleat
Used in pairs to tie off the line after the flats have been
lashed together
Stop Cleat
Attached to the back of flats to prevent the flats from
slipping past each other when they are being lashed
together in an outside corner configuration
Stop Block
Small piece of scrap wood used to prevent flats from
slipping past each other when they are being lashed
together in an inside corner configuration
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Stage: Flying Hardware
Hanger Iron
Used in conjunction with a bottom hanger iron for flying heavy scenery
Bottom Hanger Iron
Used in conjunction with a hanger iron for flying heavy scenery
Ceiling Plate
Bolted to primary structural members of the ceiling to provide a means
of attaching the flying lines to the ceiling
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Stage: Bracing
Stage Brace
Adjustable pole attached to the brace cleat and secured to the
stage floor
Brace Cleat
Attached to the stile of the flat, provides the point of attachment
between scenery and the stage floor
Rigid Foot Iron
The long leg is attached to the bottom of the scenery and the
short leg is secured to the stage floor
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Stage: Bracing
Hinged Foot Iron
Similar to the rigid foot iron, its horizontal foot is hinged to fold out
of the way when the scenic unit is shifted or flown
Stage Screw
Used to anchor a foot iron or stage brace to the stage floor
Improved Stage Screw
Doesn’t tear up the stage floor as much as the regular stage screw
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Stage: Bracing
S Hook
Latch keeper, used to hold stiffening
battens on the back of wall units made of
two or more flats
Floor Plate
Used when the stage floor is not wood or
you are not allowed to put holes in it
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Stage: Misc
Corner Plate
Used to reinforce the corners of doors, windows, door
or window casings, and picture frames
Tee Plate
Used as a substitute for keystones
Picture Hook and Eye
Used in sets of two or more for rapid hanging and
removal of decorative draperies
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Stage: Misc
Casket Lock
Heavy-duty, hidden lock used to hold platforms together
Casters
Wheeled attachments used
to easily move scenery
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Hardware: Stage Hardware
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Rope, Cable, and Wire
Manila Rope
Primary type of rope used for raising and suspending loads in the
theatre
Sisal Rope
Much stiffer than manila and easily deteriorates when used in sharp
angle bending
Clothesline
Used for operating line on travelers as well as for lashing flats together
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Rope, Cable, and Wire
Nylon Rope
Stretch too much and are too expensive for use in the theatre
Monofilament Line
Fishing line, used whenever lines need to be invisible
Aircraft Cable
Flexible and strong, used for flying heavy stage scenery
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.
Chapter 8: Tools and Materials
Rope, Cable, and Wire: Wire
Stovepipe Wire
Used for tying or wiring things together, not to be used for flying scenery
Piano Wire
Used to fly scenery
Theatrical Design and Production
© 2006 McGraw-Hill. All right reserved.