America`s No. 1 recycled product
advertisement

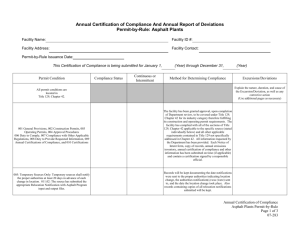
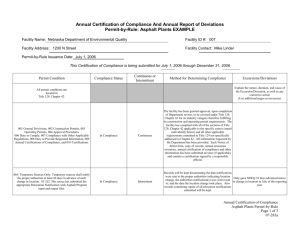
Pike Industries, Inc. Lakes Region Transportation Workshop 11/15/13 Global Factors Affecting Highway Construction Cost • The rate of global economic growth (especially developing countries) is a major driver of energy and materials demand • Volatility in crude oil prices • Fuel oil demand and conversion to lighter crudes reducing asphalt supply and increasing asphalt prices • European refinery closures will increasingly put demands on U.S. supply At the Refinery U.S. Asphalt and Road Oil Stocks at Refineries (Ergon Asphalt & Emulsions, Inc.) PII Liquid Cost % of TVC 60.00% 50.00% 40.00% 30.00% Liquid AC % VC All Other VC % 20.00% 10.00% 0.00% 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Managing Pavement Cost • 1993 EPA and Federal Highway Administration identify asphalt pavement as America's No. 1 recycled product • A wide range of waste materials are now incorporated into asphalt pavements, – including ground tire rubber, glass, foundry sand, slag, pig manure – the most widely recycled are reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) and recycled asphalt shingles (RAS). • The use of recycled materials in asphalt pavements saves hundreds of millions of cubic yards of landfill space each year Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) & Recycled Asphalt Shingles (RAS) • RAP and RAS displaces virgin materials (aggregates and liquid asphalt) • In 2011 RAP usage reached 66.7 million tons – 7% increase from 2010 and a 19% increase from 2009 – NHDOT allows 20% RAP • RAS usage increased to 1.2 million tons in 2011 – 8% increase over 2010, and a 52.5% increase from 2009. – NHDOT studying the use of RAS Warm Mix • Requires less energy to produce at lower temperatures • In 2011, total WMA tonnage in the U.S. was estimated at about 69 million tons, – 67 % increase from 2010 – 309 % increase since 2009 • 2011 NHDOT reported WMA use at 30% Other Cost Reduction Strategies • Heating fuel to dry aggregates – Specification used oil, natural gas, well draining stockpiles to reduce moisture in aggregates • Electricity for plant operations – Energy conservation, timing opening & closing dates • Fuel for mobile equipment & trucking – Limit idling, bio-diesel, fleet monitoring software systems Revenues • USFHWA and NHDOT operating under 20 year old funding rates (motor fuel user fees) • US Fleet increasing mpg + decreasing driving habits = decreasing revenues (9M gallons per year less gasoline consumed than 5 years ago) NE State & Local Motor Fuel Revenue (000’s) (http://www.gaspricewatch.com/imgs/popup.html?motor_fuel_rev.gif) 800,000 700,000 600,000 500,000 CT ME MA 400,000 NH RI 300,000 VT 200,000 100,000 0 1977 1982 1987 1992 1997 2002 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 (Transportation for America) MAP-21 Expires Sept 2014 The Effect of Increased Fuel Economy $160.00 $140.00 $120.00 $100.00 $80.00 Tax Rate Annual Tax $60.00 $40.00 $20.00 $0.00 The Challenge for the Road Construction Industry • Lack of predictability for future maintenance and construction programs hinders reinvestment in the business • Employee retention as workers seek more secure/predictable occupations • Thousands of NH families rely on this industry to make a living • Every NH family relies on this industry for safe and efficient transportation The Challenge for NH 1. NH has 2,129 bridges and 4,300 miles of roads. 2. Average pavement lifecycle in NH is between 8-12 years. 3. Must repave 500 miles of road per year to stay even but under current revenues are paving approx 300 miles annually. 4. Each $1 spent on road maintenance eliminates spending $6-14 on roadway rebuilding. 5. 83.2% of NH residents travel to work on the highways with ave commute time 25 minutes 6. Rough roads add $335/yr in vehicle repairs on average 7. Modest improvements in pavement smoothness could save up to 3.7 billion gallons of gasoline and 1.3 billion gallons of diesel for the U.S. annually. Smoothing America’s roads and highways could save $12.5 billion a year for the U.S. economy. (Auburn University 2011) 8. Increasing cost + decreasing revenues + political gridlock = a system in decline that will cost many times more to repair in the future