Learning Style & IEP Accommodations
advertisement

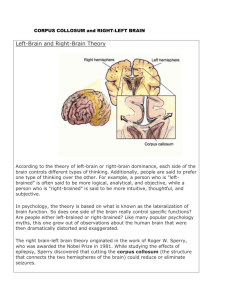
Power Point Lecture Guide Introduction -Go over Learning Objectives -Go Basic Level Activities -Take the Analyzing Your learning Style (Assessment-print results) Lecture #1 Benefits of Learning How You Learn Best A Learning Style is… Your currently preferred: -methods take in information -tasks -level of interaction with others -approach toward learning tasks -study environment More detail on this later… Learning Styles Clip Rate Yourself 1= Not very well 2=Have a good Idea 3= Very well I know my preferred learning styles? I know what strategies relate to my preferred learning styles? I know how my learning style has changed over time? True or False 1. Most people only have one preferred method of learning. 2. There is no need to work on improving your areas of weak learning styles. 3. My learning styles will most likely not change over time. 6 Benefits… 1. You can choose and use strategies that make learning easier. 2. Greater self awareness of your strengths and weaknesses. 3. Improved self-confidence 4. Better grades in school. 5. School can become rewarding and fun rather then frustrating. 6. Informed career path decisions. Explain how you could select a best fit career direction if you know what your learning preferences are? Lecture #2 Learning Styles Part 1 1. Draw a quick sketch of the photo. 2. Write two or three sentences describing the photo in detail. Share with the class. 3. Verbally describe the photo with a classmate. 4. Compare your drawing with your classmates. Study the photo for one minute. Which of the previous activities were you able to do best? How does this compare with your classmates? There are various ways of viewing and classifying learning styles. People differ in: -how they learn -methods and strategies Explains why: -some classes/subjects are easier then others -you learn better from a type of teacher style How to discover your learning style… Jot down 1. Tasks or activities you learn quickly. 2. Tasks or activities you take a while to get. 3. What are you good at… 4. What don’t you do so well? 5. What are your hobbies? 6. What are the common characteristics of your favorite teachers? You are beginning to get a better idea of your learning preferences! Take the Analyzing Your learning Style Assessment. Score the results. Lecture #3 Learning Styles Part 2 Get your results of the Analyzing Your learning Style Assessment. You will be asked to summarize in writing the results of this assessment at the end of the Power Point… so -take notes -highlight key information -note differences in your opinion of the results 5 Ways to look at Learning Styles 1st …Your preferred sensory modes to process information…. -Visual …seeing -Auditory…hearing -Kinesthetic/Tactile… movement and touch (Not asssessed) 2nd…Your preferred learning tasks. Would you rather… a. Follow detailed step by step instructions to make a wood project or … b. Conceptualize how to build the project before doing it? If a. then you may be a applied/practical learner..tasks that involve real objects and situations If b. then you may be a conceptual learner … tasks with language and ideas, you do not need practical applications to understand something Applied Conceptual Mark where you are on this scale. 3rd Spatial or Verbal -Spatial learners can visualize, or mentally see how things work and their position in space -Verbal learners have difficulty doing this and rely on language skills 4th What is your preferred level of social interaction? Social…prefer working with others peers and with teacher Independent… Prefer working alone and selfdirected Social Indep. Mark where you are on this scale. 5th and last… Your preferred approach toward learning tasks. -Creative Learners are… imaginative & innovative learn through discovery and experimentation -Pragmatic Learners… are practical, logical, systematic..seek order and following rules Creative Pragmatic Mark where you are on this scale. To review…5 possible ways to view how we all learn differently are: 1. Your preferred sensory modes to process information 2. Your preferred learning tasks/activities: applied/practical or conceptual learner (language) 3. Your ability to work with spatial relationships Spatial or Verbal 4. Your preferred level of social interaction 5. Your preferred approach toward learning tasks Creative (discovery) or Pragmatic (systematic) Learner Each of these preferences has specific learning strategies that work best!!! See pg 47. Look on page 47 of the assessment. 1st circle the 5 aspects of your learning style with the higher score 2nd check the suggestions you think will work for you Now the fun begins!!! Ok…remember what you were going to be asked to do with this information? Well… Summarize in writing the results of this assessment -hand written or word processed* -2 two paragraphs P1- summary of the results P2- Discuss some of the specific strategies that may work for you based upon this information You can use the graphic organizer. Lecture #4 Multiple Intelligences Take and score the Multiple Pathways to Learning Assessment What do you think this theory is about? Is someone who can understand someone's emotions and counsel them as intelligent as someone who can create software? The theory of multiple intelligences was proposed by Howard Gardner in 1983 to analyze and better describe the concept of intelligence. The theory's eight currently accepted intelligences are: Spatial Linguistic Logical-mathematical Bodily-kinesthetic Musical Interpersonal Intrapersonal Naturalistic Spatial the ability to visualize with the mind's eye. good with puzzles. Careers: artists, designers and architects. Linguistic This area has to do with words, spoken or written display a facility with words and languages. good at reading, writing, telling stories and memorizing words along with dates. learn best by reading, taking notes, listening to lectures learn foreign languages very easily Careers include writers, lawyers, policemen, philosophers, journalists, politicians, poets and teachers. Logical-mathematical logic, abstractions, reasoning and numbers. reasoning capabilities, recognizing abstract patterns, scientific thinking and investigation and the ability to perform complex calculations Careers include scientists, physicists, mathematicians, logicians, pilots, engineers, doctors, economists and philosophers. Bodily-kinesthetic The core are control of one's bodily motions capacity to handle objects skillfully learn better by involving muscular movement (e.g. getting up and moving around into the learning experience), and are generally good at physical activities such as sports or dance. Careers include: athletes, pilots, dancers, musicians, actors, surgeons, doctors, builders, police officers, and soldiers. Musical This area has to do with sensitivity to sounds, rhythms, tones, and music. Since there is a strong auditory component to this intelligence, may learn best via lecture will sometimes use songs or rhythms to learn. Careers include instrumentalists, singers, conductors, discjockeys, orators, writers and composers. Interpersonal This area has to do with interaction with others. tend to be extroverts, characterized sensitivity to others' moods, feelings, temperaments and motivations communicate effectively and empathize easily with others learn best by working with others and often enjoy discussion and debate. Careers that suit those with this intelligence include sales, politicians, managers, teachers and social workers Intrapersonal This area has to do with introspective and self-reflective capacities, intuitive and typically introverted skillful at deciphering their own feelings and motivations deep understanding of the self; what are your strengths/ weaknesses, People with intrapersonal intelligence also prefer to work alone. Careers include philosophers, psychologists, theologians, lawyers and writers Naturalistic This area has to do with nature, nurturing and relating information to one’s natural surroundings. Careers which suit those with this intelligence include naturalists, farmers and gardeners On pg. 70 3.2… Circle your highest 2-3 Intelligences check the suggestions you think will work for you in those areas Write a one paragraph summary of the results Lecture #5 Global vs. Analytical Learners (right Brain vs. left Brain) There are a number of ways to compare the two sides of the brain: -Global vs. Analytical Learners -Right Brain vs. Left Brain -Linear Vs. Holistic Processing -Logical Vs. Intuitive Processing Do we use our entire brain to learn? YES! Is one dominant side an advantage or better then the other? NO! Some considerations: First, no one is totally left-brained or totally right-brained. Just as you have a dominant hand, dominant eye, and even a dominant foot, you probably have a dominant side of the brain. Second, you can and must develop both sides of your brain. TAKE THE “What is Your Dominant Brain? Test and score the results. Right Brain (Global) vs. Left Brain (Analytical) Right Brain Characteristics Here are some of the basic characteristic traits associated with the right brain. Random Intuitive Holistic Synthesizing Subjective Left Brain Characteristics Here are some of the basic characteristic traits associated with the left brain. Logical Sequential Rational Analytical Objective Right and Left Brain Differences There are many differences between the two hemispheres of the brain. The persons nature largely depends on which part of his brain dominates the nervous system. The right brain is intuitive, meaning it is led by feelings, while the left brain is analytical, meaning it is led by logical approach towards problems. The right brain is visual, stressing on music and pattern, while the left brain is verbal, stressing on words, numbers and symbols. People with right brain don't give attention to minute details, but people with left brain tend to focus on each and every minute detail and step taken. When given a task of assembling a particular thing, right brain people will start working promptly without reading the instructions, while left brained people will carefully go through the instructions and then start working. Learning Implications: The Right-Brain Student Right-brain students prefer to work in groups. They like to do art projects, and graphic design. They would prefer to design and make a poster rather than write a term paper. The Left-Brain Student Left-brain students prefer to work alone. They like to read independently and incorporate research into their papers. They favor a quiet classroom without a lot of distraction. Possible right-brain learning preferences Possible left-brain learning preferences overheads, videos, music, role playing, dance, or group projects direct teaching, lecturing, or more individual and/or research-oriented projects Prefer visual over auditory Prefer auditory over visual Study Implications of right or left brain dominance. In two groups represented by both right and left brain folks..Discuss the following questions and be prepared to share with the class. What strategies do you think a right brain person would use to learn best? What strategies do you think a left brain person would use to learn best? In one paragraph writing discuss what you learned in this lecture. How does this information compare with the Learning Style Assessments? Counts as a reaction on LC. Lecture #6 Four Major Parts of an IEP OK…so what’s an IEP? Individualized Education Program For school age students with a disability and benefits from specially designed instruction Developed with an educational team including: -Your case manager -Input from your teacher -formal educational assessments -Parents/ Guardians' -and YOU! Get a copy of your IEP. The four major parts are: 1. II. Present Levels of Academic Achievement 2. III. Transition 3. IV. Goals 4. V. Program Modifications and Specially Designed Instruction Present Levels of Academic Achievement -Information on your current educational progress/ levels/grades/MBIT/after HS plans -Strengths and Needs III. Transition Your post (after) secondary (HS) Goals -Education/training -Employment -Independent Living IV. Goals Must have at least one goal -Annual -Short Term Is monitored on-goingly as stated and reported on each 9-weeks V. Program Modification and Specially Designed Instruction (SDI) -Lists the Modifications and SDI all teachers must follow as indicated to help you be successful in school ??Do you understand each of these SDIs? ??Are there any SDI’s you do not use or could use? The IEP is a working document… -can be changed or modified -is given to all of the staff/teachers who work with you in school You need to go to your IEP Meeting and provided input You need to know your SDI and advocate for yourself or seek support when required Accommodations in College or Trade Schools You must “Declare” That you have a disability and are seeking support Has no bearing on the approval/admissions process Different Application of the SDI See handout… ANY QUESTIONS or COMMENTS Lecture #6 Naviance: About Me & Career Inventory