INTRODUCTION TO MICROCONTROLLER
advertisement

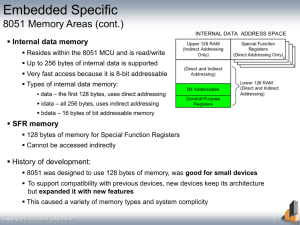
INTRODUCTION TO MICROCONTROLLER What is a Microcontroller • A microcontroller is a complete microprocessor system, consisting of microprocessor, limited amount of ROM or EPROM, RAM & I/O ports all built on a single integrated circuit. • Microcontroller can be used to perform control functions so it is comparable with a microcomputer. • It must include full or nearly full implementation of a standard microprocessor, ROM or EPROM, RAM, parallel I/O ports, serial ports, timer, clock. • More complex than a microprocessor. Advantages of Microcontroller over Microprocessor • Cost of microcontroller is less than microprocessor based system • Microcontroller has more I/O components than microprocessor based system. • Unlike microprocessors Microcontrollers can be used in wide variety of intelligent products like personal computers keyboards or can be used in devices with artificial intelligence. • Many low cost products like toys, washing machines, microwave ovens, electric drills etc are based on microcontrollers & not on microprocessor based system Features of Microcontroller 8051 • 8051 microcontroller has an 8-bit ALU. • 4 KB (4K x 8 bit) ROM EPROM • 128 byte (128 x 8 bit) RAM • Dual 16-bit timer, event counter. • 32 I/O lines for four 8- bit I/O ports. • Full featured serial port. • It can address 64 KB of program memory • It can address 64 KB of data memory • Powerful instruction set with 111 instructions. • Two external interrupt. • Clock upto 12-MHz frequency. Memory mapping of Microcontroller 8051 Memory mapping of Microcontroller 8051 Program Memory Data Memory Read-Only Memory (ROM) space Random Access Memory (RAM) space Used for storing programs & variable data Used for general read/write data storage Instruction fetches are taken from program memory space. It is a read/write memory space Processor can read instruction from this space, but cannot write the data into this memory. It reads instructions to be executed from this memory space. Processor can read data from this memory space & can write data to this memory space. It cannot execute instructions from this memory space. It has internal ROM(EPROM) It has internal RAM 128 bytes. 4 Kbytes program memory can be expanded by additional 60Kbytes, making it 64KB program memory. & 22 special function registers .memory can be expanded by additional 60Kbytes, making it 64Kbytes data memory. Microcontroller 8051 family 8048, 8049, 8050 • 8048 was Intel’s 1st microcontroller. All 8048, 8049, 8050 have same architecture except memory size. • The memory size doubles in each case.8048 supports 1Kbytes of internal memory (ROM). 8049 supports 2Kbytes of internal ROM & 8050 supports 4Kbytes of internal ROM. • 8048 has 64 bytes internal RAM, including 32 bytes of register memory. 8049 & 8050 have a total of 128 & 256 bytes of RAM respectively. • 27 I/O lines. 8-bit timer event counter. • Low cost & hence very popular. 8052 • 8052 is a simple expansion of 8051. • 8Kbytes of onboard ROM & 256 Kbytes onboard RAM. • Allows programmer to write larger programs that can use more data. • Cost of 8052 is more than 8051. • Has one extra 16-bit counter-timer which gives more flexibility. Microcontroller 8051 family 8031, 8032 • 8031 is alternative version of 8051 & 8032 is alternative version of 8052. • They do not have onboard ROM. They may use external ROM for program memory. • Excellent devices for prototyping & low volume products. 8052 AH-BASIC • 8052 AH-BASIC is another form of 8052. • Programmer can use BASIC for writing instructions rather than using assembly language. Compare between 8051 & 8052 8051 8052 4Kbytes of onboard ROM or EPROM 8Kbytes of onboard ROM or EPROM 128 bytes of onboard RAM 256 bytes of onboard RAM Has a dual 16-bit timer event counter Has an extra 16-bit timer event counter Cost is less Cost is more Used in high volume applications & allows to write large programs Used in high volume applications & allows to write large programs, larger than in 8051 Applications of Microcontroller • Microcontroller is a single chip microcomputer. • They are used as independent controllers in machines or as slaves in distributed processing. • They are used as machine tools, chemical processors, medical instrumentation & sophisticated guidance control. • Many low cost products such as toys, microwave oven etc are based on microcontroller. • The personal computer keyboards are implemented with microcontroller. It replaces scanning, debounce, matrix decoding & serial transmission circuits.